Tutorializer
Tutorial framework helps to describe behavior of UI based on real view. Definitely, UX should be clear and intuitive, but sometimes it is not easy to do, espesially, when you implement uncommon behaviour, therefore you have to bring idea for user how to use it. The framework will help to create simple, responsive to device orientation tutorial flow based on real view.
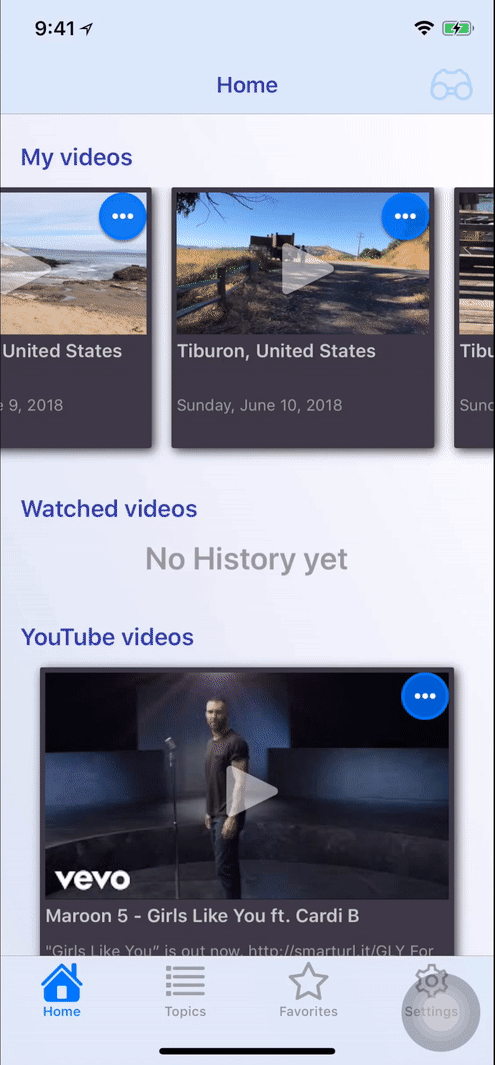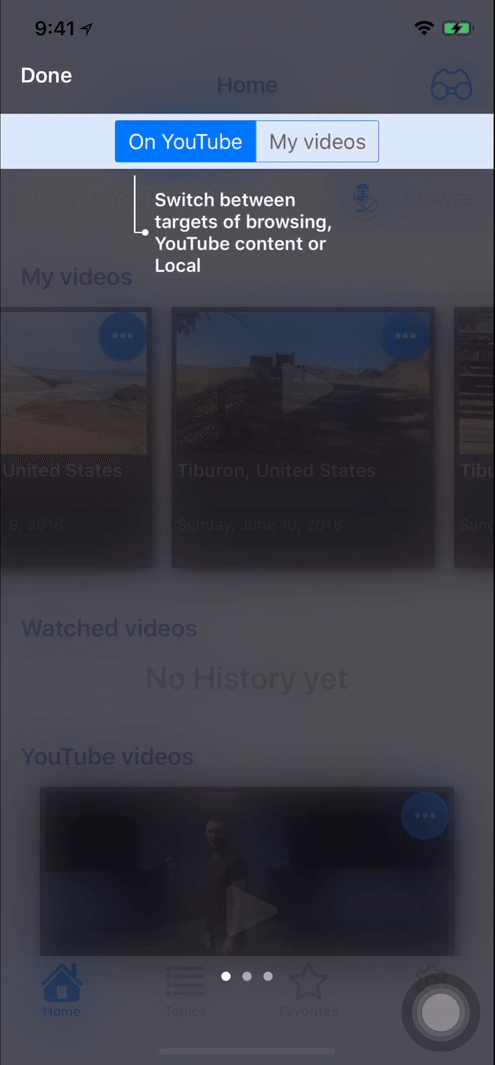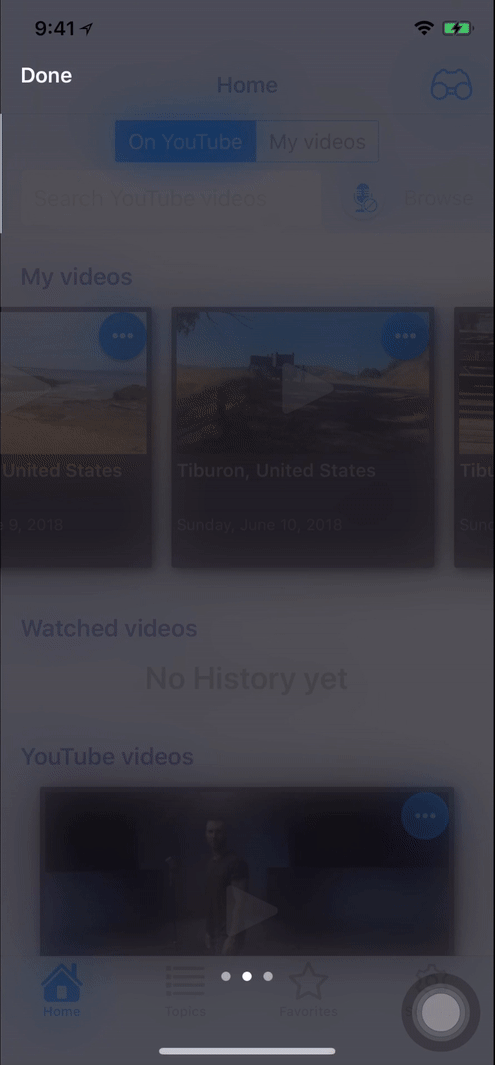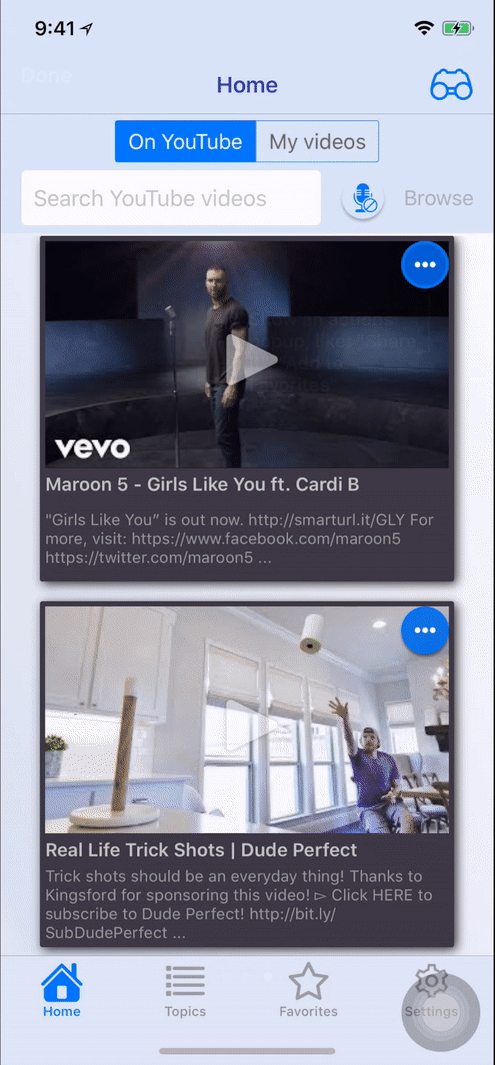
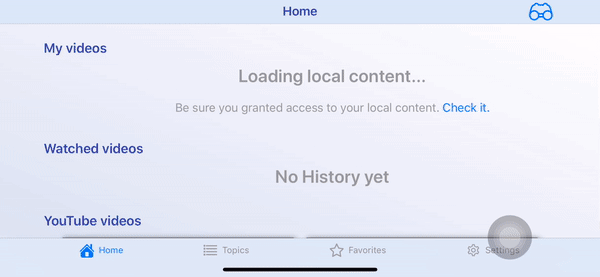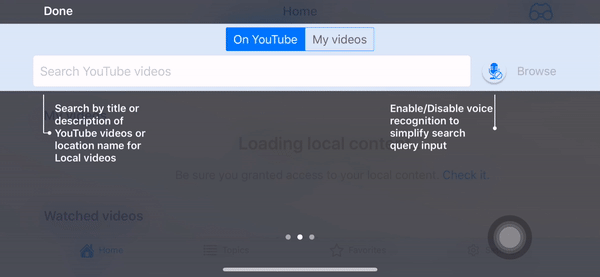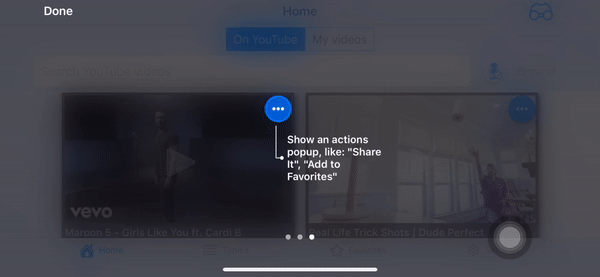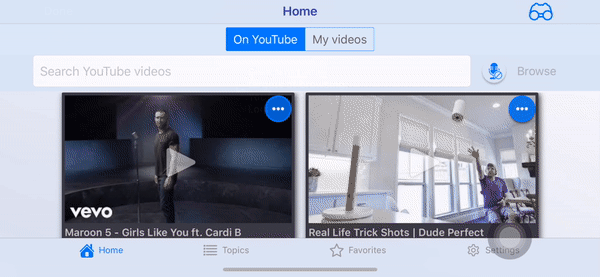
Screenshots
- Portrait
- Landscape
How to use
Example how to use it you can find at https://github.com/MaximKomlev/BLERadariOS.git project.
if you don't need customization and tutorial flow pretty straightforward you can use TutorialViewController as is. It is the basic class responsible for showing and layouting description(s) of describble view|control. It can be used dirrectly like:
let vc = TutorialViewController()
...
vc.tutorialDelegate = self
vc.modalTransitionStyle = .crossDissolve
vc.modalPresentationStyle = .overFullScreen
self.present(tnvc, animated: true, completion: nil)or you can use sequence of tutorial pages to describe complex behaviour (you can see on screenshots):
...
let tnvc = TutorialNavigationController()
let vc1 = TutorialViewController()
vc1.tutorialViewId = "page1"
...
tnvc.addTutorialViewController(tutorialController: vc1)
let vc2 = TutorialViewController()
vc1.tutorialViewId = "page2"
...
tnvc.addTutorialViewController(tutorialController: vc2)
tnvc.tutorialDelegate = self
tnvc.modalTransitionStyle = .crossDissolve
tnvc.modalPresentationStyle = .overFullScreen
self.present(tnvc, animated: true, completion: nil)
...One important thing we need to do it to say to TutorialViewController what to describe and how:
...
let vc = TutorialViewController()
var tutorialDescriptions = Dictionary<String, DescribableElementInfo>()
let text1 = NSMutableAttributedString(string: localizedString("Some text here..."))
text1.addAttribute(NSAttributedStringKey.font, value: UIFont.boldSystemFont(ofSize: font_size_button14), range: NSMakeRange(0, text1.length))
text1.addAttribute(NSAttributedStringKey.foregroundColor, value: UIColor.white, range: NSMakeRange(0, text1.length))
tutorialDescriptions["describable ui control or view identificator 1"] = DescribableElementInfo(descriptionPosition: .bottom, descriptionWidth: 140, descriptionText: text1)
let text2 = NSMutableAttributedString(string: localizedString("Another text here..."))
text2.addAttribute(NSAttributedStringKey.font, value: UIFont.boldSystemFont(ofSize: font_size_button14), range: NSMakeRange(0, text2.length))
text2.addAttribute(NSAttributedStringKey.foregroundColor, value: UIColor.white, range: NSMakeRange(0, text2.length))
tutorialDescriptions["describable ui control or view identificator 2"] = DescribableElementInfo(descriptionPosition: .bottom, descriptionWidth: 140, descriptionText: text2)
let text3 = NSMutableAttributedString(string: localizedString("Third text here..."))
text3.addAttribute(NSAttributedStringKey.font, value: UIFont.boldSystemFont(ofSize: font_size_button14), range: NSMakeRange(0, text3.length))
text3.addAttribute(NSAttributedStringKey.foregroundColor, value: UIColor.white, range: NSMakeRange(0, text3.length))
tutorialDescriptions["describable ui control or view identificator 3"] = DescribableElementInfo(descriptionPosition: .bottom, descriptionWidth: 140, descriptionText: text3)
...
vc.initializeTutorialDescriptions(tutorialDescriptions)
...DescribableElementInfo provides information about description, it is text, desirable text view size and position (above or below describable view).
TutorialViewController will interact with describable view controller through delegate: TutorialViewDataDelegate. Describable view controller must implement: TutorialViewDataDelegate:
@objc func fetchDescribableElement(for tutorialView: TutorialViewProtocol?, complete: @escaping (_ view: UIView?) -> ())and additionally it can implement interface of TutorialNavigationControllerDelegate:
func getDoneButtonLocation(_ button: UIButton) -> CGPoint?
func doneButtonClicked(_ tutorialNavigationController: TutorialNavigationController)example of implementation:
// the method should return view or control, which you want to describe
func fetchDescribableElement(for tutorialView: TutorialViewProtocol?, complete: @escaping (UIView?) -> ()) {
if (tutorialView?.tutorialViewId == "page1") {
complete(view1)
} else if (tutorialView?.tutorialViewId == "page2") {
complete(view2)
} else if (tutorialView?.tutorialViewId == "page3") {
if (_videos.count > 0) {
UIView.animate(withDuration: 0.5, animations: {
self._collectionView.scrollToItem(at: IndexPath(item: 0, section: 0), at: .top, animated: false)
}) { (success) in
let cell = self._collectionView.cellForItem(at: IndexPath(item: 0, section: 0))
complete(cell)
}
} else {
complete(nil)
}
}
}
// returns position of done button associated with TutorialNavigationController
func getDoneButtonLocation(_ button: UIButton) -> CGPoint? {
if let buttonTitle = button.title(for: .normal), buttonTitle.count > 0, let buttonFont = button.titleLabel?.font {
let bHeight = sizeOfString(text: buttonTitle, font: buttonFont).height
var x = leftRightMargin
var y = UIApplication.shared.statusBarFrame.height
if let v = navigationController {
let nbHeight = v.navigationBar.frame.height
y += (nbHeight - bHeight) / 2
if #available(iOS 11.0, *) {
x += v.view.safeAreaInsets.left
}
}
return CGPoint(x: x, y: y)
}
return nil
}
// called when done button was touched
func doneButtonClicked(_ tutorialNavigationController: TutorialNavigationController) {
tutorialNavigationController.dismiss(animated: true, completion: nil)
}The describable view|control must implement TutorialDescribableViewDelegate:
var tutorialDelegate: TutorialViewRenewalDelegate? { get set }
func getDescribableEntities() -> Dictionary<String, UIView>
func convertFrame(to view: UIView?) -> CGRect
func shapePath(for frame: CGRect) -> CGPathexample of implementation:
class UIDescribableBasicView: UIBasicView, TutorialDescribableViewDelegate {
// MARK: View life cycle
override func layoutSubviews() {
super.layoutSubviews()
tutorialDelegate?.layoutViews()
}
// MARK: Properties
...
// MARK: TutorialDescribableViewProtocol
weak var tutorialDelegate: TutorialViewRenewalDelegate? = nil
// returns dictionary of view identificator and view|control
func getDescribableEntities() -> Dictionary<String, UIView> {
var config = Dictionary<String, UIView>()
config["describable ui control or view identificator 1"] = view1
config["describable ui control or view identificator 2"] = view2
config["describable ui control or view identificator 3"] = view3
return config
}
// returns coordinates of area associated with describable view according to tutorial view controller
func convertFrame(to view: UIView?) -> CGRect {
if let parent = self.superview,
let coordinateSpace = view?.window?.screen.coordinateSpace {
return parent.convert(self.frame, to: coordinateSpace)
}
return CGRect.zero
}
// returns shape of area associated with describable view
func shapePath(for frame: CGRect) -> CGPath {
return CGPath(rect: frame, transform: nil)
}
// MARK: Helpers
...
}So, basicaly, the TutorialViewController is responsible for layouting descriptions (using custom algorithm) and drawing shape of area associated with describable view, TutorialNavigationController is responsible for managing multiple tutorial controllers (pages). For more complicated logic you can derive Tutorial View Controller and add own behaviour.
License
This project is licensed under the terms of the MIT license.