This is a repo about whole slide image(WSI) registration for re-stained slides.
In clinical practice, we occasionally use different chemicals (such as H&E and IHC) to stain and re-stain to identify particular cells in the same tissue.
To enable cell level analysis, WSIs should be aligned. However, traditional methods (such as SIFT[1], ECC[2] and FFT[3]) may fail due to the drastic discrepancy in two WSIs,as showing below.
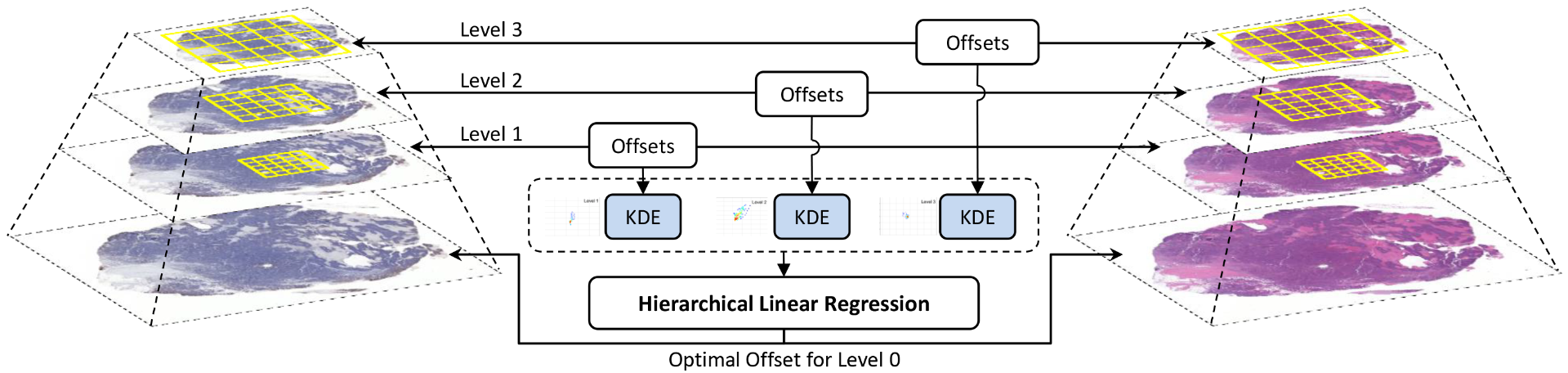
Our method provide a way to integrate these methods into a simple but effective framework, and help these methods perform more robust. If you find this repo is helpful for your project, please cite our paper:
@article{jiang2019robust,
title={Robust Hierarchical Density Estimation and Regression for Re-stained Histological Whole Slide Image Co-registration},
author={Jiang, Jun and Larson, Nicholas and Prodduturi, Naresh and Flotte, Thomas and Hart, Steven},
journal={BioRxiv},
pages={565564},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
- install dependent python packages
conda install -c conda-forge scipy scikit-learn scikit-image opencv openslide
You may need to install OpenSlide library other than python interface.
- Copy our src folder to local, use the following code to calculate shifting offset.
from wsi_registration import TissueDetector, MatcherParameters, WSI_Matcher
import logging
fixed_wsi = "/fixed_file_name" # file name of your fixed (template) whole slide image
float_wsi = "/float_file_name" # file name of your float (moving) whole slide image
# define the tissue detector, so the patches can be sampled
tissue_detector = TissueDetector("LAB_Threshold", threshold=80) # option 1
# tissue_detector = TissueDetector("GNB", threshold=0.5) # option 2
matcher_parameters = MatcherParameters() # use the default parameters
matcher = WSI_Matcher(tissue_detector, matcher_parameters)
offset = matcher.match(fixed_wsi, float_wsi)
logging.debug("Shifting offset: %d %d" % offset)
print("Shifting offset: %d %d" % offset)We use OpenSlide to parse WSI pairs, please make sure your file format is supported by this API.
09/30/2019
- upload an easy to use version.
Previous code contains lots of bulky parts for methods comparison/evaluation, now the code has been dramatically simplified.
Code and example can be find in ./src/wsi_registration.py.
You just need to copy tsv file ./src/tissue_detection/tissue_others.tsv and ./src/wsi_registration.py to your project, and it's ready to run.
- tools: WSI matching tools for manually registration and validation
- src: implementation of method presented in the paper, you can have more details in the readme.md in this folder. You can see how to use this method in ./src/wsi_registration.py The old src code will not be maintained.
- data: data for replicating the figures in the paper.
Because each WSI takes up more than 4GB, we are not able to upload the original WSIs for demonstration. Some intermediate data in our experiments are provided to replicate our results.
- Lowe, David G. "Object recognition from local scale-invariant features." In iccv, vol. 99, no. 2, pp. 1150-1157. 1999.
- Kim, Jeongtae, and Jeffrey A. Fessler. "Intensity-based image registration using robust correlation coefficients." IEEE transactions on medical imaging 23, no. 11 (2004): 1430-1444.
- Reddy, B. Srinivasa, and Biswanath N. Chatterji. "An FFT-based technique for translation, rotation, and scale-invariant image registration." IEEE transactions on image processing 5, no. 8 (1996): 1266-1271.