!!!NO USERNAME, PASSWORD HERE!!!
- Hadoop Cluster Requirements
- Knowledge Background
- Notes About Hardware
- Steps to Follow
- Pitfalls
- How to Re-create the Cluster
- Basic Network Troubleshooting
- OS: CentOS 7/ Ubuntu 14.04
- Network Structure: NAT,
losalamosneed to be the NAT server.losalamoscan be connected to the port on wall through "eno2". - Install Choice: Link to installation
- You need to install
HDFS,MapReduce2 + YARN,Ambari Metrics, andZooKeeperand you must install the package we are currently learning. - You must keep a wiki of the necessary steps you think may be helpful to the next group here. Change of the wiki also is part of the grading.
- You have 3 whole days minus 2h for grading from 1:00 PM the first day to 11:00 AM the last day.
- Beyond expectation, more than TA would write (12')
- Meet expectation (10')
- Basically meet expectation, missing some points that TA think is necessary for other groups (8')
- Below expectation (6')
- Less than 10 lines of wiki added/Modified, or modification makes no sense (2')
- Beyond expectation, test some points that TA would not think of (12')
- Meet expectation (10')
- Basically meet expectation (8')
- Below expectation, there are some essential points are not tested (6')
- Demo does not work will add another 3 points penalty on the previous grade.
- Demo requires TA intervention will add 1~2 points penalty on the previous grade depending on the time spend on intervention.
- Iptables is up on losalamos and has basic protection with minimum iptables (2')
- Primary Name Node and Data Nodes should be on separate machines. (2')
- Primary Name Node and Secondary Name Nodes should be on separate machines. (2')
- NAT test, get google home page on other three machines. (2')
- Strong Password, password including at least a number and a letter and longer than 6 characters (2')
- No Alert in Ambari. (1' each alert, 2' max)
target prot opt in out source destination
ACCEPT all -- any any anywhere anywhere ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED
ACCEPT all -- lo any anywhere anywhere
ACCEPT icmp -- any any anywhere anywhere
REJECT all -- any any anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
- Ubuntu Command Line, Network Config (hostname, hosts, etc)
- Basic Computer Network knowledge, like DNS, Subnet (IP, Mask), Gateway;
- SSH, NAT, Forwarding
- Hadoop structure
- Basic understanding of above topics would make this work much easier
- There are four servers to set up, but only the first one (Losalamos) has access to the Internet;
- The box connecting the servers is just a switch, not a router. So “forwarding” is needed to get the other three servers connected to the Internet;
- Every server has two network adapters,
eth0andeth1, and it can only connects to the Internet byeth1. So please double-check the connection ports; - Since
losalamosuseseth1to connect to the Internet, it should useeth0for the sub network. - Keep the roles of
eth0andeth1in mind when you are configuring iptables with the linked tutorials: you may need to change the bash command given in those tutorials.
-
System installation of
losalamos. When you finish, you can log in with the username and password when you set up during the installation. Also, you can input command lineping google.comto test whetherlosalamoshave the right access to Internet. -
System installation of three slave machines, (which is
alpha,betaandgamma, according to your choice of naming). When you finish, you can log in with the username and password when you set up during the installation. -
Configuration of
/etc/network/interfacesand/etc/hosts. When you finish, you can ping other machines using the hostname or ip. -
Configuration of
iptables. When you finish, you can inputping google.comon the three slave machines to test whether they have access to Internet.
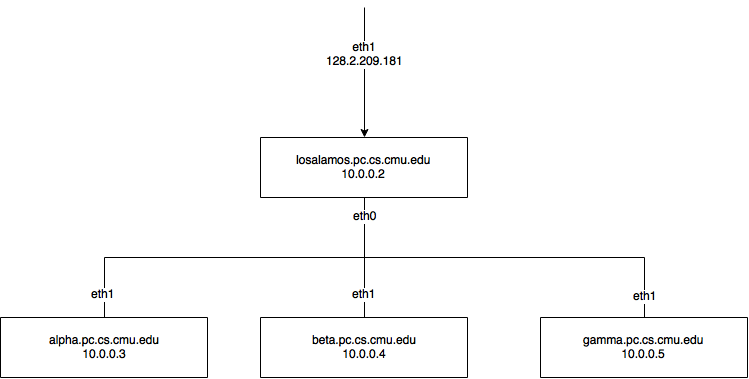
Overview: Given four blank server, we need to install system and establish a subnet. Finally install the requested hortonwork components. The network should be built as this image
Install Ubuntu (recommend 14.04) on each machine. The hard disks of four machines should already be erased. If not, press F11 when the system is starting and choose to start from the CD rom.
It may be hard to create a bootable USB stick on mac OS X. Failures occured for the following two approaches:
- burn by command
dd[ref] - burn by UNetbootin [ref] Please update if there are methods that work. A convenient method is to install Ubuntu from CD (the CD is already provided, you can find it near the machines).
###Bullet points when installation
- Insert the disk and press the power button to turn-off the machine. The lights on the machine should turn-off after a few seconds. Then press the pwer button again to start the machine.
- Once the machine starts, press F11 to enter Boot menu. Select
boot from diskoption. - Select the
Install Ubuntu Serveroption. - Make the appropriate language realted settings.
- Detect keyboard layout? Select
No - Select the appropriate time settings.
- Encrypt your home directory? Select
No - Partition method:
Guided - use entire diskif there is such a choice. If there is multiple partition selections, just take the default one. - Write changes to disks? Select
Yes - Network configuration. Choose
eth1as the primary device forlosalamos,alpha,betaandgamma(eth0is not plugged in three slaves). Automatic network configuration will fail foralpha,betaandgamma. SelectDo not configure netwrok. - HTTP proxy information?
Continuewith blank - How do you want to manage upgrades on this system?
Install security updates automatically - Choose software to install: Press space on
OpenSSH serverand there is a*ensures that you have chosen the software. Then pressContinue. - Install the GRUB boot loader to the master boot record? Choose
YES. - Before finishing installation, choose
YesforSet clock to UTCoption - Unmount partitions that are in use?
YES - To install OpenSSH server, use
sudo apt-get update; sudo apt-get install openssh-server. - Then make a back up of your
sshd_configfile by copying it to your home directory,sudo cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/ssh/sshd_config.factory-defaults - Then typing
sudo chmod a-w /etc/ssh/sshd_config.factory-defaults. - Runs the standard text editor in Ubuntu or more recent
sudo restart ssh - If getting error, “Unable to connect to Upstart”: try
sudo systemctl restart sshYou can find detailed OpenSSH tutorial here.
Here is a step-by-step installation video.
- In the image above, the three innet machines' hostname are
alpha,betaandgamma. You can change them to whatever you like. - Sometimes the system may get stuck when reboots after completing installation, in such rare cases, just press the reboot button on the back of the server for more than 10 seconds and restart the system.
- During the installation, we need configured network of
losalamoswith eth1 and we don't need to configure the network of three innet machines during the install process. Thus when installing Ubuntu on the three innet machines, you can either chose eth0 or eth1 during network configuration step, and it will eventually show "network auto configuration failed", just ignore and continue. - You probably want to install the OpenSSH during installation, so that you can then connect to the server using terminal in your own laptops. If you choose
not to update the server automaticallywhen you install the server, you might need to install the OpenSSH usingsudo apt-get install openssh-server. If you still cannot install OpenSSH, please refer to Here. - The openssh-server should be installed on all of the four machines for ssh to function properly, try
apt-get updatebefore install openssh-server. losalamosshould have access to the internet already after installation. Usingping google.comorping + other known IP addressto check the connection.- You need to choose unmount the disk partition before installation step. Choose the
guided use entire disk, if there is multiple partition selections, just take the default one. If you get a note like this: "Note that all data on the disk you select will be erased, but not before you confirm that you really want to make changes. Select disk to partition:" and select "SCSI3 (2,0,0) (sda) - 72.7 GB DELL PERC 5/i"
Notice: during the entire process (even after you finish this part), you’d better not reboot any of the four machines after you have done with following establish subnet steps, otherwise you may lose your network connection and need to install the OS once again (Welcome for the notes if you could solve this problems without reinstalling OS).
There are two ways, which is DHCP and static IP, to setup connection between losalamos and the other threes machine alpha, beta and gamma. Static IP is easier and safer, so the following step instruction is based on static IP method. If you want to use DHCP, please refer to the instruction below the Steps part.
- Connect servers physically, through the switch and network adapter ports on each machine. That is, connect the gray ethernet cables from each machine to the switch (small white box at the top corner of the server rack).
- Start from the
losalamos. Configureeth0in the file/etc/network/interfaces, using the command linesudo vim /etc/network/interfaces. The content would be
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address 10.0.0.2
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 10.0.0.2
broadcast 10.0.0.255
dns-nameservers 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4
You can find an example here, in the Configuring the interface manually section.
Attention: comment the keyword loopback and dhcp if you use static ip method (This is not needed!). loopback and dhcp are the default keywords which have already been in the files.
3. (Recommended)Still in the configuration of losalamos. Configure the file /etc/hosts, using the command line sudo vim /etc/hosts. The content would be
127.0.0.1 localhost
10.0.0.2 losalamos.pc.cs.cmu.edu losalamos
10.0.0.3 alpha.pc.cs.cmu.edu alpha
10.0.0.4 beta.pc.cs.cmu.edu beta
10.0.0.5 gamma.pc.cs.cmu.edu gamma
This page can give you more info.
4. When you finished the configuration of losalamos, DO NOT reboot losalamos. Use sudo ifdown eth0, sudo ifup eth0 and sudo ifconfig eth0 up to enable the configuration (Note eth0 for losalamos, not eth1! If it returns error information after executing second command, you can ignore it as long as the third command can be executed successfully). Otherwise you may lose your connection to external network.
5. Modified the above two files similarly in the three slave machines. There are some minor modifications needed to make. The following is an example when configuring alpha. Other information refer to the image above.
When configuring eth1 in /etc/network/interfaces in alpha, use sudo vim /etc/network/interfaces. The content would be
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet static
address 10.0.0.3
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 10.0.0.2
broadcast 10.0.0.255
dns-nameservers 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4
The dns-nameservers can be the IP of any DNS service, not necessarily the one provided in the example(which is that of Google). If you need more help, please refer to link.
6. For slaves machine, after making the configurations above, remember the configurations will take effect only after 1) you reboot the machine OR 2) shut down port using sudo ifdown eth1 and then restart using sudo ifup eth1. Though the command may return error information, it actually works.
7. You should be able to ping each other now using IP.
- To prevent warning for Ambari part, you can set the hosts as 'ip_address domain_name alias', each node should maintain the same copies of hosts configuration file.
- If you want to set the hosts as 'ip_address domain_name alias'. In the file
/etc/hosts, you should listall the hostsbelow the localhost on each machine. Otherwise you would receive warningTransparent Huge Pagesas you can see below when deploying the Ambari Server. - The warning for 'Transparent Huge Pages' can be removed by using the following commands:
i) Install hugepages:
>> apt-get install hugepages
ii) Then type the following command:
>> hugeadm --thp-never
iii) Check if [never]
cat /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled
- Using DHCP
- Set up a DHCP server on
losalamosfirst. Here is a video tutorial about how to set up a DHCP server on Ubuntu server. Be carefule about compatability. The system we install is Ubuntu 14.01. So download the version of DHCP server which is compatable with our system. The DNS server of CMU are here And you can check this for DHCP configuration.
- Here is some quick tips for setting up the dhcp server. After installed dhcp in
losalamos, you need to configure it in file/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf. In this file, you need to configure an internal subnet withsubnet,netmask,range,domain-name-servers,default-lease-timeandmax-lease-time. You can configure the other parameters, but the stuff above is considered necessary to let your dhcp server work. After configuration, run/etc/init.d/isc-dhcp-server restartto restart your dhcp server. As always, please use sudo.
- Switch to innet machines, up the
eth1, and set up eacheth1todhcp. You can check this page to help.
For now, the machines in the subnet are unable to connect the real internet. This is because the gateway does not forward their tcp/udp requests to the outside world. Thus we use iptables to tell gateway forwarding them.
- Configure
losalamos. Input the following command line,sudo bash -c 'echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward'sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth1 -j MASQUERADEsudo iptables -A FORWARD -i eth1 -o eth0 -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPTsudo iptables -A FORWARD -i eth0 -o eth1 -j ACCEPTIf the above command lines don't work in your case, please refer to this HOWTO WIKI. If you want to know more about forwarding, check this. Attention:HOWTO WIKIis not totally same as our case, according to the image above.eth0andeth1are supposed to be swapped in our case, compared with the examples in the wiki. Don't overthink the command lines in HOWTO WIKI. Just type in the commands, they are not script. After configuring iptables, all four machines should be able to connect to the Internet now, you can try to ping www.google.com on all four machines to test your configuration.
You may want to configure the iptables to block some incoming traffic and allow access only to particular protocols and ports. Here is a quick introduction. Use iptables -L -v to check current valid rules. In case you wrongly add a certain rule, use iptable -D [rules] to delete a cerain rules, check this for reference.
If you block or drop some important ports (i.e., 22, 80, 8080), you might lose the SSH connection or HTTP connection.
IPtables are like rule books that are used when a connection tries to establish itself on the server. The tables find a matching rule and take the corresponding action or use the default rule if no match is found. In the assignment we could add the ACCEPT rule for connections through ports that we know are being used by the required services (Such as port 22 for ssh etc.) and place a default rule to block all connections. Thus all required connections would be allowed and others would automatically be blocked.
It is very important to remember and save the changes that have been made to the iptable, otherwise all the rules will get deleted the next time the ip table servise is restarted. To save the ip table use the following command in Ubuntu:
sudo /sbin/iptables-save
To further understand IP tables here are a few good resources:
- If you cannot ping external resources on the inner machines, you can: 1) check if your server is able to ping outside or not; 2) check if the
dns-nameserversis set in all four configuration files;(In order to resolve DNS host name you should add dns-nameservers line when you configure etc/network/interfaces on four machines as indicated above, otherwise the inner machine can only ping external IP address.) or 3) check carefully the spelling of your configuration files. 4) check/etc/sysctl.confis well modified. - When setting the iptable protection, make sure you don't block the SSH. Just set the iptable on the
losalamosaccording to the iptable minimum requirements table shown above. - When you are setting the iptable protection, if you want to set the REJECT all -- any any anywhere anywhere reject-with icmp-host-prohibited, make sure that you should first accpet the port 22 and port 8080, or you may lose the SSH connection. After that, it might become very slow to connect through SSH but it can still use SSH to connect. So do not panic and be patient.
- For minimum iptables protection, as you can see in the principle figure above, for the local processes as the host
losalamos, it seems you can drop some of the PREROUTING, FORWARD, or INPUT. But after attempting, the PREROUTING cannot be changed. Therefore, you can change FORWARD and INPUT for protecting. After setting, you can also usenmap losalamos.pc.cs.cmu.eduandnmap losalamos.pc.cs.cmu.edu -Pnto see the status of the PORT for protecting status checking. - Remember when you use a machine outside cluster to SSH in losalamos, you should try
ssh username@losalamos.pc.cs.cmu.edu. Do #not# use its subnet IP adress. But inside the cluster, each machine can access another through either domain name or subnet IP(10.X.X.X). - Apart from the above mentioned ports, remember to also accept the port for the additional service that is required to be enabled (E.g. port 8088 for Zepplin in our case).
- The IP tables are stored in memory. You should save their state in case a reboot is required (Do not reboot for any reason, if avoidable). This tells you how to do it.
- It is also a good idea to keep a backup of your command history, in case you want to repeat what you did earlier, or if you want to figure out at which step you were probably going wrong. This can be done using
history > historyLogAmbari is a automatical deploy system for Hadoop. Link to installation.
To setup, configure and deploy parts, you may also refer to This and This.
-
Set up environment: manual section 1.4
-
Install ambari-server on master: manual section 2.1.6
-
Configure cluster through web UI: manual section 3
(You may encounter some warnings when verifying system, execute required command and rerun checks. Be sure to modify hosts on each machine.)
- Go through the “Getting Ready” section to check and configure if you could meet with the basic environment requirements. Take care of part 1.4.
- It's better to follow the Official installation document. Link has been given above. But for the password-less SSH setting, the links behind in the tips are more detailed(although basically they are the same), you may get puzzled follow the official document.
- Do not skip the 1.4 “Prepare the Environment” for the sake of less possible problems in the later installation process:
- Do 1.4.1 Set Up Password-less SSH use links behind in the tips
- no need do 1.4.2: there is default account
- Do 1.4.3 NTP on all four hosts, there is no ubuntu version command in the official installation document, refer to here. Follow these steps on all four machines:
i)
>> sudo apt install ntp
ii)
>> sudo vi /etc/ntp.conf
iii) Change the pool of servers:
*for losalamos*
server 0.north-america.pool.ntp.org
server 1.north-america.pool.ntp.org
server 2.north-america.pool.ntp.org
server 3.north-america.pool.ntp.org
OR
server 0.us.pool.ntp.org
server 1.us.pool.ntp.org
server 2.us.pool.ntp.org
server 3.us.pool.ntp.org
*for others, put the above lines as well as the one below*
server losalamos.pc.cs.cmu.edu prefer iburst
iv)
watch ntpq -cpe -cas
v)
>> sudo service ntp restart
-
no need do 1.4.4: Offitial installation document gives hosts name and network setting on redhat and centOS. for ubuntu, hostname and network are set in etc/network/interfaces already in the "Establish Subnet" process。
-
no need for 1.4.5: detailed iptable setting guide has been given above.
-
Do 1.4.6. Ubuntu 14 has no selinux pre-installed, therefore you don't need to do anything.
-
You can set ulimit at /etc/security/limits.conf, make sure you change the ulimit of the ACCOUNT YOU USE(e.g root) to install Ambari. Do not reboot the system when you finish the ulimit installation. If do, you may need to reinstall the machine.
-
You do not need to do the section 1.5 of "Using a Local Repository"
This will help you when setting
ulimit. Notice that in this instruction,usermeans[user]. Thus you need to replace it with your system username.While using ulimit, and referring to the link in the above tip, do not reboot the system but make sure to log out of all active sessions and then login to see effective changes by using the command:ulimit -a -
Set up the SSH carefully. After this part being done, you can remotely control those four machines with your own laptop. If you did not install OpenSSH during installation, you can install it using
apt-get install openssh-server. You can only directly SSH intolosalamosfrom the outside, but you can SSH into other machines withinlosalamos(like Inception!). -
You need to set up password-less SSH during the process:
- Overview for password-less SSH: produce a pair of public key and private key on one host, copy the public key to other hosts, then you could visit those hosts without inputting password. It's like give away your public key to others, you have the access to them.
- The goal is that you can ssh from any one of the four machines to the root of all (including itself) without typing in password manually.
- Before you try to set up the password-less SSH, you need to enable ssh root access on Ubuntu 14.04. For detailed instructions, please follow the link: http://askubuntu.com/questions/469143/how-to-enable-ssh-root-access-on-ubuntu-14-04
- One way to achieve password-less SSH is that: for each node, login as root user by su and put the same copy of rsa key pair in the /.ssh directory of root user account.
- The other way is: allow the SSH login root account and then follow this steps in four machines (you need to set the pw-less SSH from a root acount in any machine to another root acount of any other machine, so every username in this example should be replaced by root. You may also check next 3 instruction for reference.And be careful that you should still use
ssh-keygenwhile generating key pairs, otherwise it could not ssh the root properly later). - A much easier way to achieve password-less SSH from server A to server B (under root account) would be:
1. ssh-keygen -t rsa -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa
2. cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
3. chmod 700 ~/.ssh && chmod 600 ~/.ssh/*
4. cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub | ssh root@B 'cat >> .ssh/authorized_keys'
5. ssh root@B
Explaination: The private key is just the key for a server and the pubic key is like a lock that the private key could solve. If you append the public key to the authorized_keys file in the remote server, the private key in current server can match with it automatically and you can ssh to B without password.
- Ubuntu system has no pre-set password for root user, in order to login as root user, you need to set password first, use command
sudo passwd - The manual from Hortonworks have covered the basic steps. You can also check this if you need more help.
- You need to use root permission to set up password-less SSH. To set the root password see this.
- If you change the ssh configuration, you may need to restart ssh by
sudo service ssh restart. - Make sure the password-less SSH works in both directions among four machines: scp the private and public key to the .ssh folder of four machines and modify authorized_key file. Sometimes when you reinstall the cluster, you would encounter a problem that you cannot have the remote connection with the correct ssh key. In this time, you can type
chmod 400+ key name or vim into the file that store the original key to delete the original one.
-
If something goes wrong with the password-less SSH, you may get timeout error in building cluster. Then try Installing Ambari Agents Manually, look at this. For Ubuntu, use apt-get instead of yum.
-
You may generate the public key or private key from the user account which is not root, check it carefully or you may not be able to automatically install the hadoop system. The public key and private key is under the file /root/.ssh. .ssh file is invisible file there.
When input the private key in the Ambari installation, don't forget to include the first line and last line. It is best to just scp the private key of losalamos to your local system and use it by selecting the file from the GUI.
-
Remember to set id_rsa.pub as authroized_keys in the
losalamosif you want other slave machines to login usingssh losalamos. -
If you come accross failures in registering four machines, check:
- If you set the ssh correctly, and can login in other machine from root@losalamos without password.
- Use the private key:
id_rsa. Copy this withscpto your laptop beforehand. You could use this link for reference. Upload the file. Do not copy paste the key from terminal (there might be extra white-spaces or lines added/missing). - All machine, /etc/hosts need to have their FQDN inside. Also, according to Install Documentation, check
hostname -fis return its FQDN. - You may meet message telling you to uninstall zlibc. Don't. It will remove ambari-agent and you will have to set up the whole machine again.
-
Before Install the services, better to carefully handle the warning from the registeration section. Check whether NTP is intalled.If you meet warings when confirms hosts which said ntp services error, you may check whether you have already started up the ntp on each machine, if not, use this command line 'sudo service ntp start'.
-
The services you need to install are
HDFS,MapReduce2,Yarn,ZooKeeperandAmbari Metrics. Some other services may fail so do not install services that you do not need. -
You need to install both
ambari-serverandambari-agentonlosalamos, and nothing needed for innet machines. -
But if everything goes smoothly, you only have to manually install
ambari-serveronlosalamos, and everything else can be done through the Ambari Web in web browser. -
If any/all of the 'target hosts' fail to register, it might be because of the following problems:
- Hostname conflict. Look for errors in the log. If there is a hostname conflict (eg: expecting alpha.pc.cs.cmu.edu but got alpha), you can change the hostname by using the
hostname <name>command. - Misconfiguration of the ambari agents. Remove the ambari installation and try again with a clean slate. (Not for losalamos)
- Hostname conflict. Look for errors in the log. If there is a hostname conflict (eg: expecting alpha.pc.cs.cmu.edu but got alpha), you can change the hostname by using the
-
While installing
ambari-serveronlosalamos, java 1.8 will be installed with your choice during the process, but you need to configure the environment variables by yourself this page will help on your configurations. -
Your java directory should be under
/usr/jdk64/. You can find your $JAVA_HOME path in this directory and carefully set it to your configuration file as the previous instruction indicates. -
Remember to use
sudo source /etc/profileafter you modify the environment variables. After that, you should be able to check the version of your java by usingjava -version. -
Sometimes you may encounter the problem when you execute the “source command” and the shell may remind you that “command not found: source”. You can try
source –s <filename>here. It might works. -
While going through the Ambari Install Wizard, there are several parts you should watch out:
- Make sure password-less SSH is correctly set up, which will let you SSH from any one of the four machines to other three without typing in password manually. Otherwise if may gave you failure when registering three inner machines.
- When choosing services to install, only choose those are required. One safe way to do this is to first install only
HDFS,MapReduce2,Yarn,ZooKeeperandAmbari Metrics. And go back to install other required services after confirming your hadoop can run correctly by runing a MapReduce task. - When assinging master, name node, data node, go through the
Grading CriteriainRequirementssection carefully. - When install extra service, you should not omit the warning. You need to handle it one by one.
- Restart the service before runing Demo
-
You should be aware of that
losalamosshould be one of the clients since it is the only interface to run Hadoop programs from outside. -
Select default setting when installing Ambari Server.
-
During installation, the setup may prompt a warning related to increasing the heap size. Go to the previous page and make all the required changes. On clicking
Next, the same warning will be shown again. Do not worry about it and proceed to the next step. -
If you come across errors when starting the server, Check this.
-
Once the cluster is installed, make sure this page shows each host has correct IP address (10.0.0.x).s If the IP address is 127.0.0.1 that's not correct, check whether the four
/etc/hostsfiles are same with each other. Modify/etc/hostsif necessary, then restart both ambari-server and all ambari-clients. -
If something goes wrong, check your firewall settings or you may find causes by looking at log files under
/var/log -
If run into Transparent Huge Pages error, check out this. this. You may first try the following commands to disable THP and see if the problem can be fixed:
# echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled
# echo never > /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/defrag
- For installing Ambari (except for logging into node for debug), you DON'T need to install python2.6, Ambari is compatible with python2.6 or later version.
- If you decide to install python yourself, actually for anything, DO NOT use any personal repository, use official ones. Otherwise it may lead to cluster building failure and probably reinstallation of OS.
- SName Node and Name node should be on different machines. Data Node and Name Node should be on different machines. Name node(Not SName Node) is the primary Name Node.
- You may meet ambari problems like it cannot start the service or it cannot install some services required during your installation, if you clear your machine, it cannot work. You should reinstall ubuntu and start from a clean system.
If everything is green on the dashboard of Ambari, you can follow this to run a mapreduce job on the machines.
- Create a input directory under the user of
hdfs(use commandsu hdfs) - Write the test MapReduce program (eg. wordcount)
- Compile the java files to class files with
javacand archive the class files intojar - Use command
yarnto run the project and remember to set the output directory of your project or you will hard to find it - Run the program under the user
hdfs(HADOOP_USER_NAME=hdfs). - If you want to move the files to HDFS via Ambari UI, you could follow the steps mentioned here. Also, it is better to create a separate user 'hdfs' instead of 'admin' in Ambari if you follow this approach and give it root permissions in Ambari.
- If you meet any permission problem of
hdfs, check this or try usingsudo. - Make sure the file paths provided will creating the jar and running are correct.
- Log in through SSH to
losalamosand perform all you tests here since this server should be the only interface; - Switch to other Hadoop users (ex. hdfs, but you can still create a new one) and upload or create your files on HDFS;
- The output folder of your map reduce program should not exist when executing the jar program.
- If there's any "permission" problem, try using su (root), or
sudoin each command; - Remember that in MapReduce 2.0, you should use the command
yarnbut nothadoop. - If you have trouble running your wordcount program, you may need to install the Java Jre before. You can choose the default one.
- If you have already run the wordcount program successfully and want to run it again, make sure to remove two things. The first one is the output folder. Using hdfs 'dfs -rm -r StartsWithCount/output'. And anther one is the previous version's result. Or you may meet problems say 'File exits'.
- If you meet some problems when you try to compile the java files, you might meet some errors. You might need to install or import some libraries. You do not need to reinstall the cluster.
- Make sure the physical connection is correct;
- You should down/up network adapters or reboot machines to make your network configurations work;
- Make sure your configurations are permanent, otherwise they will remain unchanged after reboot, like iptables;
- Ambari Server should be installed on
losalamossince it is the only server you can get access to from outside the subnet;losalamosshould also hold a Ambari Agent to be part of the cluster; - Keep in mind that
losalamosshould be one of the clients; - Make sure you use
ulimitto change file descriptors limit before installing Ambari, or you may encounter problems in running the cluster. - If by any chance you mapped the History Server incorrectly, you can change it using the steps given here instead of re-doing everything.
- Do not reboot losalamos after installing the OS. If you reboot the losalamos after install the ulimit and lose ssh and net connection, you don't need to restart all the machine. Just the losalamos. Install it from the beginning.
- Edit this instruction file with carefulness, wrong tips can lead to a huge waste of time of other people.
In case anything you configured wrong, you might want to rebuild the cluster again. Please follow the below steps.
##(Two groups have indicated that the following 5 steps may cause components of ambari not being able to install and the ambari to fail rebooting, so be careful if you need to reconfigure the server)
- Stop all services from Ambari first, both in losalamos and 3 slave machines. On slave machines,
sudo ambari-client stop. On losalamos, dosudo ambari-client stopandsudo ambari-server stop. - Clean installed services on all four machines
python /usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/ambari_agent/HostCleanup.py - Stop Ambari Server
sudo ambari-server stop - Reset Ambari Server
sudo ambari-server reset - Start Ambari Server again
sudo ambari-server start - Login to Ambari webpage and create the cluster
If you can't create iptables by following the steps above, you can refer to this script created by Hsueh-Hung Cheng Here, make sure you understand each line of script (it may not work). When you make use of this script, if there is permission denied alert, try to add sudo at the head of most of the lines and refer to the tips in Iptables above to modify the rest one.
- Is the interface configured correctly? (Related command or files: ifconfig, /etc/network/interfaces, lspci, lsmod, dmesg)
- Is DNS/hostnames configured correctly? (Related command or files: /etc/hosts, /etc/resolv.conf, bind)
- Are the ARP tables correct? (arp -a)
- Can you ping the localhost? (ping localhost/127.0.0.1)
- Can you ping other local hosts (hosts on the local network) by IP address? How about hostname? (Related command: ping)
- Can you ping hosts on another network (Internet)? (Related command: ping) All you are doing is going either up or down the network model layers.
route -n: To see your routing tables.-nmeans return numeric outputping: Ping your computer (by address, not host name) to determine that TCP/IP is functioning. You can also use option-cto determine how many packets you'are sending.ifconfig: Tell you everything about the network interfaceiptables -L -vCheck current valid rule in iptablescpPlease refer to Here