A Novel Multiresolution-Statistical Texture Analysis Architecture: Radiomics-Aided Diagnosis of PDAC Based on Plain CT Images
This repo contains the implementation of the “A Novel Multiresolution-Statistical Texture Analysis Architecture: Radiomics-Aided Diagnosis of PDAC Based on Plain CT Images” paper published at IEEE transactions on Medical Imaging (January 2021).
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is a type of tumor, which has poor diagnosis. Early diagnosis of PDAC has great significance. The paper uses Plain CT images to diagnose PDAC.
-
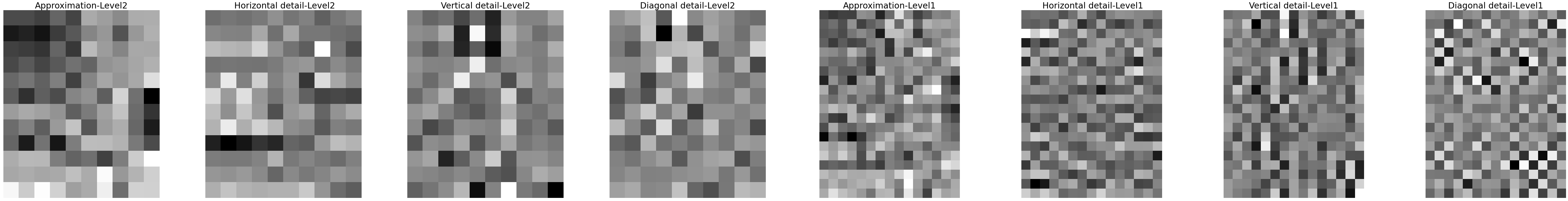
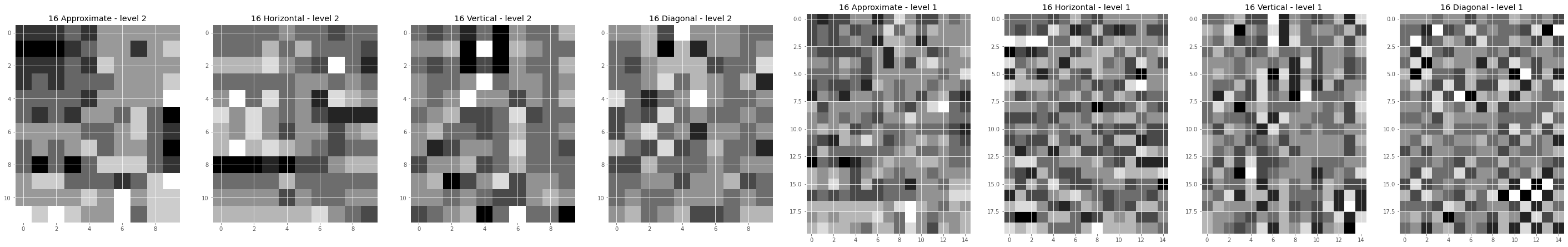
Multiresolution analysis decomposes an ROI into multiple low-/high-frequency sub-band components.2
- 2D wavelet transform was used
-
Random Partitioning
The dataset (i.e., the ROIs) randomly divided into a training set and a test at a ratio of 7:3.
-
Analysis of coefficients characteristics
- Finding the average of maximums and minimums - ROIs are group by components are labels, and maximums and minimums of each group determined.
- Restructure the interval based on maximum and minimum determined previously for each component separately.
-
Discretize ROIs
- Number of bins used is 8
-
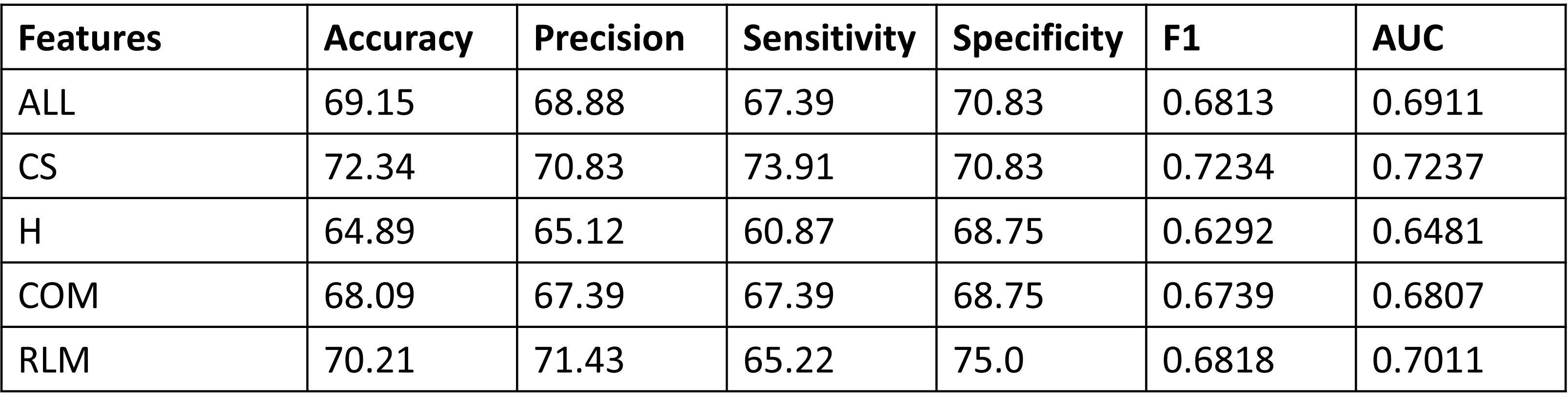
Statistical Analysis and feature extraction, following statistical methods were used.
- Histogram (H) - mean, variance, skewness, kurtosis, entropy
- Co-efficient statistics (CS) - mean, standard deviation, energy
- Co-occurrence matrix (COM) - contrast, energy, homogeneity, correlation
- Run-length matrix (RLM) - All 11 features mentioned in the paper
-
Feature selection (based on training dataset)
- ILFS - infinite latent feature selection algorithm : rank the features based on the training set and selected the first k features. (k<20)
-
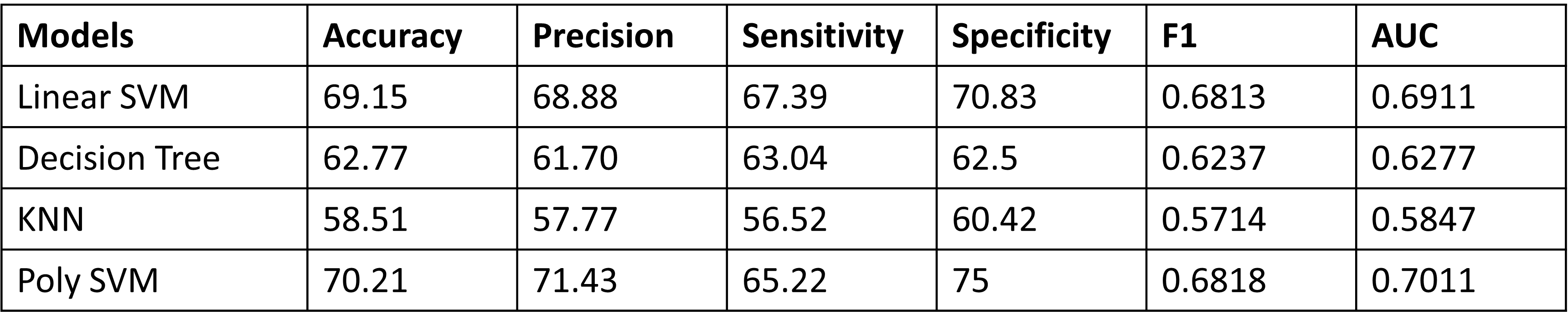
Classification
- SVM (linear kernel)
- Decision Tree, KNN and Poly SVM were also implemented
-
Significance Testing
- Mann-Whitney U test
Followings are the results achieved with SVM classifier, with wavelet transform as multi resolution analysis method (number of bins = 8, number of features = 20) for different statistical analysis methods.
Followings are the results achieved with different machine learning classifier, with wavelet transform as multi resolution analysis method (number of bins = 8, number of features = 20) when all the statistical analysis methods used to extract features.
For number of features = 32
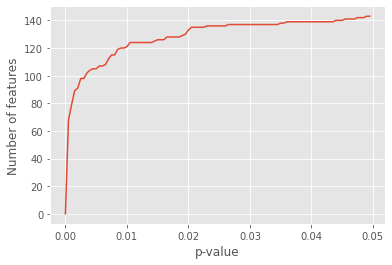
Non-parametric significance test - Mann-Whitney U test was used. Here the median are compared instead of mean. Number of significance features for different p-values.
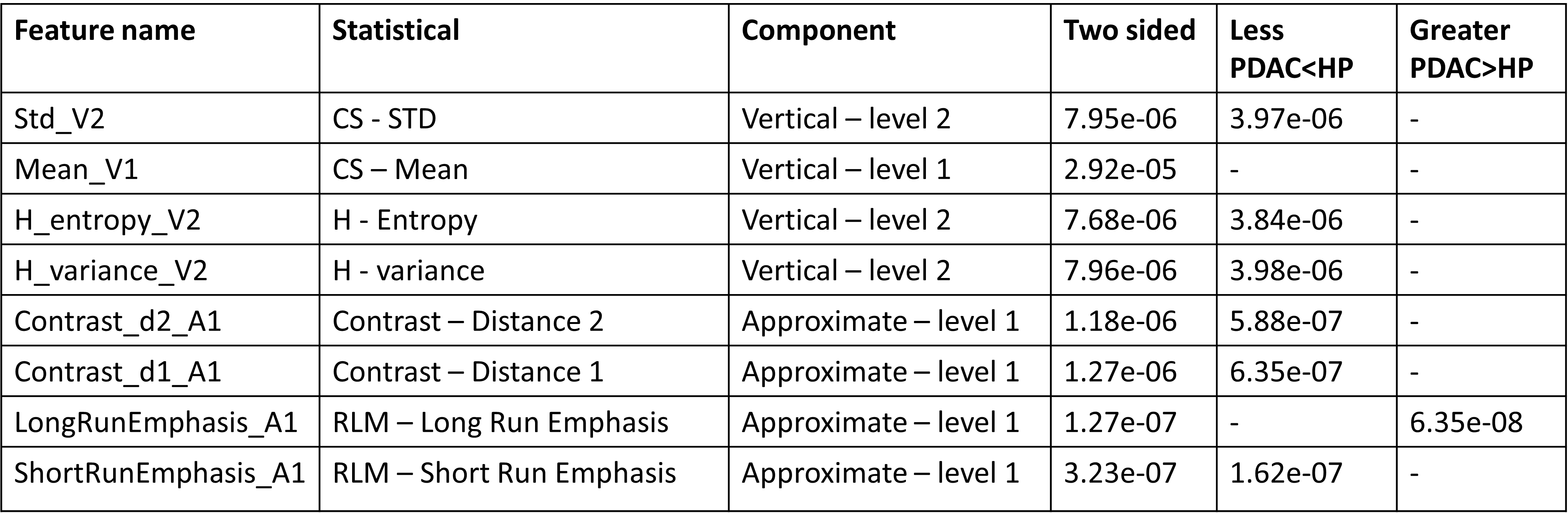
Two features with smallest p-value in one-tailed test from each statistical analysis method (except - ALL case) selected. Results of two tailed test (left and right tailed tests) were given below.
Interpret the above table :
- Standard deviation of vertical wavelet component of level 2 is higher in Healthy Pancreas (HP) than PDAC.
- Mean of vertical wavelet component of level 1 is significantly different for PDAC and HP.
- Long Run Emphasis of approximation wavelet component of level 1 is significantly higher in PDAC than HP.
I would like to express my special thanks of gratitude to Dr. Nuwan Dayananda and Dr. Ranga Rodrigo who gave me the opportunity to work on the implementation of a journal paper.
Qiu, J.J., Yin, J., Qian, W., Liu, J.H., Huang, Z.X., Yu, H.P., Ji, L. and Zeng, X.X., 2020. “A Novel Multiresolution-Statistical Texture Analysis Architecture: Radiomics-Aided Diagnosis of PDAC Based on Plain CT Images”. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 40(1), pp.12-25.