Kureikin Maks
The Distributed File System (DFS) is a file system with data stored on a server. The data is accessed and processed as if it was stored on the local client machine. The DFS makes it convenient to share information and files among users on a network.
Use the docker engine docker and docker hub to install DFS.
Installation base for each instance:
sudo apt-get update
sudo snap install dockerInstallation of Naming server maxitosh/namingserver:
docker pull maxitosh/namingserver
docker-compose updocker-compose.yml for Naming server.
version: "3.8"
services:
namingserver:
container_name: namingserver
image: maxitosh/namingserver:latest
environment:
- "PYTHONUNBUFFERED=1"
command: ["python3", "NamingServer.py"]
ports:
- 8800:8800
mongodb:
image: mongo:latest
container_name: mongodb
ports:
- 27017:27017
volumes:
- ./MongoDB/data:/data/db/
- ./MongoDB/:/usr/src/app/Installation of Storage server maxitosh/storageserver:
docker pull maxitosh/storageserver
docker-compose updocker-compose.yml for Storage server.
version: "3.8"
services:
namingserver:
container_name: storageserver
image: maxitosh/storageserver:latest
environment:
- "PYTHONUNBUFFERED=1"
- "HOSTNAME=ss1"
entrypoint: ["python3", "StorageServer.py"]
volumes:
- ./data/:/usr/src/app/data/
ports:
- 8800:8800For each Storage server use different HOSTNAME.
Naming and Storage servers should be launched on distinct machines and located in the subnet for communication purposes.
Installation of Client console maxitosh/clientconsole
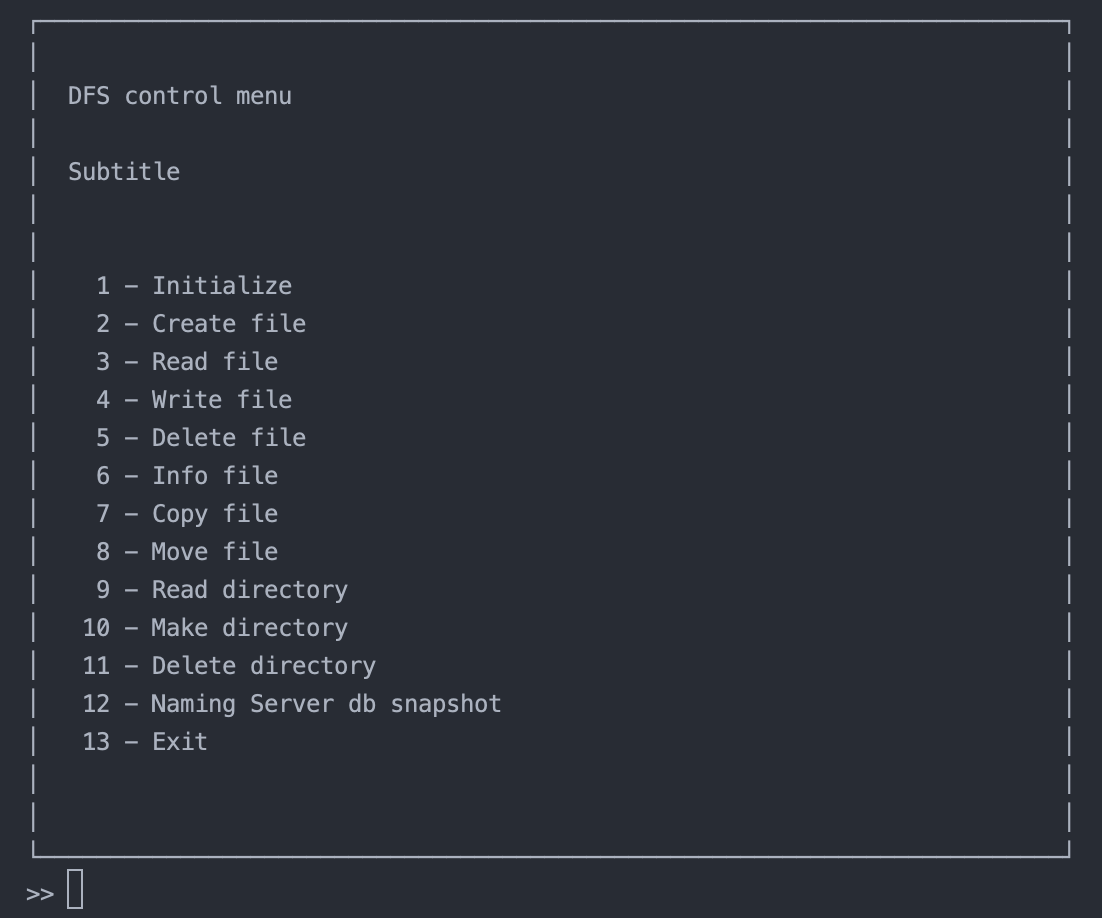
Available commands in client console.
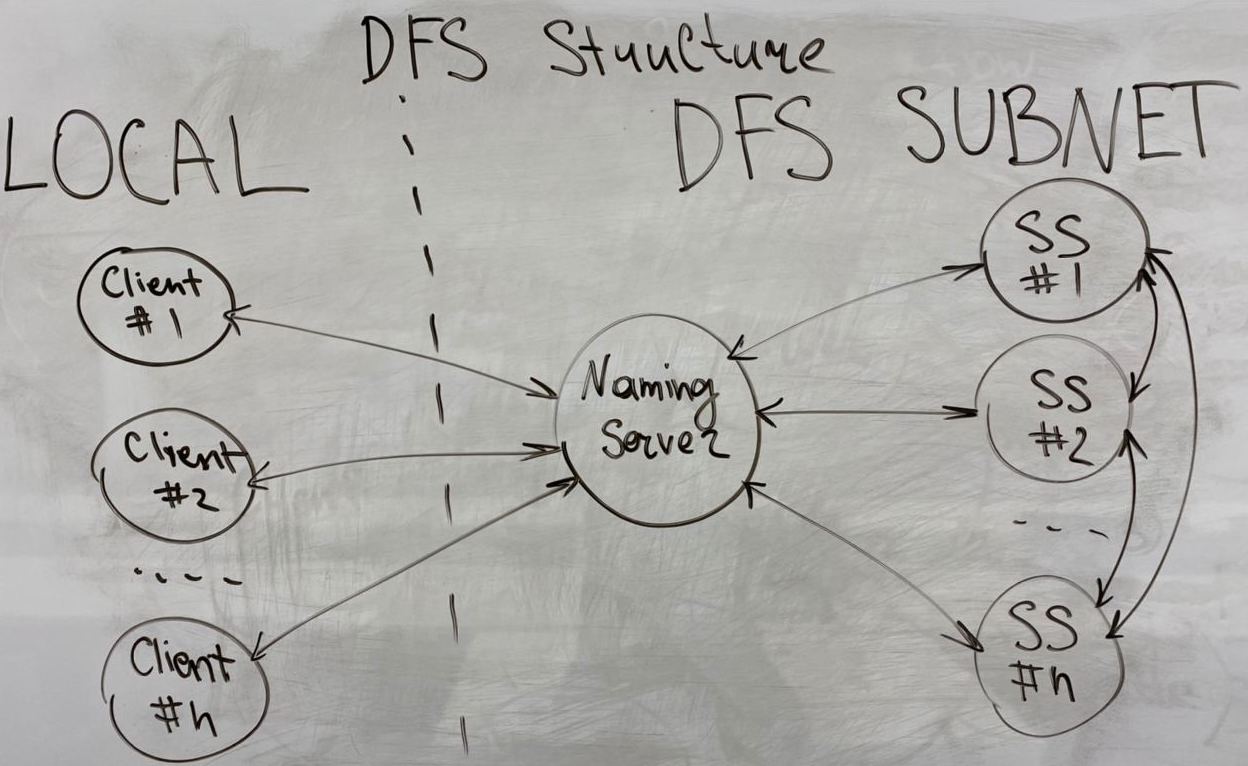
The idea of this DFS structure is to split the area between clients and DFS
system itself.
Nodes of DFS are in private, isolated subnet so that provides
security measurements.
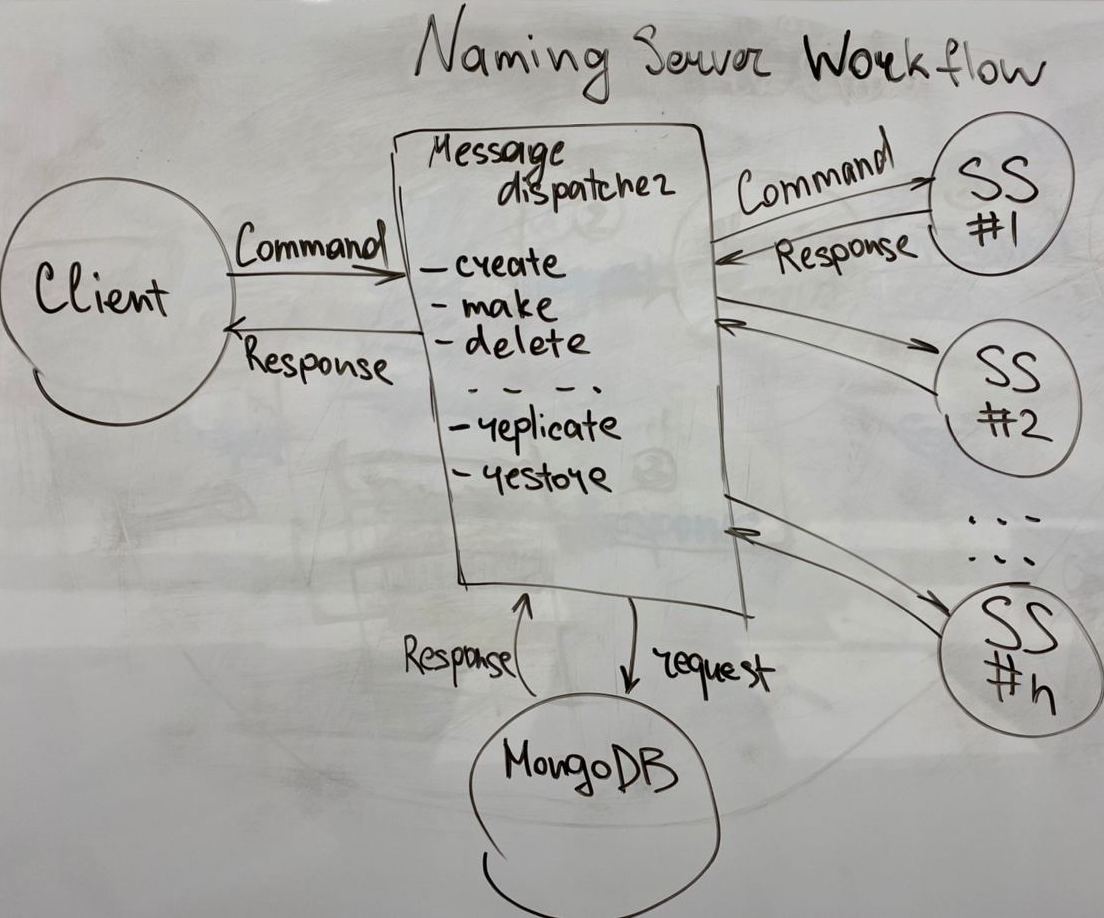
Naming server is an entry point which controls incoming
requests and manipulates the recourses of DFS.
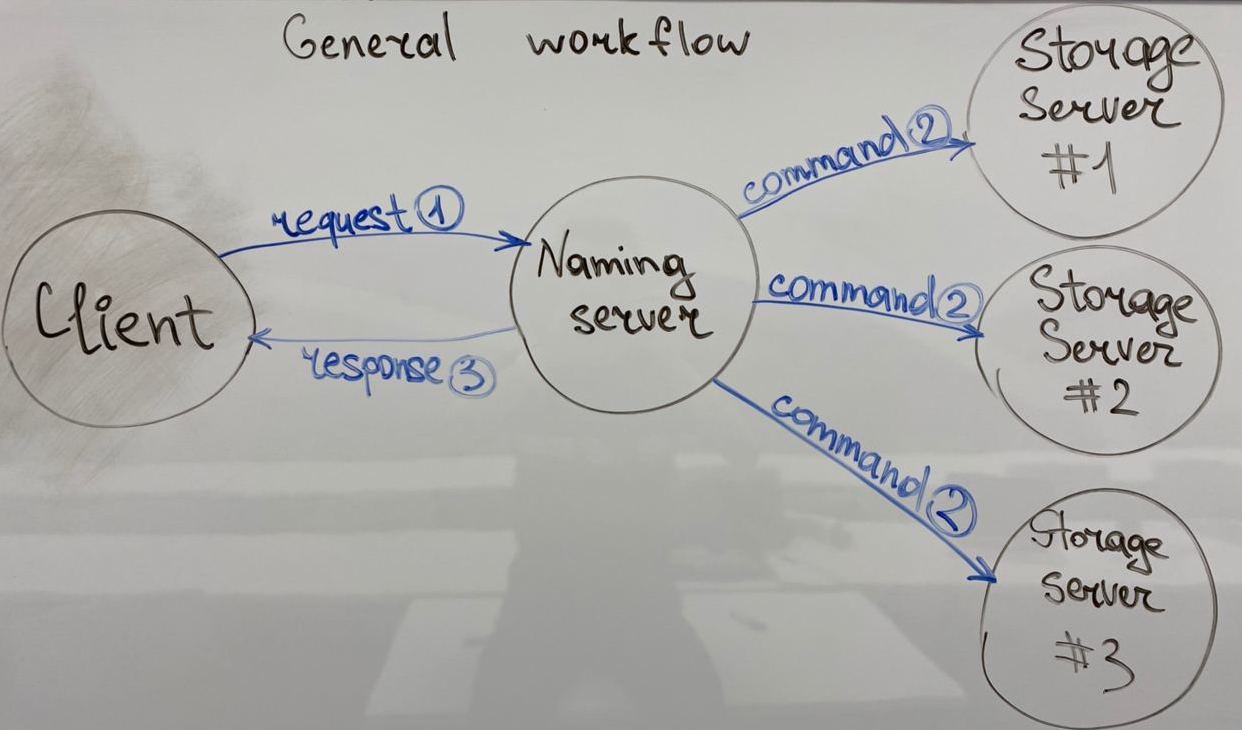
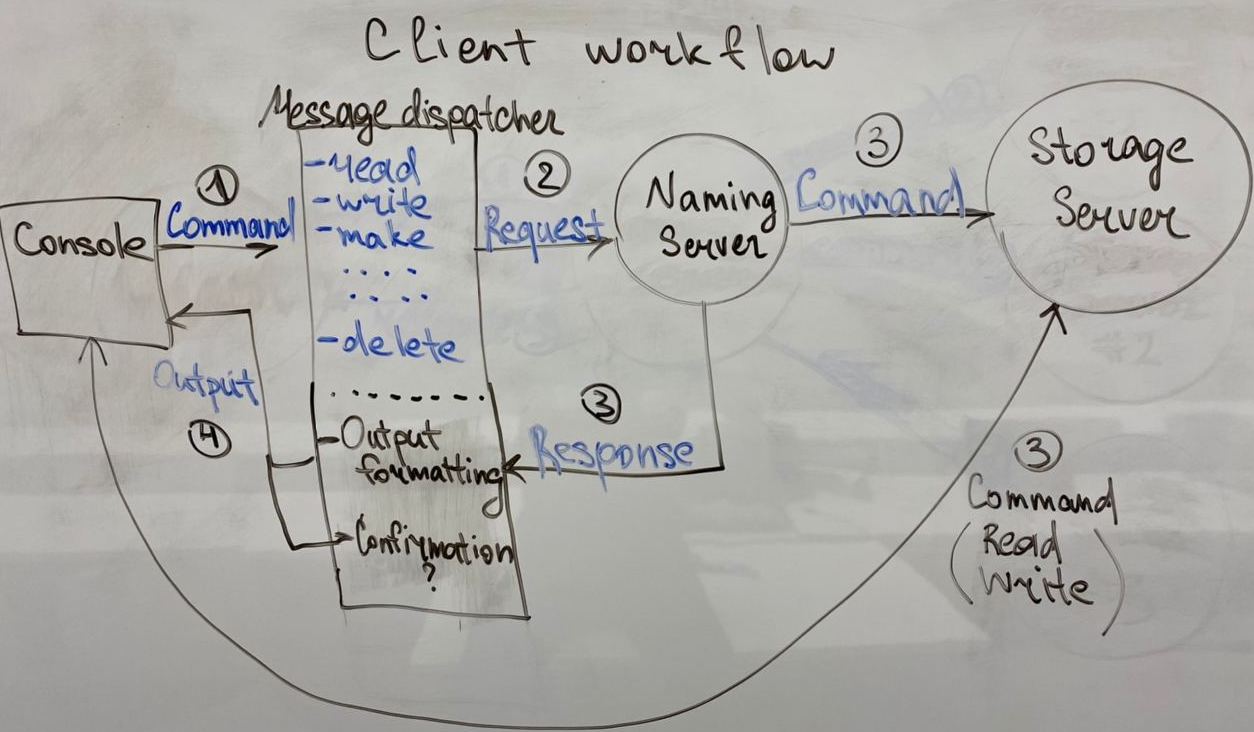
When a client wishes to access a file, it:
- contacts the naming server to obtain information about the storage server hosting it
- communicates directly with the storage server to complete the operation
Usage of client console allows user to manipulate over the DFS, using an interface that makes the distributed nature of the system transparent to the user.
The naming server tracks the file system directory tree, and associates each file in the file system to storage servers.
When a client wishes to perform an operation on a file, it first contacts the naming server to obtain information about the storage server hosting the file, and then performs the operation on a storage server.
Naming servers also provide a way for storage servers to register their presence.
The naming server can be thought of as an object containing a data structure which represents the current state of the file system directory tree, and providing several operations on it.
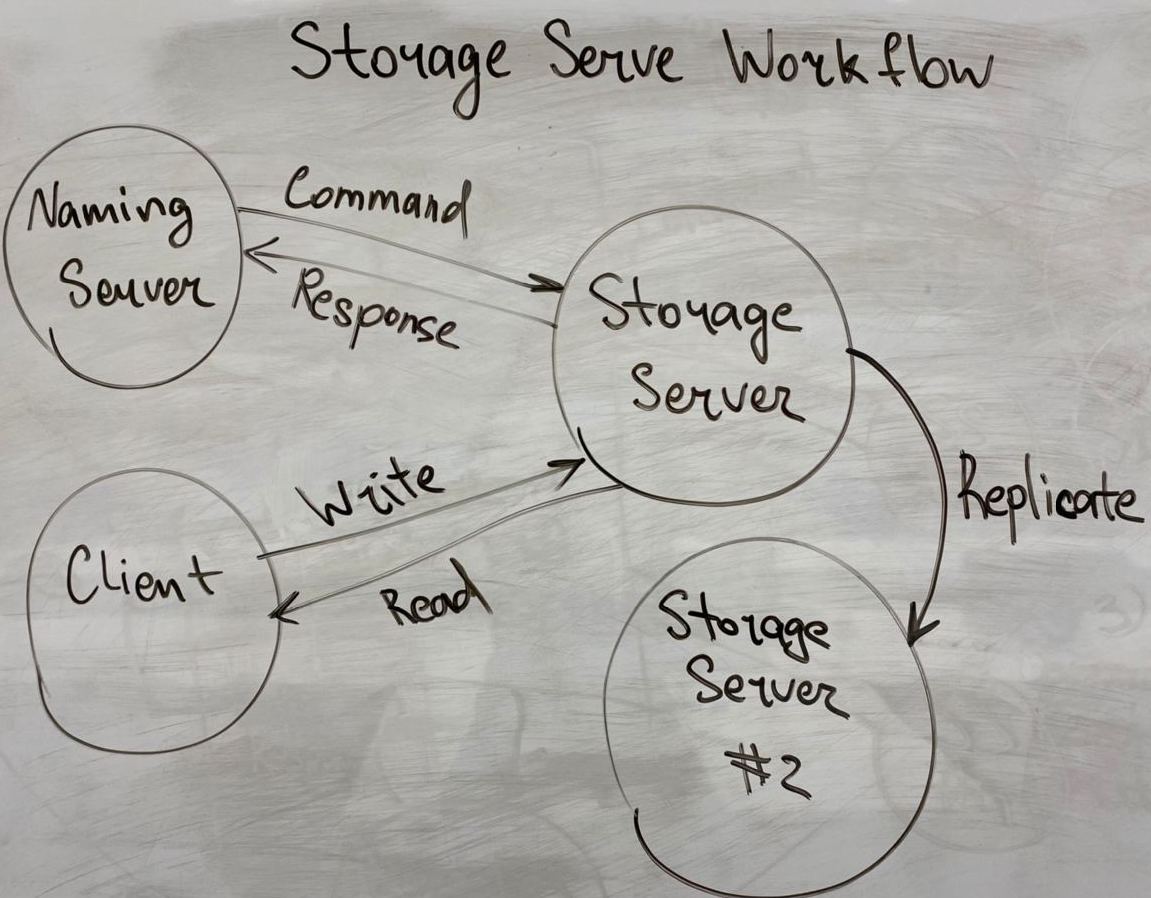
The primary function of storage servers is to provide clients with access to file data.
Clients access storage servers in order to read and write files.
Storage servers must respond to certain commands from the naming server.
All nodes in DFS uses such structure of messages to communicate:
{'command': '[COMMAND_NAME]', 'arg[1]':'arg[1]_value', ..., 'arg[n]': 'arg[n]_value'} For example, command for file uploading:
message = {'command': 'write_file', 'file_name': file_name, 'size': file_size}On each mode exists message dispatcher that takes message and calls appropriate function:
def dispatch_command(self, command):
return getattr(self, 'do_' + command["command"], None)
def do_init(self, args)
def do_create_file(self, args)
...
...
def do_delete_directory(self, args)Also nodes send response message of the same form, to handle either a success or an occurred error:
{'status': 'OK'}
{'status': 'Failed'}