GTMiner is a link prediction framework to discover geospatial relationships between entities and construct a Knowledge Graph (KG). It relies on advanced text-analysis techniques and refinement procedures, in order to identify such relationships in absence of exact geometrical shapes for the involved entities.
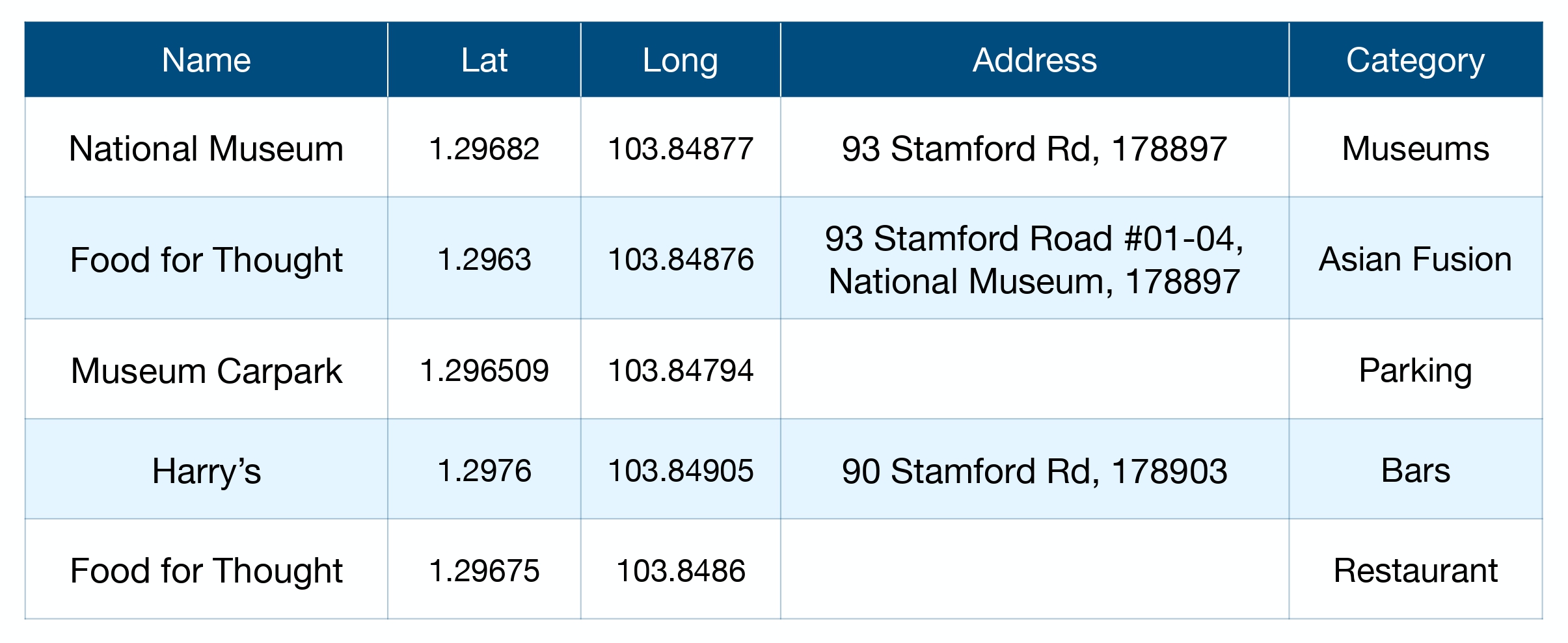
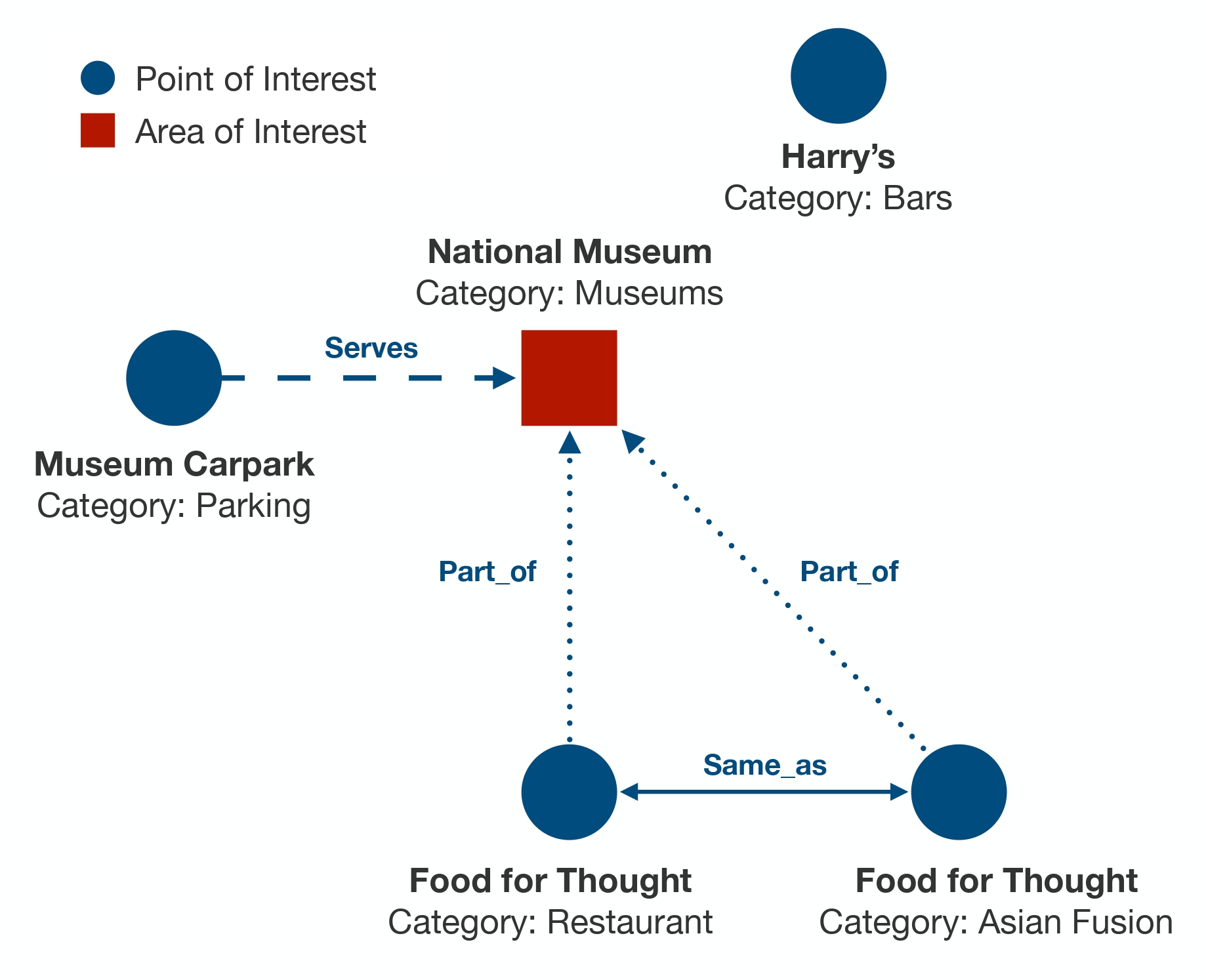
The following image (left) depicts a typical geospatial database. On the right, a geospatial KG links the entities from the database with fine-grained relationships.
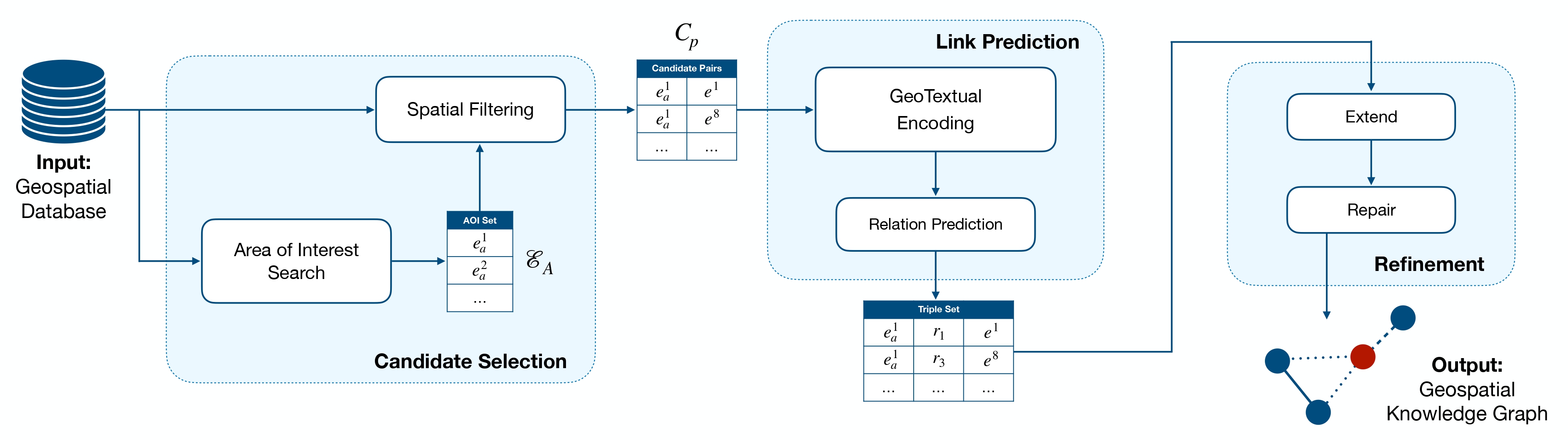
The image below shows the proposed framework. GTMiner is composed of:
- A Candidate Selection step, to reduce the combinatorial explosion caused by the total number of possible triples
$(h, r, t)$ to be discovered; - A Link Prediction model to identify if a geospatial relationship exist between two entities (and which);
- A Refinement module to increase the coverage and correctness of a geospatial KG.
- Python 3.7.7
- PyTorch 1.9
- HuggingFace Transformers 4.9.2
- wget 3.2
Install required packages
pip install -r requirements.txt
Triples are represented as follows:
<entity:head> \t <entity:tail> \t <relation:r>
Relations with corresponding ID are stored in config.py
Data points are represented as follows:
<entity:e> \t <label:{0,1}>
python train_GTMiner.py \
--city sin \
--lm bert \
--lr 3e-5 \
--n_epochs 10 \
--batch_size 32 \
--max_len 128 \
--device cuda \
--finetuning \
--do_extend \
--do_repair \
--save_model
--city: Specify which city's data you wish to use for training. Possible values aresin,tor,sea,mel.--lm: Pre-trained language model. Possible values arebert,distilbert,roberta.--lr: Learning rate.--n_epochs: Number of epochs.--batch_size: Batch size.--max_len: Max length of the textual sequence in input to the language model.--device: Device, can be:cpuorcuda.--finetuning: Language models pre-trained weights can be fronzen. We strongly encourage to use finetuning, instead.--do_extend: If this flag is set, the Refinement Extend will be applied.--do_repair: If this flag is set, the Refinement Repair will be applied.--save_model: If this flag is set, the best model on the validation set, will be saved (the path can be specified in config.py).
python train_AOI_Classifier.py \
--city sin \
--fe bert \
--lr 3e-5 \
--alpha 2.0 \
--beta 1.0 \
--n_epochs 10 \
--batch_size 32 \
--max_len 128 \
--device cuda \
--save_model
--city: Specify which city's data you wish to use for training. Possible values aresin,tor,sea,mel.--fe: The Feature Extractor. Possible values arebert,lstm. (choosinglstmwill trigger the download of GloVe embeddings)--lr: Learning rate.--alpha: The weight for positive class in the loss function.--beta: The weight for negative class in the loss function.--n_epochs: Number of epochs.--batch_size: Batch size.--max_len: Max length of the textual sequence in input to the language model (Suggested values are 32 for bert and 16 for lstm).--device: Device, can be:cpuorcuda.--save_model: If this flag is set, the best model on the validation set, will be saved (the path can be specified in config.py).
@article{10.1145/3588947,
author = {Balsebre, Pasquale and Yao, Dezhong and Cong, Gao and Huang, Weiming and Hai, Zhen},
title = {Mining Geospatial Relationships from Text},
year = {2023},
issue_date = {May 2023},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
volume = {1},
number = {1},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3588947},
doi = {10.1145/3588947},
journal = {Proc. ACM Manag. Data},
month = {may},
articleno = {93},
numpages = {26},
}