RecipeMind: Guiding Ingredient Choices from Food Pairing to Recipe Completion using Cascaded Set Transformer
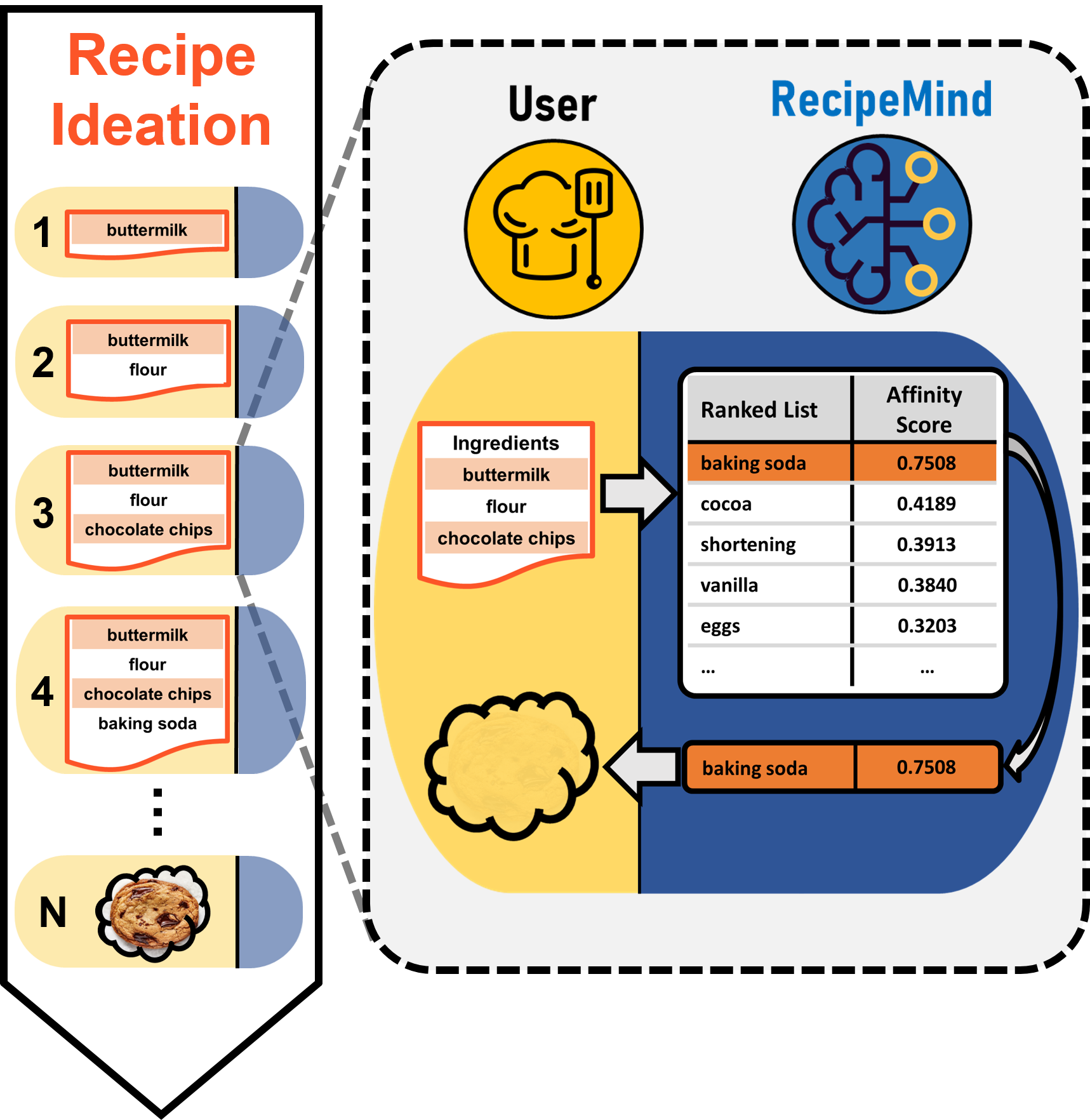
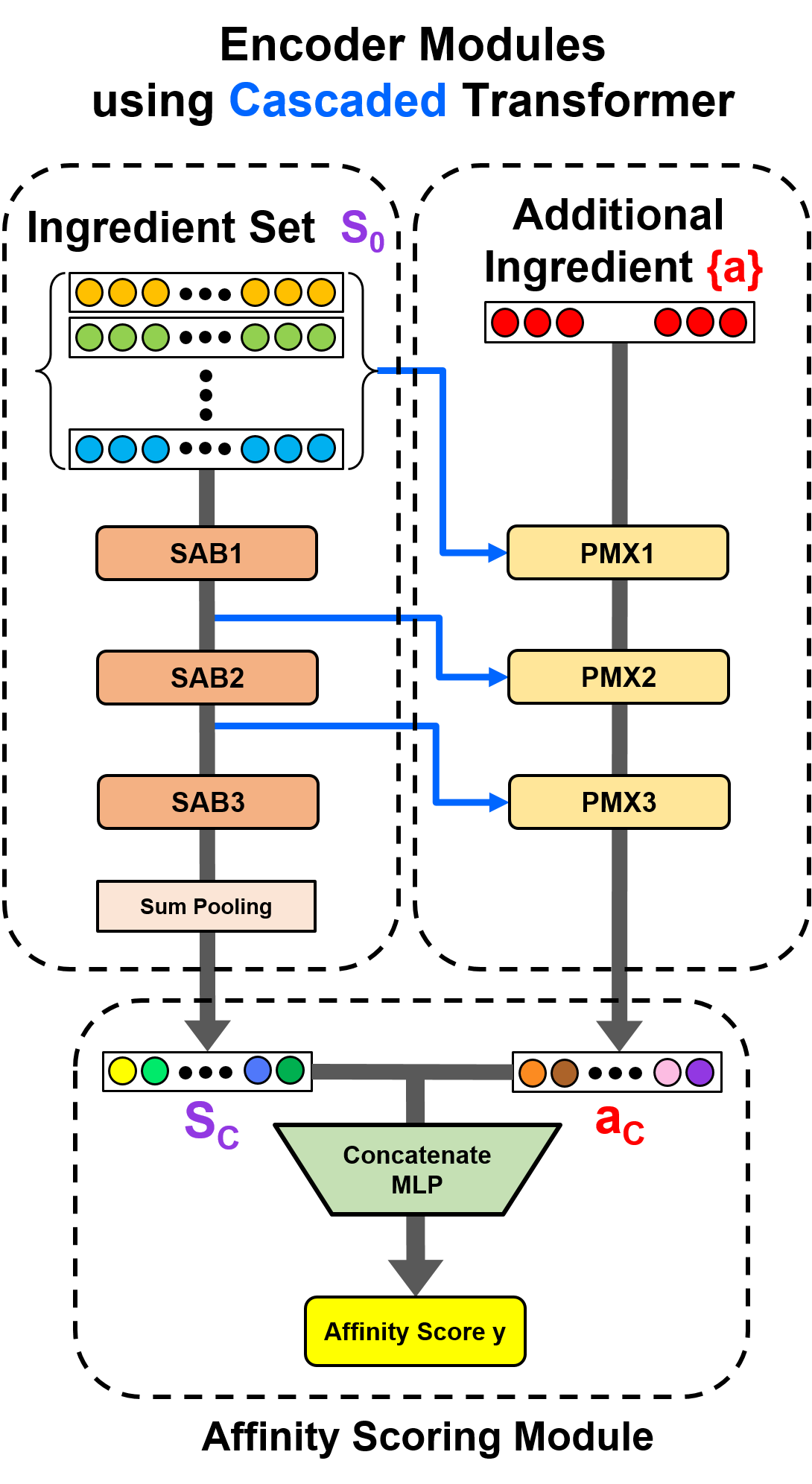
We propose a computational approach for recipe ideation, a down-stream task that helps users select and gather ingredients for creating dishes. To perform this task, we developed RecipeMind, a food affinity score prediction model that quantifies the suitability of adding an ingredient to set of other ingredients. We constructed a large-scale dataset containing ingredient co-occurrence based scores to train and evaluate RecipeMind on food affinity score prediction. Deployed in recipe ideation, RecipeMind helps the user expand an initial set of ingredients by suggesting additional ingredients. Experiments and qualitative analysis show RecipeMind’s potential in fulfilling its assistive role in cuisine domain.
- Python 3.8.12
- CUDA: 11.X
- Download and extract data.tar.gz (link, 388.4MB) at directory ./data. These files are the datasets containing ingredient n-tuplets with food affinity scores and ingredient word embeddings.
- Download and extract saved.tar.gz (link, 115.3MB) at directory ./saved. These files are the model checkpoints for each random seed (1001 ~ 1005).
conda env create -f recipemind.yml
conda activate recipemind
Run the following code,
./train_script.sh {your_session_name} {random_seed_integer}
Run the following code,
./test_script.sh {your_session_name} {random_seed_integer}
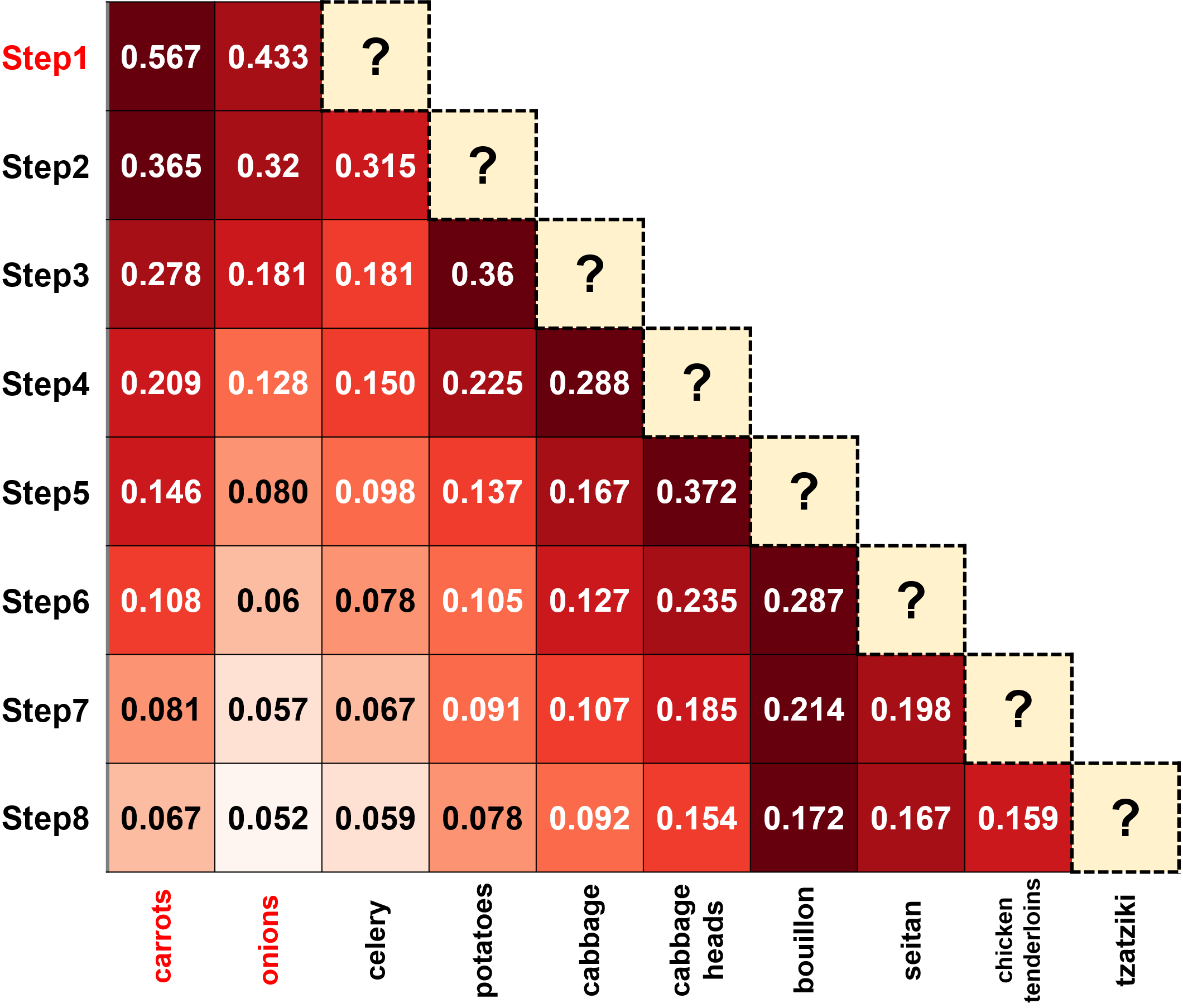
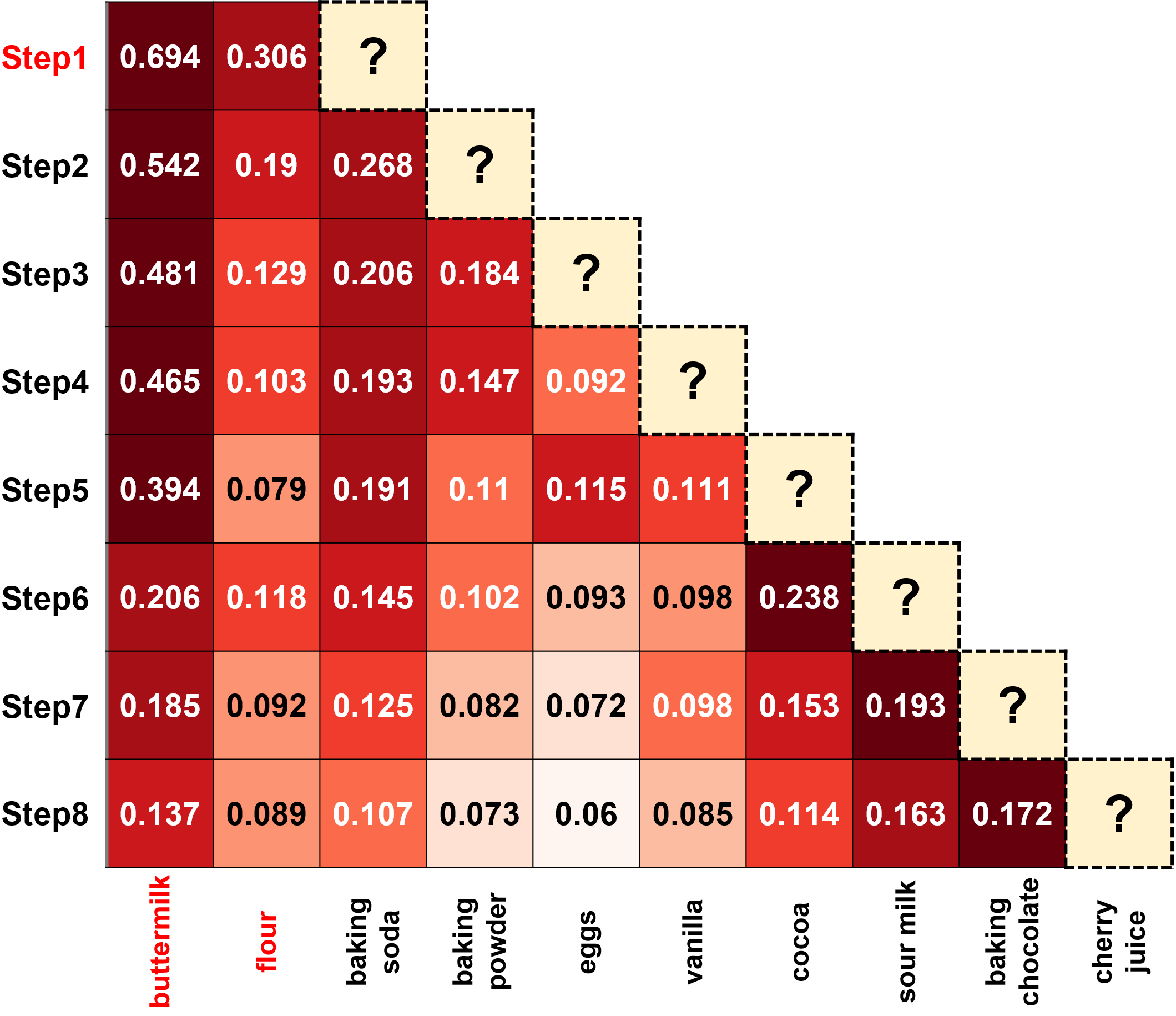
The jupyter notebook RecipeMind Post Analysis.ipynb contains the source code for deploying the trained RecipeModel model in recipe ideation scenarios starting with any number of ingredients. We provided example cells that output the ideation results and attention heatmaps for interpretation purposes. The example heatmaps are the following,
| Name | Affiliation | |
|---|---|---|
| Mogan Gim† | Data Mining and Information Systems Lab, Korea University, Seoul, South Korea |
akim@korea.ac.kr |
| Donghee Choi† | Data Mining and Information Systems Lab, Korea University, Seoul, South Korea |
choidonghee@korea.ac.kr |
| Kana Maruyama | Sony AI, Tokyo, Japan | Kana.Maruyama@sony.com |
| Jihun Choi | Sony AI, Tokyo, Japan | Jihun.A.Choi@sony.com |
| Donghyeon Park* | Food & Nutrition AI Lab, Sejong University, Seoul, South Korea |
parkdh@sejong.ac.kr |
| Jaewoo Kang* | Data Mining and Information Systems Lab, Korea University, Seoul, South Korea |
kangj@korea.ac.kr |
- †: Equal Contributors
- *: Corresponding Authors