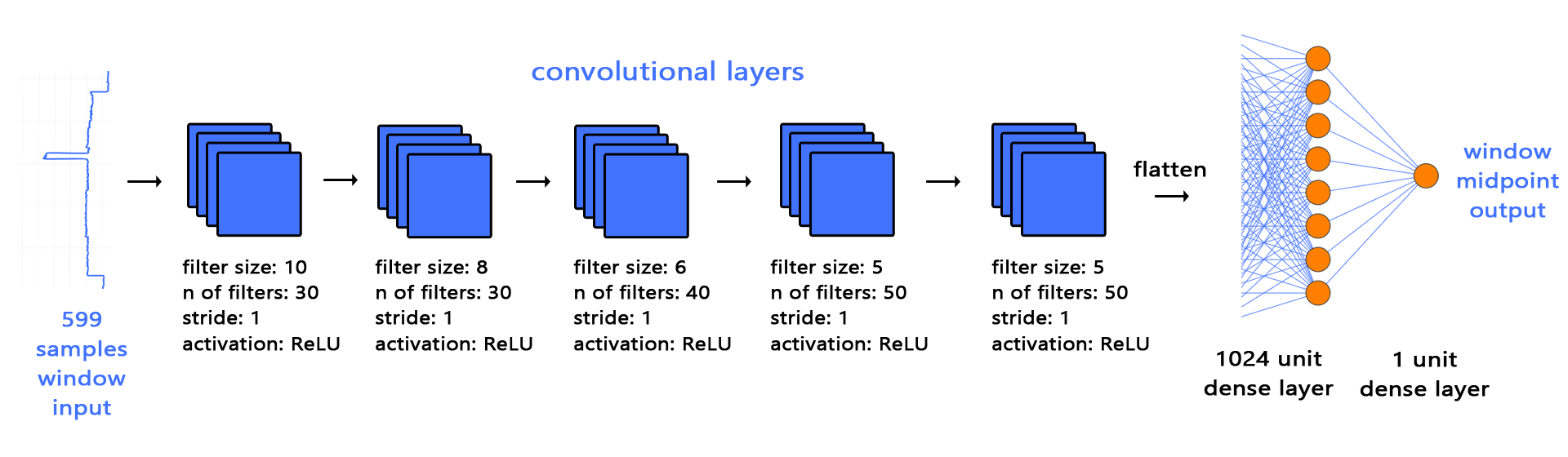
This code implements the sequence-to-point (seq2point) learning model which was propsoed in [2]. The code then implements transfer learning for NILM. Precisely, we studied transfer learning for NILM using the seq2point learning framework.
Note: the latest seq2point leaning code using TensorFlow-2.0 can be found here https://github.com/MingjunZhong/seq2point-nilm
We proposed two approaches for transfer learning:
[1] One is cross-domain transfer learning where you we want to transfer knowledge from domain to domain, for example, we can train a model on UK data and transfer the trained model to US households;
[2] The other is appliance transfer learning where you want to transfer learned knowledge from appliance to applaince, for example, we can train a model on Washing Machine and then transfer it to Kettle. For more details, see the paper [1].
This code is written by Michele D'Incecco and Mingjun Zhong based on the code from https://github.com/MingjunZhong/NeuralNetNilm
Any questions please drop me an email at mingjun.zhong@abdn.ac.uk
References:
[1] DIncecco, Michele, Stefano Squartini, and Mingjun Zhong. "Transfer Learning for Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring." IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, (accepted on 20 August 2019.)(arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.08835)
[2] Chaoyun Zhang, Mingjun Zhong, Zongzuo Wang, Nigel Goddard, and Charles Sutton. "Sequence-to-point learning with neural networks for nonintrusive load monitoring." Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-18), Feb. 2-7, 2018.
Seq2point model: the input is the mains windows (599 timepoints); and output is the midpoint of the corresponding appliance windows.
Requirements
-
This software was tested on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
-
Create your virtual environment Python > 3.5
-
Install Tensorflow > 1.4
-
Follow official instruction on https://www.tensorflow.org/install/
-
Remember a GPU support is highly recommended for training
-
-
Install Keras > 2.1.5
- Follow official instruction on https://keras.io/
-
Clone this repository
For instance, the environments we used are listed in the file environment.yml -
you could find all the packages there. If you use conda,
you may type conda env create -f environment.yml to set up the environment.
With this project you will be able to use the Sequence to Point network. You can prepare the dataset from the most common in NILM, train the network and test it. Target appliances taken into account are kettle, microwave, fridge, dish washer and washing machine. Directory tree:
├── Arguments.py
├── cnnModel.py
├── DataProvider.py
├── dataset_management
│ ├── functions.py
│ ├── redd
│ │ ├── create_trainset_redd.py
│ │ └── redd_parameters.py
│ ├── refit
│ │ └── create_dataset.py
│ └── ukdale
│ ├── create_trainset_ukdale.py
│ └── ukdale_parameters.py
├── environment.yml
├── images
│ ├── model.png
│ ├── s2p.png
│ └── washingmachine.png
├── Logger.py
├── models
├── NetFlowExt.py
├── nilm_metric.py
├── result
├── seq2point_test.py
└── seq2point_train.pyThis script allows the user to create CSV files of training dataset of power measurments. The output will be 3 CSV files for training, validation and test.
You should select the following arguments for the argument parser:
python create_dataset -h
--data_dir DATA_DIR The directory containing the CLEAN REFIT data
--appliance_name APPLIANCE_NAME which appliance you want to train: kettle,
microwave,fridge,dishwasher,washingmachine
--aggregate_mean AGGREGATE_MEAN Mean value of aggregated reading (mains)
--aggregate_std AGGREGATE_STD Std value of aggregated reading (mains)
`--save_path SAVE_PATH The directory to store the training data
Example:
Create a REFIT dataset (mains and appliance power measurments) for kettle:
python create_dataset.py --data_dir './' --appliance_name 'kettle' --aggregate_mean 522 --aggregate_std 814 --save_path './'
Download the REFIT raw data from the original website (https://pureportal.strath.ac.uk/en/datasets/refit-electrical-load-measurements-cleaned). Appliances and training set composition for this project:
| Appliances | training | validation | test |
|---|---|---|---|
| kettle | 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 12, 13, 19, 20 | 5 | 2 |
| microwave | 10, 12, 19 | 17 | 4 |
| fridge | 2, 5, 9 | 12 | 15 |
| dish washer | 5, 7, 9, 13, 16 | 18 | 20 |
| washing machine | 2, 5, 7, 9, 15, 16, 17 | 18 | 8 |
Download the UK-DALE raw data from the original website (http://jack-kelly.com/data/). Validation is a 13% slice from the final training building. Appliances and training set composition for this project:
| Appliances | training | validation | test |
|---|---|---|---|
| kettle | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| microwave | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| fridge | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| dishwasher | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| washingmachine | 1 | 1 | 2 |
Download the REDD raw data from the original website (http://redd.csail.mit.edu/). Validation is a 10% slice from the final training building. Appliances and training set composition for this project:
| Appliances | training | validation | test |
|---|---|---|---|
| microwave | 2,3 | 3 | 1 |
| fridge | 2,3 | 3 | 1 |
| dishwasher | 2,3 | 3 | 1 |
| washingmachine | 2,3 | 3 | 1 |
The seq2point_train.py script is the entry point for the training phase. It loads the training dataset, including validation, and it starts the training. It uses a script to load CSV dataset file into memory, prepares pairs of 599 samples aggregate data and 1 sample midpoint ground truth. After randomly shuffle them, batches of BATCHSIZE size are input to the network for backpropagation purpose. Once the training is cmplete, according to the eary stopping criterion, the trained KERAS model (and model's parameters) will be available into the folder you have selected.
Training default parameters:
-
Input window: 599 samples
-
Number of maximum: epochs 50
-
Batchsize: 1000
-
Early stopping
- min epochs: 5
- patience: 5
-
Adam optimiser:
- Learning rate: 0.001
- Beta1: 0.9
- Beta2: 0.999
- Epsilon: 10^{-8}
python seq2point_train.py --help
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--appliance_name APPLIANCE_NAME
the name of target appliance
--datadir DATADIR this is the directory of the training samples
--pretrainedmodel_dir PRETRAINEDMODEL_DIR
this is the directory of the pre-trained models
--save_dir SAVE_DIR this is the directory to save the trained models
--batchsize BATCHSIZE
The batch size of training examples
--n_epoch N_EPOCH The number of epochs.
--save_model SAVE_MODEL
Save the learnt model: 0 -- not to save the learnt
model parameters; n (n>0) -- to save the model params
every n steps; -1 -- only save the learnt model params
at the end of training.
--dense_layers DENSE_LAYERS
: 1 -- One dense layers (default Seq2point); 2 -- Two
dense layers; 3 -- Three dense layers.
--transfer_model TRANSFER_MODEL
True: using entire pre-trained model. False: retrain
the entire pre-trained model; This will override the
'transfer_cnn' and 'cnn' parameters; The
appliance_name parameter will use to retrieve the
entire pre-trained model of that appliance.
--transfer_cnn TRANSFER_CNN
True: using a pre-trained CNN False: not using a pre-
trained CNN.
--cnn CNN The CNN trained by which appliance to load (pretrained
model).
--gpus GPUS Number of GPUs to use: n -- number of GPUs the system
should use; -1 -- do not use any GPU.
--crop_dataset CROP_DATASET
for debugging porpose should be helpful to crop the
training dataset size
--ram RAM Maximum number of rows of csv dataset can handle
without loading in chunks
Example:
Train the whole model, randomly initialised, using 10000 data points:
python seq2point_train.py --appliance_name 'kettle' --datadir './dataset_management/refit/' --save_dir './trained_model' --transfer_model False --crop_dataset 10000
Transfer learning: train the whole model, starting from a pre-trained model: you must provide the pre-trained model directory (kettle in this example).
python seq2point_train.py --appliance_name 'kettle' --datadir './dataset_management/refit/' --save_dir './trained_model' --transfer_model True --pretrainedmodel_dir './pretrained_model' --crop_dataset 10000
Transfer learning: only train the dense layers starting from a pre-trained CNN; you must provide the pre-trained model directory (washingmachine in this example).
python seq2point_train.py --appliance_name 'kettle' --datadir './dataset_management/refit/' --save_dir './trained_model' --transfer_cnn True --cnn washingmachine --pretrainedmodel_dir './pretrained_model' --crop_dataset 10000
The seq2point_test.py script is the entry point for testing the network. In a similar way to the training windows are prepared, without shuffling, and sent to the network. The prediction is stored and saved in .npy file together with aggregate and ground truth. If selected, the script will generate a plot (an example below).
python seq2point_test.py -h
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--appliance_name APPLIANCE_NAME
the name of target appliance
--datadir DATADIR this is the directory to the test data
--trained_model_dir TRAINED_MODEL_DIR
this is the directory to the trained models
--save_results_dir SAVE_RESULTS_DIR
this is the directory to save the predictions
--nosOfWindows NOSOFWINDOWS
The number of windows for prediction for each
iteration.
--test_type TEST_TYPE
Type of the test set to load: test -- test on the
proper test set; train -- test on a aready prepared
slice of the train set; val -- test on the validation
set; uk -- test on UK-DALE; redd -- test on REDD.
--dense_layers DENSE_LAYERS
: 1 -- One dense layers (default Seq2point); 2 -- Two
dense layers; 3 -- three dense layers the CNN.
--transfer TRANSFER Using a pre-trained CNN (True) or not (False).
--plot_results PLOT_RESULTS
To plot the predicted appliance against ground truth
or not.
--cnn CNN The trained CNN by which appliance to load.
--crop_dataset CROP_DATASET
for debugging porpose should be helpful to crop the
test dataset size
Example:
Test the model using 10000 data points:
python seq2point_test.py --appliance_name 'kettle' --datadir './dataset_management/refit/' --trained_model_dir './trained_model' --save_results_dir './result' --transfer False --crop_dataset 10000 --plot_results False
Transfer learning (Testing on kettle, but the CNN was trained by using washing machine):
python seq2point_test.py --appliance_name 'kettle' --datadir './dataset_management/refit/' --trained_model_dir './trained_model' --save_results_dir './result' --transfer True --cnn washingmachine --crop_dataset 10000 --plot_results False
Test output example plot for washing machine:
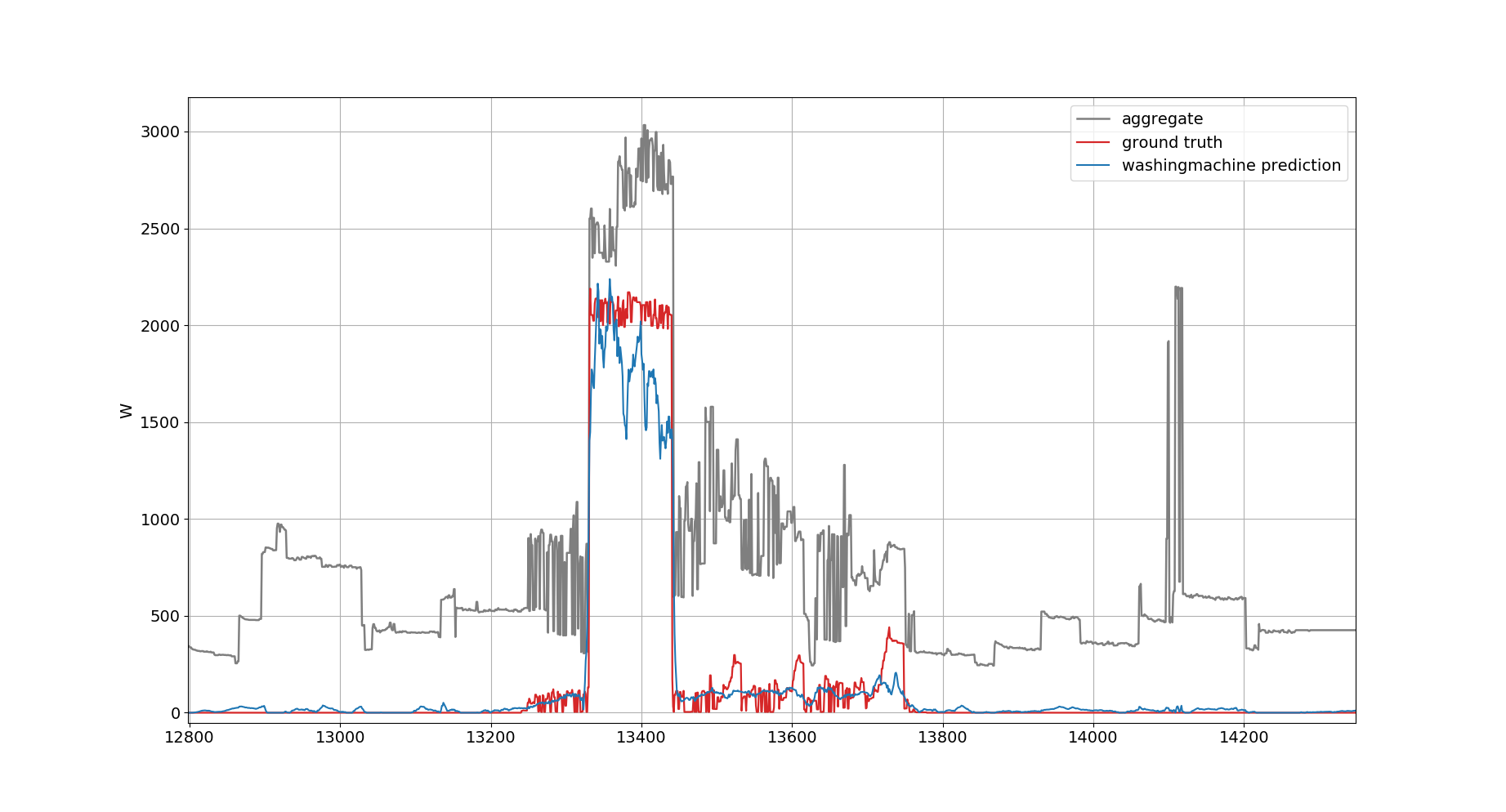
Washing machine for REDD (source: http://redd.csail.mit.edu/data/low_freq.tar.bz2)
Building 1 as test dataset in the file redd_parameters.py, the label for washing machine is 19, but it is all zero. Instead, the correct channel number is 20. See the issue: #1