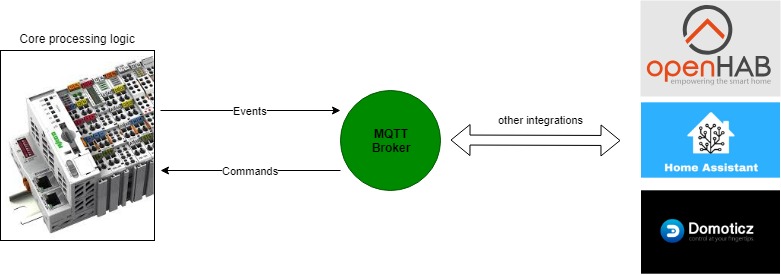
This CoDeSys 3.5 project is built for home automation purposes. The goal of the approach is to perform any critical operations like reading inputs, switching light, controlling sunscreens, etc. Inside the PLC itself and make use of MQTT events to send events to an MQTT broker. Using MQTT subscriptions it's possible to send commands to the PLC to control -for example- outputs.
The purpose? Redundancy on a software level but also on a hardware level!
- PLCs are very (very) robust controllers: no PC, SoC, etc. is more robust and failure resistant.
- Hardware continuity: Home automation providers often renew their modules every X years, modules aren't sold anymore or a full upgrade is required when something breaks. PLCs models and their modules are sold decades after their initial release date. For an example, check out the Wago 750 series controllers and modules.
- Avoid performing critical operations that should work 24/7 inside a less redundant controller (it will fail sooner or later).
- Keep your wife/girlfriend happy when you're not at home and your Rpi, Odroid, Banana Pi, Pc crashes (running your MQTT broker, OpenHab, Home Assistant, etc.).
The project is developed using the IEC 61131-3 standard, there are multiple development environments with their own runtime that support the standard:
- CODESYS V3 by 3S-Smart Software Solutions
- é!COCKPIT by WAGO (WAGO PLCs only)
- ...
Core processing logic is executed in the (robust) PLC. Meaning that events like reading pushbuttons/switches, updating outputs are executed in the PLC software. To enable integration with external software the PLC sends out events to an MQTT broker when events occur (like pushbutton events, outputs that change state). MQTT subscriptions are enabled as well to allow control from the external software to control -for example- outputs.
More information on the software architecture here.
Basic function blocks for basic IO events and operations.
- FB_INPUT_PUSHBUTTON_MQTT
- FB_INPUT_PUSHBUTTON_DIMMER_MQTT
- FB_INPUT_BINARYSENSOR_MQTT
- FB_OUTPUT_BINARY_MQTT
- FB_OUTPUT_DIMMER_MQTT
- FB_OUTPUT_COVER_MQTT
- FB_OUTPUT_BISTABLE_MQTT
Function blocks developed to easily set and get values from the processing logic through MQTT.
With many PLCs having a onboard RS485 serial port it is a popular protocol to create a robust Modbus RTU sensor network.
How to use Modbus RTU differs depending on the PLC/development environment used. The topics belows address the usage of Modbus RTU in several development environments:
To translate the byte array received by the modbus device to their actual value and send their values through MQTT the function blocks below have been developed. Note that a specific function block is required for each type of Modbus RTU device.
- FB_RS485_EASTRON_SDM220_MQTT
- FB_RS485_EASTRON_SDM_POWER_MQTT
- FB_RS485_DUCO_DUCOBOX_MQTT
- FB_RS485_ESERA_1WIRE_GATEWAY_MQTT & FB_RS485_ESERA_OWD_MQTT
In addition to the above a buscontroller function block (FB_RS485_BUSCONTROLLER) is used to control access to the RS485 bus between multiple RS485 device function blocks.
Control DALI drivers using the WAGO DALI modules (753-647).
Control DMX drivers.
- MQTT related settings
- MQTT Discovery
- Controlling Wago PFC user leds (é!COCKPIT runtime)
- Controlling Wago PFC user leds (Codesys 3S runtime)
- Contributing guidelines
- Getting started guide (CODESYS 3S runtime)
- Getting started guide (é!COCKPIT runtime)
- How-to: adding a new MQTT subscription
- How-to: verifying resource usage on a Wago PFC PLC
- How-to: updating function blocks to the latest version
- RS485: tips and tricks
- I'm missing some functionality
The following libraries are used in this PLC project and can be found under src\Libraries:
- MQTT (stefandreyer/CODESYS-MQTT)
- CommonTypesAndFunctions (stefandreyer/CODESYS-Common)
- PRO_JSON (stefandreyer/JSON-Library)
- OSCAT_NETWORK_TYPES (stefandreyer/OSCAT-NETWORK)
- BASIC_Extension (stefandreyer/OSCAT-BASIC)
- OSCAT NETWORK (link)
- OSCAT BASIC (link)
- OSCAT BUILDING (link)
Special thanks to Stefan Dreyer for his assistance in some of the MQTT aspects of this project and his great work on his open-source CoDeSys MQTT library.