The regex-centric, fast lexical analyzer generator for C++ with full Unicode support.
RE/flex is compatible with Flex lexer specifications and Bison parsers. RE/flex is faster than Flex while providing a wealth of new features and contributions. RE/flex is also much faster than regex libraries such as Boost.Regex, C++11 std::regex, PCRE2 and RE2. For example, tokenizing a 2 KB representative C source code file into 244 tokens takes only 8 microseconds:
| Command / Function | Software | Time (μs) |
|---|---|---|
| reflex --fast --noindent | RE/flex 2.0.0 | 8 |
| reflex --fast | RE/flex 2.0.0 | 9 |
| flex -+ --full | Flex 2.5.35 | 17 |
| reflex --full | RE/flex 2.0.0 | 18 |
| boost::spirit::lex::lexertl::actor_lexer::iterator_type | Boost.Spirit.Lex 1.66.0 | 40 |
| pcre2_jit_match() | PCRE2 (jit) 10.32 | 60 |
| hs_compile_multi(), hs_scan() | Hyperscan 5.1.0 | 209 |
| reflex -m=boost-perl | Boost.Regex 1.66.0 | 230 |
| pcre2_match() | PCRE2 10.32 | 318 |
| RE2::Consume() | RE2 (pre-compiled) 2018-04-01 | 417 |
| reflex -m=boost | Boost.Regex POSIX 1.66.0 | 450 |
| RE2::Consume() | RE2 POSIX (pre-compiled) 2018-04-01 | 1226 |
| flex -+ | Flex 2.5.35 | 3968 |
| pcre2_dfa_match() | PCRE2 POSIX (dfa) 10.32 | 4094 |
| regcomp(), regexec() | GNU C POSIX.2 regex | 5800 |
| std::cregex_iterator() | C++11 std::regex | 5979 |
The performance table is indicative of the impact on performance when using PCRE2 and Boost.Regex with RE/flex. PCRE2 and Boost.Regex are optional libraries integrated with RE/flex for Perl matching because of their efficiency. By default, RE/flex uses DFA-based extended POSIX matching, which is the fastest method as shown in the table.
The RE/flex matcher tracks line numbers, column numbers, and indentations,
whereas Flex does not (option noyylineno) and neither do the other regex
matchers in the table (except PCRE2 and Boost.Regex when used with RE/flex).
Tracking this information incurs some overhead. RE/flex also automatically
decodes UTF-8/16/32 input and accepts std::istream, strings, and wide strings
as input.
Note: Best times of 30 tests with average time in microseconds over 100 runs executed on the command line using Mac OS X 10.12.6 clang 9.0.0 -O2, 2.9 GHz Intel Core i7, 16 GB 2133 MHz LPDDR3. Hyperscan disqualifies as a scanner due to its "All matches reported" semantics resulting in 1915 matches for this test, and due to its event handler requirements. Download the tests Timings on other platforms may differ, though in the worst cases tested, reflex ran equally fast or slightly faster than the best times of Flex.
Features
- Compatible with Flex and Bison to eliminate a learning curve, making a transition from Flex++ to RE/flex frustration-free.
- Generates reusable source code that is easy to understand.
- Integrates seamlessly with Bison and supports reentrant, bison-bridge,
bison-locations, Bison 3.0 C++ interface
%skeleton "lalr1.cc"and Bison complete symbols. - Fully supports Unicode and Unicode properties
\p{C}, including Unicode identifier matching for C++11, Java, C#, and Python source code. - Auto-detects UTF-8/16/32 input to match Unicode patterns.
- Supports file encodings ISO-8859-1 through ISO-8859-15, CP 1250 through 1258, CP 437, CP 850, CP 858, KOI8, MACROMAN, EBCDIC, and custom code pages.
- Generates scanners for lexical analysis on files, C++ streams, (wide) strings, and memory such as mmap files.
- Includes many examples, such as a mini C compiler to Java bytecode, a tokenizer for C/C++ source code, a tokenizer for Python source code, a tokenizer for Java source code, and more.
- Extensive documentation in the online User Guide.
- Indent/nodent/dedent anchors to match text with indentation, including
custom
\t(tab) widths. - Lazy quantifiers, no hacks are needed to work around greedy repetitions.
- Word boundary anchors.
- Freespace mode option to improve readability of lexer specifications.
%classand%initto customize the generated Lexer classes.%includeto modularize lexer specifications.- Multiple lexer classes can be combined and used in one application, e.g. by multiple threads in a thread-safe manner.
- Configurable Lexer class generation to customize the interface for various parsers, including Yacc and Bison.
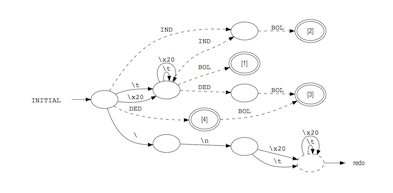
- Generates Graphviz files to visualize FSMs with the Graphviz dot tool.
- Includes an extensible hierarchy of pattern matcher engines, with a choice of regex engines, including the RE/flex regex engine, PCRE2, and Boost.Regex.
- The RE/flex regex library makes C++11 std::regex, PCRE2, and Boost.Regex much easier to use for pattern matching on (wide) strings, files, and streams.
- Lots of other improvements over Flex++, such as
yypush_buffer_statesaves the scanner state (line, column, and indentation positions), not just the input buffer; no input buffer length limit (Flex has a 16KB limit);line()returns the current line (e.g. for error reporting).
The RE/flex software is fully self-contained. No other libraries are required. PCRE2 and Boost.Regex are optional to use as regex engines.
The RE/flex repo includes a Mini C compiler demo and tokenizers for Java, Python, C/C++, JSON, XML, YAML.
Installation
Windows users
Use reflex/bin/reflex.exe from the command line or add a Custom Build
Step in MSVC++ as follows:
-
select the project name in Solution Explorer then Property Pages from the Project menu (see also custom-build steps in Visual Studio);
-
add an extra path to the
reflex/includefolder in the Include Directories under VC++ Directories, which should look like$(VC_IncludePath);$(WindowsSDK_IncludePath);C:\Users\YourUserName\Documents\reflex\include(this assumes thereflexsource package is in your Documents folder). -
enter
"C:\Users\YourUserName\Documents\reflex\bin\win32\reflex.exe" --header-file "C:\Users\YourUserName\Documents\mylexer.l"in the Command Line property under Custom Build Step (this assumesmylexer.lis in your Documents folder); -
enter
lex.yy.h lex.yy.cppin the Outputs property; -
specify Execute Before as
PreBuildEvent.
If you are using specific reflex options such as --flex then add these in step 3.
Before compiling your program with MSVC++, drag the folders reflex/lib and
reflex/unicode to the Source Files in the Solution Explorer panel of
your project. Next, run reflex.exe simply by compiling your project (which
may fail, but that is OK for now as long as we executed the custom build step
to run reflex.exe). Drag the generated lex.yy.h (if present) and
lex.yy.cpp files to the Source Files. Now you are all set!
In addition, the reflex/vs directory contains batch scripts to build projects
with MS Visual Studio C++.
Unix/Linux and Mac OS X
On macOS systems you can use homebrew to install RE/flex
with brew install re-flex.
On NetBSD systems you can use the standard NetBSD package installer (pkgsrc): http://cdn.netbsd.org/pub/pkgsrc/current/pkgsrc/devel/RE-flex/README.html
Otherwise, you have two options: 1) quick install or 2) configure and make.
Note: GCC 8 and greater may produce warnings of the sort "note: parameter passing for argument ... changed in GCC 7.1". These warnings should be ignored.
Quick install
First clone the code:
$ git clone https://github.com/Genivia/RE-flex
Then simply do a quick clean build, assuming your environment is pretty much standard:
$ ./clean.sh
$ ./build.sh
This compiles the reflex tool and installs it locally in reflex/bin. For
local use of RE/flex in your project, you can add this location to your $PATH
variable to enable the new reflex command:
$ export PATH=$PATH:/your_path_to_reflex/reflex/bin
Note that the libreflex.a and libreflex.so libraries are saved locally in
reflex/lib. Link against the library when you use the RE/flex regex engine
in your code, such as:
$ c++ <options and .o/.cpp files> -L/your_path_to_reflex/reflex/lib -lreflex
or you could statically link libreflex.a with:
$ c++ <options and .o/.cpp files> /your_path_to_reflex/reflex/lib/libreflex.a
Also note that the RE/flex header files that you will need to include in your
project are locally located in include/reflex.
To install the man page, the header files in /usr/local/include/reflex, the
library in /usr/local/lib and the reflex command in /usr/local/bin:
$ sudo ./allinstall.sh
Configure and make
The configure script accepts configuration and installation options. To view these options, run:
$ ./configure --help
Run configure and make:
$ ./configure && make
To build the examples also:
$ ./configure --enable-examples && make
After this successfully completes, you can optionally run make install to
install the reflex command and libreflex library:
$ sudo make install
Unfortunately, cloning from Git does not preserve timestamps which means that you may run into "WARNING: 'aclocal-1.15' is missing on your system." To work around this problem, run:
$ autoreconf -fi
$ ./configure && make
Optional libraries to install
-
To use PCRE2 as a regex engine with the RE/flex library and scanner generator, install PCRE2 and link your code with
-lpcre2-8. -
To use Boost.Regex as a regex engine with the RE/flex library and scanner generator, install Boost and link your code with
-lboost_regexor-lboost_regex-mt. -
To visualize the FSM graphs generated with reflex option
--graphs-file, install Graphviz dot.
Improved Vim syntax highlighting
Copy the lex.vim file to ~/.vim/syntax/ to enjoy improved syntax
highlighting for both Flex and RE/flex.
Usage
There are two ways you can use this project:
- as a scanner generator for C++, similar to Flex;
- as a flexible regex matching API for C++.
For the first option, simply build the reflex tool and run it on the command line on a lexer specification:
$ reflex --flex --bison --graphs-file lexspec.l
This generates a scanner for Bison from the lexer specification lexspec.l and
saves the finite state machine (FSM) as a Graphviz .gv file that can be
visualized with the Graphviz dot tool:
$ dot -Tpdf reflex.INITIAL.gv > reflex.INITIAL.pdf
$ open reflex.INITIAL.pdf
Several examples are included to get you started. See the manual for more details.
For the second option, simply use the RE/flex matcher API classes to start pattern matching on strings, wide strings, files, and streams.
You can select matchers that are based on different regex engines:
- RE/flex regex:
#include <reflex/matcher.h>and usereflex::Matcher; - PCRE2:
#include <reflex/pcre2matcher.h>and usereflex::PCRE2Matcherorreflex::PCRE2UTFMatcher. - Boost.Regex:
#include <reflex/boostmatcher.h>and usereflex::BoostMatcherorreflex::BoostPosixMatcher; - C++11 std::regex:
#include <reflex/stdmatcher.h>and usereflex::StdMatcherorreflex::StdPosixMatcher.
Each matcher may differ in regex syntax features (see the full documentation), but they all share the same methods and iterators, such as:
matches()returns nonzero if the input matches the specified pattern;find()search input and returns nonzero if a match was found;scan()scan input and returns nonzero if input at current position matches;split()returns nonzero for a split of the input at the next match;find.begin()...find.end()filter iterator;scan.begin()...scan.end()tokenizer iterator;split.begin()...split.end()splitter iterator.
For example, using Boost.Regex (alternatively use PCRE2 reflex::PCRE2Matcher):
#include <reflex/boostmatcher.h> // reflex::BoostMatcher, reflex::Input, boost::regex
// use a BoostMatcher to check if the birthdate string is a valid date
if (reflex::BoostMatcher("\\d{4}-\\d{2}-\\d{2}", birthdate).matches() != 0)
std::cout << "Valid date!" << std::endl;
With a group capture to fetch the year:
#include <reflex/boostmatcher.h> // reflex::BoostMatcher, reflex::Input, boost::regex
// use a BoostMatcher to check if the birthdate string is a valid date
reflex::BoostMatcher matcher("(\\d{4})-\\d{2}-\\d{2}", birthdate);
if (matcher.matches() != 0)
std::cout << std::string(matcher[1].first, matcher[1].second) << " was a good year!" << std::endl;
To search a string for words \w+:
#include <reflex/boostmatcher.h> // reflex::BoostMatcher, reflex::Input, boost::regex
// use a BoostMatcher to search for words in a sentence
reflex::BoostMatcher matcher("\\w+", "How now brown cow.");
while (matcher.find() != 0)
std::cout << "Found " << matcher.text() << std::endl;
The split method is roughly the inverse of the find method and returns text
located between matches. For example using non-word matching \W+:
#include <reflex/boostmatcher.h> // reflex::BoostMatcher, reflex::Input, boost::regex
// use a BoostMatcher to search for words in a sentence
reflex::BoostMatcher matcher("\\W+", "How now brown cow.");
while (matcher.split())
std::cout << "Found " << matcher.text() << std::endl;
To pattern match the content of a file, where the file may use UTF-8, 16, or 32 encodings that are automatically converted when a UTF BOM is present:
#include <reflex/boostmatcher.h> // reflex::BoostMatcher, reflex::Input, boost::regex
// use a BoostMatcher to search and display words from a FILE
FILE *fd = fopen("somefile.txt", "r");
if (fd == NULL)
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
reflex::BoostMatcher matcher("\\w+", fd);
while (matcher.find())
std::cout << "Found " << matcher.text() << std::endl;
fclose(fd);
Same again, but this time with a C++ input stream:
#include <reflex/boostmatcher.h> // reflex::BoostMatcher, reflex::Input, boost::regex
// use a BoostMatcher to search and display words from a stream
std::ifstream file("somefile.txt", std::ifstream::in);
reflex::BoostMatcher matcher("\\w+", file);
while (matcher.find())
std::cout << "Found " << matcher.text() << std::endl;
file.close();
Stuffing the search results into a container using RE/flex iterators:
#include <reflex/boostmatcher.h> // reflex::BoostMatcher, reflex::Input, boost::regex
#include <vector> // std::vector
// use a BoostMatcher to convert words of a sentence into a string vector
reflex::BoostMatcher matcher("\\w+", "How now brown cow.");
std::vector<std::string> words(matcher.find.begin(), matcher.find.end());
Use C++11 range-based loops with RE/flex iterators:
#include <reflex/stdmatcher.h> // reflex::StdMatcher, reflex::Input, std::regex
// use a StdMatcher with std::regex to search for words in a sentence
reflex::StdMatcher matcher("\\w+", "How now brown cow.");
for (auto& match : matcher.find)
std::cout << "Found " << match.text() << std::endl;
RE/flex also allows you to convert expressive regex syntax forms such as \p
Unicode classes, character class set operations such as [a-z--[aeiou]],
escapes such as \X, and (?x) mode modifiers, to a regex string that the
underlying regex library understands and will be able to use:
std::string reflex::Matcher::convert(const std::string& regex, reflex::convert_flag_type flags)std::string reflex::PCRE2Matcher::convert(const std::string& regex, reflex::convert_flag_type flags)std::string reflex::BoostMatcher::convert(const std::string& regex, reflex::convert_flag_type flags)std::string reflex::StdMatcher::convert(const std::string& regex, reflex::convert_flag_type flags)
For example:
#include <reflex/matcher.h> // reflex::Matcher, reflex::Input, reflex::Pattern
// use a Matcher to check if sentence is in Greek:
static const reflex::Pattern pattern(reflex::Matcher::convert("[\\p{Greek}\\p{Zs}\\pP]+", reflex::convert_flag::unicode));
if (reflex::Matcher(pattern, sentence).matches() != 0)
std::cout << "This is Greek" << std::endl;
We use convert with optional flag reflex::convert_flag::unicode to make .
(dot), \w, \s and so on match Unicode and to convert \p Unicode character
classes.
Conversion is fast (it runs in linear time in the size of the regex), but it is
not without some overhead. Making converted regex patterns static as shown
above saves the cost of conversion to just once to support many matchings.
How to contribute?
Please see CONTRIBUTING.
Where do I find the documentation?
Read more about RE/flex in the manual.
License and copyright
RE/flex by Robert van Engelen, Genivia Inc. Copyright (c) 2016-2020, All rights reserved.
RE/flex is distributed under the BSD-3 license LICENSE.txt. Use, modification, and distribution are subject to the BSD-3 license.
Reporting bugs
Visit GitHub to report bugs: https://github.com/Genivia/RE-flex
Changelog
- Nov 14, 2016: 0.9.0 beta released
- Nov 15, 2016: 0.9.1 improved portability
- Nov 17, 2016: 0.9.2 improvements and fixes for minor issues
- Nov 19, 2016: 0.9.3 replaces
%importwith%include, adds freespace option-x, fixes minor issues - Nov 20, 2016: 0.9.4 fixes minor issues, added new examples/json.l
- Nov 25, 2016: 0.9.5 bug fixes and improvements
- Dec 1, 2016: 0.9.6 portability improvements
- Dec 6, 2016: 0.9.7 bug fixes, added option
--regexp-file, Python tokenizer - Dec 9, 2016: 0.9.8 fixes minor issues, improved reflex tool options
--fulland--fast, generates scanner with FSM table or a fast scanner with FSM code, respectively - Jan 8, 2017: 0.9.9 bug fixes and improved Flex compatibility
- Jan 15, 2017: 0.9.10 improved compatibility with Flex options, fixed critical issue with range unions
- Jan 25, 2017: 0.9.11 added C++11 std::regex matching engine support, moved .h files to include/reflex, requires
#include <reflex/xyz.h>from now on, fixederrno_tportability issue - Mar 3, 2017: 0.9.12 refactored and improved, includes new regex converters for regex engines that lack regex features such as Unicode character classes
- Mar 4, 2017: 0.9.13 improved warning and error messages
- Mar 6, 2017: 0.9.14 reflex option
-vshows stats with execution timings, bug fixes - Mar 8, 2017: 0.9.15 added
wtext(),wpair(),winput()methods, other improvements - Mar 22, 2017: 0.9.16 bug fixes, speed improvements, improved option
--unicoderegex conversion, also with(?u:), changedwtext()towstr()and added astr()method - Mar 24, 2017: 0.9.17 improvements
- Mar 26, 2017: 0.9.18 added reflex option
-p(--perf-report) for performance debugging, added doc/man/reflex.1 man page, added interactive readline example - Mar 31, 2017: 0.9.19 fixed reflex option
-m,lexer.in(i)now resets the lexer, fixed reassigning the same input to the lexer that caused UTF BOM to be read twice - Apr 5, 2017: 0.9.20 EBCDIC file translation, other improvements
- Apr 10, 2017: 0.9.21 fixed option
-Pto support multiple lexer classes in one application, addedconfigureinstallation script, optional quick install withallinstall.sh(renamed frominstall.sh) - Apr 12, 2017: 0.9.22 improved explanations of
matches(),find(),scan(),split()that return nonzero for a match, other minor improvements - May 24, 2017: 0.9.23 improved portability, added file encoding conversions for CP-1250 to CP-1258, CP 437, and CP 850/858
- Jun 24, 2017: 0.9.24 added an option for users to define their own custom code pages to translate input, fixed
#in free space mode - Jun 28, 2017: 0.9.25 fixed
--fastFSM not always halting on EOF after a mismatch; fixed buffer realloc, added new examples/csv.l - Jul 5, 2017: 0.9.26 fixed
wstr()always returning UTF-16 strings (should be UTF-16 only whenstd::wstringrequires it) - Sep 26, 2017: 0.9.27 the Flex-compatible
yy_scan_string(),yy_scan_bytes()andyy_scan_buffer()functions now create a new buffer as in Flex, delete this buffer withyy_delete_buffer(); fixed examples to work with newer Bison versions (Bison 3.0.4) - Dec 12, 2017: 0.9.28 added
yy_scan_wstringandyy_scan_wbufferfor wide string scanning with Flex-like functions - Jan 28, 2018: 1.0.0 removed dynamic exception specifications to comply with C++17, upgraded to stable release 1.0
- Feb 24, 2018: 1.0.1 added Unicode IsBlockName categories
- Mar 6, 2018: 1.0.2 added namespace nesting with
%option namespace=NAME1.NAME2.NAME3 ... - Mar 7, 2018: 1.0.3 fixed
--namespaceand%option namespace - Apr 22, 2018: 1.0.4 updated to Unicode 10, cleaned up code to remove tool warnings
- Jun 29, 2018: 1.0.5 updated
--namespacefor options--fastand--fullto support the generation of multiple optimized lexers placed in namespaces. - Jul 9, 2018: 1.0.6 added
--bison-ccoption to generate scanners for Bison 3.0%skeleton "lalr1.cc"C++ parsers, included two examplesflexexample9xxandreflexexample9xxto demo this feature. - Jul 12, 2018: 1.0.7 added
--bison-cc-namespaceand--bison-cc-parseroptions to customize Bison 3.0%skeleton "lalr1.cc"C++ parsers. - Jul 30, 2018: 1.0.8 updated to Unicode 11.
- Aug 21, 2018: 1.0.9 fixed reflex regex library matching with range quantifiers by correcting coding typo.
- Dec 8, 2018: 1.0.10 fixed
columno()to take tab spacing into account. - Jan 18, 2019: 1.0.11 fixed GCC 8.2 warnings, additional enhancements.
- Jan 21, 2019: 1.0.12 the reflex tool now reads files using
reflex::Input. - Feb 20, 2019: 1.1.0 code quality updates.
- Mar 6, 2019: 1.1.1 fixed
configureandmake installheader files, updated--bison-locationsoption. - Mar 7, 2019: 1.1.2 fixed reflex tool handling of backslashes in file paths.
- Mar 11, 2019: 1.1.3 updated to Unicode 12, examples can now be built with
./configure --enable-examples. - Mar 27, 2019: 1.1.4 fixed reflex tool common top code block insertion for all inclusive states.
- Apr 6, 2019: 1.1.5 improved reflex tool command-line option handling, updated documentation.
- Apr 29, 2019: 1.2.0 added
--bison-completeoption, new ugrep utility example, updated manual, fixes minor issues. - May 15, 2019: 1.2.1 added
reflex::convert_flag::basicto convert BRE syntax to ERE syntax, used by ugrep. - May 28, 2019: 1.2.2 fixed MinGW builds, fixed
reflex::Input::get()to return positive character code, matcher option"N"forscanandfindmatches empty input (^$). - Jun 21, 2019: 1.2.3 fixed reflex long regex string generation, namespaces with option
--full, updated documentation and other improvements. - Jun 24, 2019: 1.2.4 fixed an issue with
reflex::StdMatcher(std::regex) causing failures to match input withsplit. - Jul 2, 2019: 1.2.5 added
reflex::Input::in(const char *memptr, size_t memlen)to read a memory segment (for scanning etc.), addedreflex::Input::streambufclass to use areflex::Inputobject as astd::streambuf, improvedyy_scan_bufferandyy_scan_bytes. - Jul 3, 2019: 1.2.6 fixed a problem with lazy quantifiers used within negative patterns.
- Jul 4, 2019: 1.2.7 added
reflex::Input::dos_streambufto convert DOS CRLF to LF, other improvements. - Jul 8, 2019: 1.2.8 added support for inverted mode modifiers
(?-imsux)toreflex::convertandreflex::Pattern. - Jul 11, 2019: 1.2.9 portability improvements.
- Jul 14, 2019: 1.2.10 added
AbstractMatcher::set_bob(), movedAbstractMatcher::peek()to public, minor improvements. - Jul 21, 2019: 1.3.0 added subtractive start condition scoping with
<^...>, added undent\kanchor to undo indenting changes ("undenting") with an example inexamples/indent2.l, improved indent\iand dedent\janchors and other improvements. - Jul 24, 2019: 1.3.1 added
matcher().tabs(n)to set tab size, used bycolumno()and indent\iand dedent\janchors, newreflex::Patternmethods, other improvements. - Jul 27, 2019: 1.3.2 added defined name expansion in bracket lists for the union
||, intersection&&, and subtraction--operations, e.g.[||{letter}||{digit}]expands into[a-zA-Z0-9]whenletteris defined as[a-zA-Z]anddigitis defined as[0-9], see Character Classes in the documentation. - Aug 5, 2019: 1.3.3 fixed
reflex::BoostMatcher(and derivedreflex::BoostPosixMatcher,reflex::BoostPerlMatcher) regression bug that crept into the 1.2.4 update. - Aug 7, 2019: 1.3.4 speed improvements for non-fast options.
- Aug 8, 2019: 1.3.5 further speed improvements for both fast and non-fast options (15% to 30% faster).
- Aug 12, 2019: 1.3.6 added lexer and matcher
buffer(base, size)methods and improved Flex-compatibleyy_scan_buffer(base, size), these functions scan memory fast with zero copy overhead; addedmmap.lexample to scan an mmap-ed file fast with mmap(2) andbuffer(base, size); other improvements. - Aug 16, 2019: 1.3.7 added
reflex::BufferedInput::dos_streambufto improvedos_streambufspeed by buffering (reflex::Input::dos_streambufis unbuffered), fixed%option token-typeto apply without restrictions. - Aug 17, 2019: 1.3.8 added caching of
lineno()andcolumno()to increase speed, which is essential for large buffers such as large mmap-ed files scanned withbuffer(base, size); other improvements. - Sep 4, 2019: 1.4.0 added reflex option
-S(--find) for efficient searching instead of scanning input (i.e. efficiently ignoring unmatched input) demonstrated with newfindfastandfindsearchexamples; changed--nodefaultto throw an exception when option--flexis not used and when the default rule is triggered. - Sep 10, 2019: 1.4.1 fixed
lineno()caching issue (1.3.8 bug); fasterfind. - Sep 15, 2019: 1.4.2 faster
findfor patterns beginning with optional repetitions such as.*. - Sep 29, 2019: 1.4.3 added
reflex::AbstractMatcher::clone()to clone a referenced concrete matcher object. - Oct 23, 2019: 1.4.4 improved option
--flexfor Flex compatibility; fixed option--token-typewith option--flex, now properly definesYY_NULLandyyterminate; fixedAbstractMatcher::buffer(n)for largen; fasterfind. - Nov 5, 2019: 1.5.0 added
border(),span(),line(),wline(), andskip(c)methods; added new section on error reporting and recovery to the documentation; fixedyy_scan_string()andyy_scan_buffer()when called before callingyylex()for the first time; improved performance. - Nov 7, 2019: 1.5.1 improvements; added
dos.ldemo example ofreflex::InputBuffer::dos_streambuf. - Nov 12, 2019: 1.5.2 fixed an internal buffer allocation issue that may cause a crash when input lines are longer than 16KB (regression bug that crept into in 1.5.0).
- Nov 21, 2019: 1.5.3 added
lineno_end()andcolumno_end()methods, updatedcolumns()with clarifications in the updated documentation; expanded the documentation with additional error reporting and handling techniques with RE/flex and Bison bridge and complete configurations; FSM code generation improvements. - Nov 22, 2019: 1.5.4 added
flexexample11xxexample with Flex specification and Bison complete parser; minor improvements. - Dec 23, 2019: 1.5.5 expanded the
skip(c)methods with awchar_twide character parameter and a UTF-8 string parameter to skip input; added new option--token-eof. - Dec 28, 2019: 1.5.6 added new option
--noindentto speed up pattern matching and lexical analysis by disabling indentation tracking in the input (also disables anchors\i,\j, and\k); speed improvements. - Jan 19, 2020: 1.5.7 expanded file encoding formats to include ISO-8859-2 to 16, MacRoman, KOI8; fixed a bug in
line()andspan(). - Feb 3, 2020: 1.5.8 added
wunput()method; addedlex.vimimproved Flex and RE/flex Vim syntax highlighting; addedyaml.lexample; fixed--freespacewith--unicodewhen bracket lists contain a#; character class operators{+},{-},{&}now accept defined names as first operands and inverted character classes; indent anchor\know matches only when indent level is changed as documented. - Mar 2, 2020: 1.6.0 added PCRE2 regex matcher classes and updated reflex option
--matcher=pcre2-perl; optimized RE/flex matcherfind()with AVX/SSE2/NEON/AArch64; updated and improved regex converters. - Mar 3, 2020: 1.6.1 fixed missing PCRE2 regex type
std::stringin generated scanners. - Mar 10, 2020: 1.6.2 improved
reflex::PCRE2Matcher; fixed MSVC++ x86 32-bit build error whenHAVE_AVX512BWis enabled (requires AVX512BW). - Mar 19, 2020: 1.6.3 updated to Unicode 13; fixed start condition scope specifications for patterns that start with a
{; updated lex.vim. - Mar 22, 2020: 1.6.4 added option
--yyto enable--flexand--bison, but also defines the globalFILE*variablesyyinandyyoutfor enhanced Lex/Flex compatibility (yyinis otherwise a pointer to thereflex::Inputobject to read files, streams, and strings). - Mar 23, 2020: 1.6.5 updated to permit
}as closing marker for%top{,%class{, and%init{code blocks, i.e.%}or}may be used as closing markers. - Mar 31, 2020: 1.6.6 fixed an issue where a trailing backslash in a pattern in a lexer specification causes a reflex-generated C++ comment to extend to the next line, which results in a compilation warning and possibly a line of code being skipped.
- Apr 30, 2020: 1.6.7 minor improvements to parse and convert regex patterns to FSMs.
- May 14, 2020: 2.0.0 faster FSM construction; new FSM VM opcodes; relaxed limits of pattern length and complexity (max 16,711,679 FSM opcode words, from 65,536 words previously) for high-performance pattern matching with very long and complex regex patterns.
- May 25, 2020: 2.0.1 resolved 64-bit build warnings; fixed reflex CRLF output in C++ source code on Windows.
- Jun 29, 2020: 2.1.0 added Bison complete locations filename member access; added example Mini C compiler
minicusing RE/flex scanner with Bison 3.2 C++ complete locations, compiles C-like source code to Java bytecode (class files); added fast fuzzy (approximate) regex matcherreflex::FuzzyMatcherderived fromreflex::Matcher. - Jul 8, 2020: 2.1.1 added
%option paramsto extendlex()/yylex()parameters; updated AVX2 detection for SIMD optimizations. - Jul 9, 2020: 2.1.2 minor update to fix MSVC++ compiler error.
- Aug 3, 2020: 2.1.3 improved
--bison-bridgeoption; updated examples. - Aug 19, 2020: 2.1.4 changed
IN_HEADERtoyyIN_HEADERwhen--flexis used with--header-file; addedreflex::Input::Handlerevent handler for custom handling ofFILE*errors and non-blockingFILE*streams. - Sep 20, 2020: 2.1.5 added matcher method
lineno(n)to set or change the line number ton; addedyyset_lineno(n,s)toflexlexer.h; updated Mini C compiler example. - Oct 12, 2020: 3.0.0 fixed a regression bug since v2.x; redesigned internals to increase IO efficiency and regex pattern search speed.
- Oct 24, 2020: 3.0.1 improved handling of UTF-16/32 file encodings on Windows to prevent ^Z eof when files are opened in text mode.