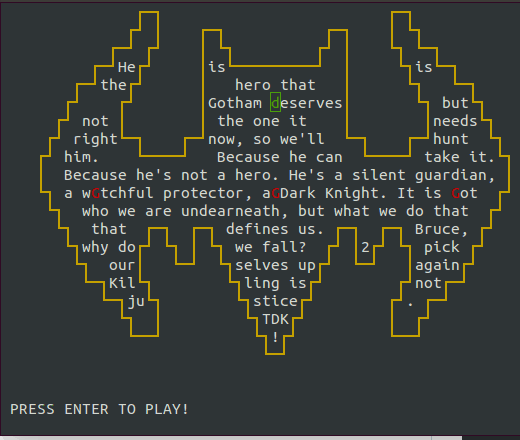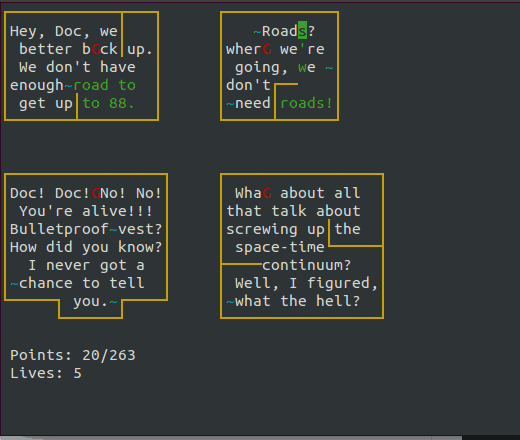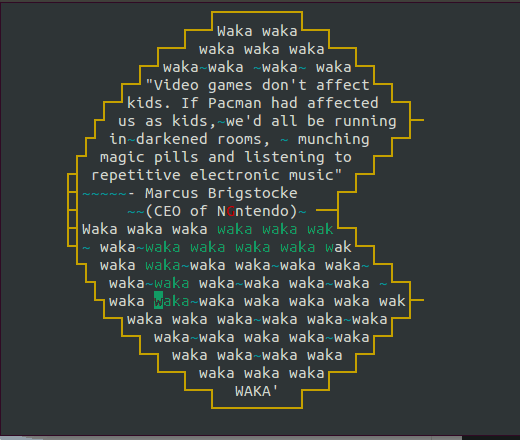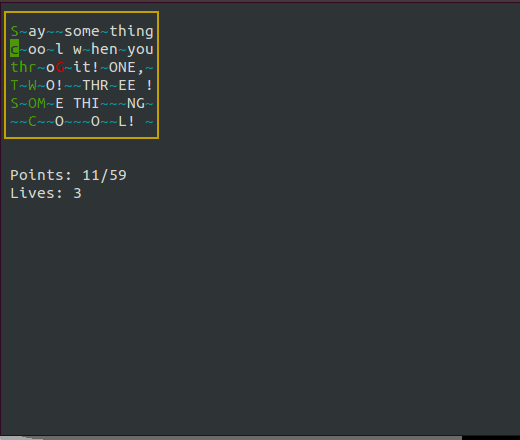
PacVim is a game that teaches you vim commands. You must move pacman (the green cursor) to highlight each word on the gameboard while avoiding the ghosts (in red).
Vim is a great tool to write and edit code, but many people, including me, struggled with the steep learning curve. I did not find a fun, free way to learn about the vim commands in-depth, and thus, PacVim was born. Inspired by the the classic, PacMan, PacVim is a game that'll give anyone plenty of practice with the vim commands while being a ton of fun to play.
Download and build the game with:
-
Download and install Curses (graphics library)
-> For Ubuntu (in terminal):sudo apt-get install libncurses5-dev-> OR This tutorial may help (have not confirmed)
-> OR build from source: Curses source files
-> For Mac OS X: Install Homebrew (brew.sh), then use
brew install ncurses && brew link ncurses --force -
git clone https://github.com/jmoon018/PacVim.git
-
cd PacVim
-
make
To play, run:
$ ./pacvim
or to start at a particular level, EG: if LEVEL_NUMBER = 4
$ ./pacvim LEVEL_NUMBER
#How To Play
The objective of PacVim is very similar to PacMan.
You must run over all the characters on the screen while avoiding the ghosts (red G).
PacVim has two special obstacles:
-
You cannot move into the walls (yellow color). You must use vim motions to jump over them.
-
If you step on a tilde character (cyan
~), you lose!
You are given three lives. You gain a life each time you beat level 0, 3, 6, 9, etc. There are 10 levels, 0 through 9. After beating the 9th level, the game is reset to the 0th level, but the ghosts move faster.
Winning conditions: Use vim commands to move the cursor over the letters and highlight them. After all letters are highlighted, you win and proceed to the next level.
Losing conditions: If you touch a ghost (indicated
by a red G) or a tilde character, you lose a life. If you
have less than 0 lives, you lose the entire game.
| key | what it does |
|---|---|
| q | quit the game |
| h | move left |
| j | move down |
| k | move up |
| l | move right |
| w | move forward to next word beginning |
| W | move forward to next WORD beginning |
| e | move forward to next word ending |
| E | move forward to next WORD ending |
| b | move backward to next word beginning |
| B | move backward to next WORD beginning |
| $ | move to the end of the line |
| 0 | move to the beginning of the line |
| gg/1G | move to the beginning of the first line |
| numberG | move to the beginning of the line given by number |
| G | move to the beginning of the last line |
| ^ | move to the first word at the current line |
| & | 1337 cheatz (beat current level) |
The maps for PacVim are loaded from text files from
the maps folder. The name of each text file must be
in a format such as: map#.txt, where # represents a number like
0, 1, 9, 14, etc. The numbers must be consecutive (can't have map0.txt,
map1.txt, and then map3.txt). MAKE SURE YOU CHANGE THE NUM_OF_LEVELS
IN GLOBALS.CPP OR ELSE YOUR NEW MAPS WON'T LOAD. It should be equal
to the highest map number.
In the map text file, the walls are denoted by ampersands #, and the
tildes come just from the tilde key. Maps must be bounded and closed,
so the player is trapped within 4 walls. Make sure walls block the top
and left of the terminal (or else the player goes offscreen). Any
shape, height, and width, within these constraints, should work
Creating Ghosts and Players
At the bottom of each map text file, parameters about the Ghost(s)
and Players are specified
Ghost:
/# X Y ... EG: /0.5 1 1
The forward slash denotes that this information describes a Ghost (instead of player).
The # denotes the time, in seconds, it takes for the Ghost to move. (#=0.5 means 2 moves/sec)
X and Y denote the starting x- and y-position of the Ghost
Player:
pX Y ... EG: p15 7
The 'p' denotes that this information describes a Player (instead of Ghost).
The X and Y denote the starting x- and y-position of the Player.
This is optional, the player spawns in the middle of the map otherwise
This should be the last line of the file
The `Ghost1` class also contains a method called `spawnGhost` which creates the ghost at the location based on its initialization parameters. The ghost will appear when `READY` (global bool) is true (this means the player is ready), and it will call `ghost.think()` one second afterwards.
`think` is a recursive method that simply moves the ghost. It uses a basic greedy algorithm based on the distance of the ghost's potential moves (up, down, right, left) and the player.
Each ghost contains its own thread. A global mutex, called mtx, is
used (in think) to ensure that resources are shared properly.
helperFns.cpp
Contains methods that allow easy changes of the screen. A few of them:
chtype charAt(int x, int y)returns the chtype at the (x,y) locationbool writeAt(int x, int y, chtype letter)writes the 'letter' at location (x,y). Returns false if location is invalid.void printAtBottom(string msg)writes a message one line below the last line
main - contains a loop that breaks when LIVES < 0. In the loop,
the proper map name is determined and loaded. Data is reset (such as as the pointers,
the ghost AI, etc). The level is incremented.
init(const char*) - called by main. Calls drawScreen(str map), creates and
spawns player and ghosts threads. Then calls playGame. After playGame
ends, all the ghost threads are deleted, and then we go back to the main method.
drawScreen(char* map) - called by init. Reads from text file given
by parameter. Loads everything onto the screen with the proper color and gets
information from the ghost and player so that they spawn in the proper place in init.
playGame(time_t, avatar player) - called by init. This contains two loops,
one that consumes everything in the input buffer (which is then deleted), the second
loop allows the player to continuously input keystrokes. When a keystroke is input,
onKeystroke is called
- More testing on `#G` and `G` commands
- G can go out of bounds on Map 8 with the boxes. #G (between boxes)
- G won't move to proper line, it can hit the last wall rather than the last word (map2)
- Refactor code, more comments