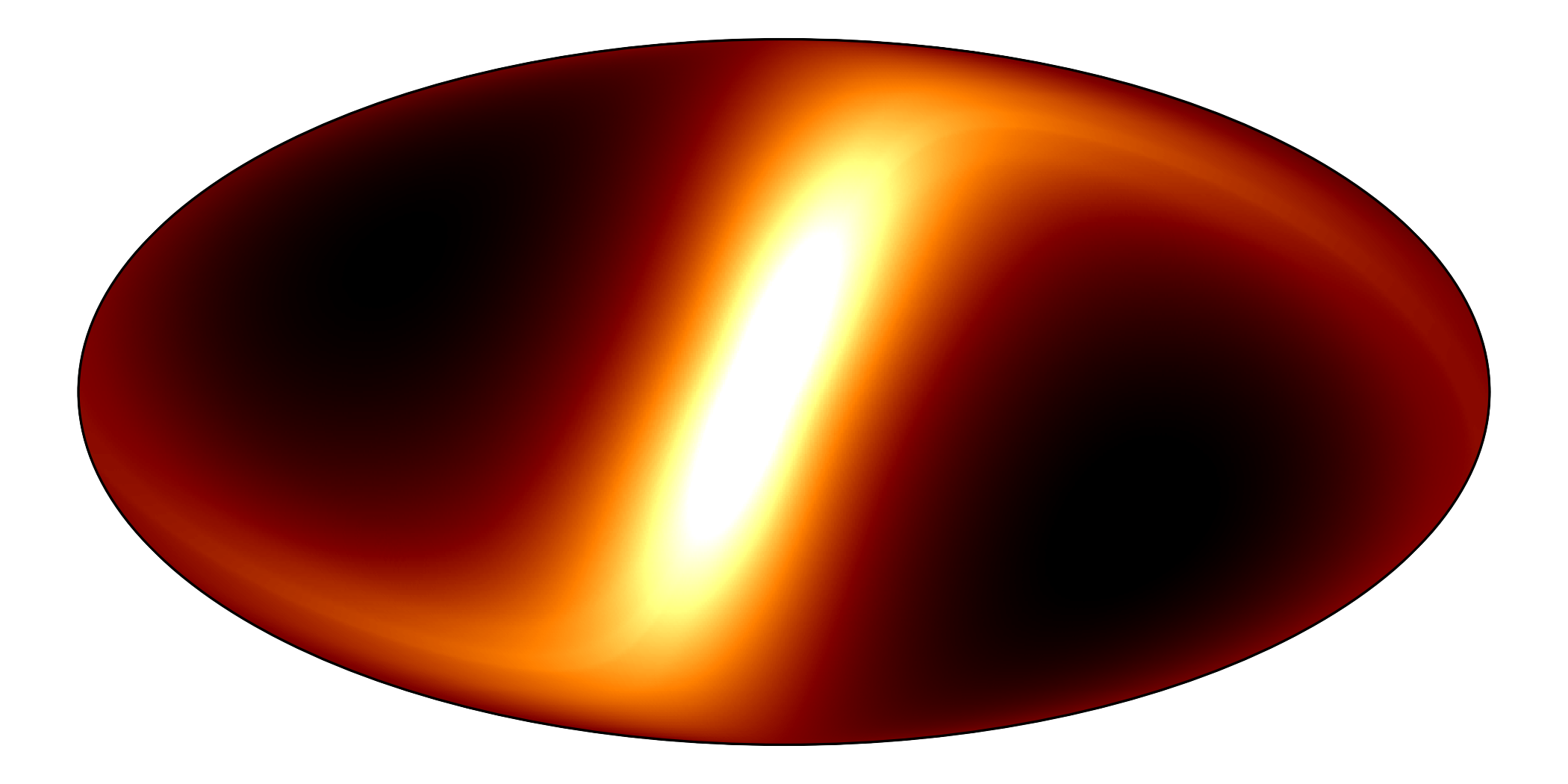
ZodiPy is an Astropy affiliated package for simulating zodiacal light in intensity for arbitrary Solar system observers.
See the documentation for more information and examples on how to use ZodiPy for different applications.
import astropy.units as u
from astropy.time import Time
from zodipy import Zodipy
model = Zodipy(model="dirbe")
emission = model.get_emission_ang(
25 * u.micron,
theta=[10, 10.1, 10.2] * u.deg,
phi=[90, 89, 88] * u.deg,
obs_time=Time("2022-01-01 12:00:00"),
obs="earth",
)
print(emission)
#> [15.35392831 15.35495051 15.35616009] MJy / srSee CITATION
- Cosmoglobe: Simulating zodiacal emission with ZodiPy (San et al. 2022).
- ZodiPy: A Python package for zodiacal light simulations (San 2024).
ZodiPy is installed using pip install zodipy.
ZodiPy supports all Python versions >= 3.9, and has the following dependencies:
Contributing developers will need to download the following additional dependencies to test, lint, format and build documentation locally:
- pytest
- pytest-cov
- hypothesis
- coverage
- ruff
- mypy
- pre-commit
- mkdocs
- pymdown-extensions
- markdown-include
- mkdocs-material
- mkdocstrings
- mkdocstrings-python
- markdown (<3.4.0)
which are required to test and build ZodiPy.
Developers can install ZodiPy through Poetry (Poetry >= 1.8.0) by first cloning or forking the repository, and then running
poetry install
in a virtual environment from the repository root. This will read the pyproject.toml file in the repository and install all dependencies.
Developers not using Poetry can install ZodiPy in a virtual environment with all dependencies by first cloning or forking the repository and then running
pip install -r requirements-dev.txt
from the repositry root. This will read and download all the dependencies from the requirements-dev.txt file in the repository.
Note that developers using Python 3.12 will need to upgrade their pip versions with python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip before being able to install ZodiPy. This is due to known incompatibilities between older pip versions and Python 3.12
The following tools should be run from the root of the repository with no errors. (These are ran automatically as part of the CI workflows on GitHub, but should be tested locally first)
- pytest: Tests are run with pytest by simply running
pytestin the command line in the root of the repository. - ruff: Formating and linting is done with
ruffby simply runningruff checkandruff formatin the command line in the root of the repository. - mypy: Type checking is done with
mypyby simply runningmypy zodipy/in the root of the repository.
Remeber to add tests when implementing new features to maintain a high code coverage.
We use MkDocs to create our documentation. The documentation is built locally with mkdocs build from the repository root, and served with mkdocs serve.
This work has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreements No 776282 (COMPET-4; BeyondPlanck), 772253 (ERC; bits2cosmology) and 819478 (ERC; Cosmoglobe).