- Detr for Panoptic Segmentation
- Data Preparation
- Training Bounding box Model
- Training the Panoptic head
- Future Work
Data Preparation Notebook
Training models Notebook
Modified DeTr code
Ground Truth
Samples for Bounding Box
Samples for Panoptic Segmentation
The objective of this capstone project is to understand and train a custom panoptic segmentation model on the dataset "construction materials". This is doen by using a Transformer based model DeTr. The basic understanding of this model is given here. In this text I will explain the various steps taken to get the end to end pipeline to train this model. At a very high level, the tasks include creating a ground truth (GT) that complies with the various annotation formats followed for coco, training the detection or bounding box model and training the panoptic segmentation model.
What is achieved so far is the understanding and the complete flow. However the training of the detr models is still pending
This repo is being created from the code that was commited to a differnet repo so far: https://github.com/MittalNeha/Extensive_Vision_AI6/tree/main/CAPSTONE
-
This step includes combining the custom dataset, understanding coco annotation formats and creating these annotations. All these steps are captured in the colab file. The scripts use for creating this ground truth are all present here.
-
The construction materials dataset that was used for this project is available here. The dataset was created and labelled using CVAT. When downloading the dataset from CVAT, it creates different directories for each class. CvattoCoco.py combined this data from various categories. It performs the following steps to achieve the same:
- Takes the categories from the coco dataset (things and stuffs) and creates a map map_coco_categories.p such that all the coco things form a new category "misc_stuff". The categories for "materials" i.e. the construction materials is appended further to this categories list.
- Split the images in each class to 80/20 train/validation dataset, hence creating
materials_trainandmaterials_val - Since Detr trains the images with the maximum height of 800. All the source images are converted to "RGB" and downscaled such that the maximum height is 800 and the maximum for the other dimension is 1333.
- All images that are missing any annotations were moved to the
materials_testfolder. - All images are have a incrementing image id and the file_name is same as the image_id.
On saving these annotations, the directory structure looks like this:
parsed_data +-- annotations | +-- train_coco.json | +-- val_coco.json +-- materials_train | +-- <image_id_1>.jpg | +-- <image_id_2>.jpg +-- materials_val | +-- <image_id_1>.jpg | +-- <image_id_2>.jpg +-- materials_test | +-- <image_id_1>.jpg | +-- <image_id_2>.jpg -
Since the final task is to make panoptic predictions, the ground truth should also have the same. In order to create the panoptic mask for the custom dataset, each image is passed through a pretrained detr_panoptic model, with the backbone of resnet50. After these coco class predictions, the mask from materials subcategory needs to be merged on top of the masks. To get this conversion to run in batches, the script was created that follows the detr code refering to the repo https://github.com/facebookresearch/detr.
!python create_panoptic_dataset.py --batch_size 2 --dataset_file coco_materials --data_path parsed_data/ --device cuda --output_dir output/ --coco_panoptic_path coco_panoptic
scores > self.threshold -
- Merge Segmentations:
```
m_id = masks.transpose(0, 1).softmax(-1)
m_id = m_id.argmax(-1).view(h, w)
```
The output of softmax here, gives the output such that each query out that satisfies the threshold from the previous step has the value closer to 1.0. Therefore taking the argmax in next step, gives the index corresponsing to the order of predicted classes to each pixel of the mask output.
*To trick these operations and give priority to the materials category, the custom_class_mask was concatenated to m_id such that the maximumvalue for the mask was 2.0 instead of 1.0. This way, the regions of overlap between the coco prediction and custom class segmentation will give priority to the custom class.*
```
custom_mask = cv.normalize(input_segments, None, alpha=0, beta=2, norm_type=cv.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv.CV_32F)
m_id = torch.cat((m_id, custom_mask.to(m_id.device)), 1)
```
- <u>Create Segment id</u>: In panoptic format, the segment_info id is calculated from the RGB values of the mask image. This is done by using the id2rgb, rgb2id api's. Hence the segment ids were created for each mask. The class id's were multiplied by 1000 just to get a good contrast for the masks
```
new_id = cur_classes*1000 + torch.Tensor(range(len(cur_classes)))
```
Some sample panoptic segmentation images are shown [here](https://github.com/MittalNeha/detr-panoptic/blob/main/Ground%20Truth%20samples.md)
After creating the ground truth dataset, the folder structure looks like this:
```
coco_panoptic
+-- annotations
| +-- panoptic_materials_train
| +-- panoptic_materials_val
| +-- train_coco.json
| +-- train_panoptic.json
| +-- val_coco.json
| +-- val_panoptic.json
+-- materials_train
| +-- <image_id_1>.jpg
| +-- <image_id_2>.jpg
+-- materials_val
| +-- <image_id_1>.jpg
| +-- <image_id_2>.jpg
+-- materials_test
| +-- <image_id_1>.jpg
| +-- <image_id_2>.jpg
```
-
Colab Notebook: https://github.com/MittalNeha/detr-panoptic/blob/main/construction_dataset.ipynb
Once proper ground truth is created, training is straightforward. Some changes were made to the detr code to incorporate custom dataset training. Reference for training detr on custom dataset for bounding box.
For this datset the num_classes is 102.
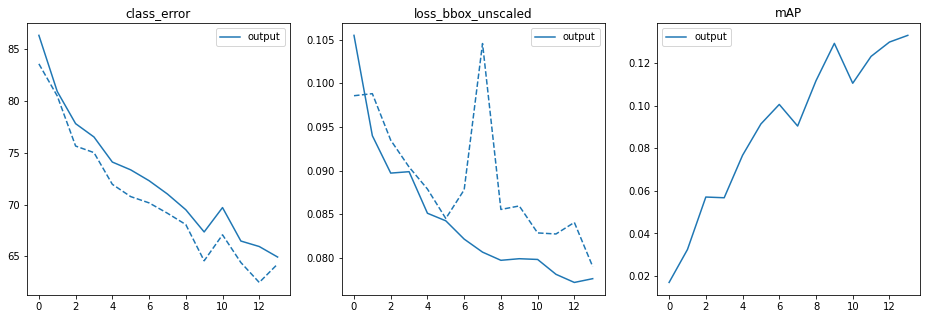
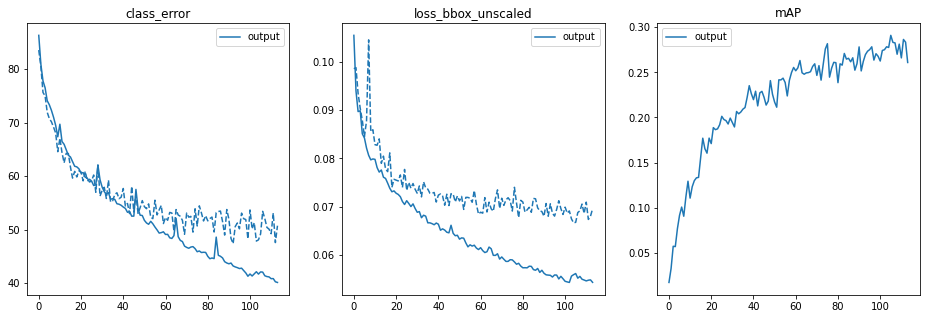
!python main.py --dataset_file materials --data_path ../coco_panoptic/ --output_dir /gdrive/MyDrive/EVA6/CAPSTONE/output --resume /content/detr/weights/detr-r50-e632da11.pth- The model was not training at all and then by plotting the
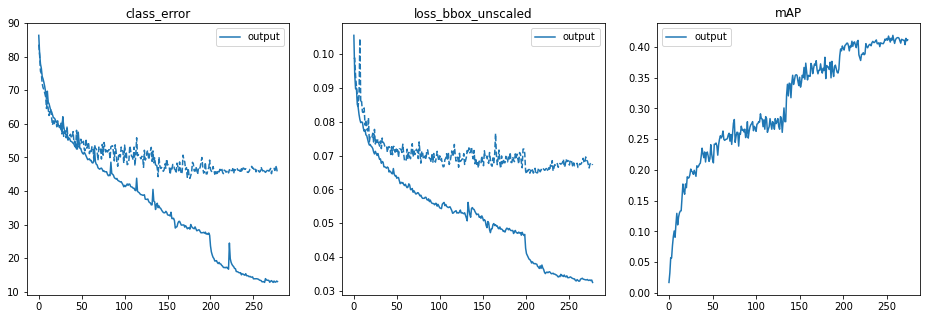
It was seen that the mAP did not go beyond 0.26 and hence found a bug with creating the ground truth class.
Notice the two spots at whihch the mAP rose dramatically. One was right after the bug fix and the other at epoch 200 when the learning rate dropped.
This network was trained for a total of 278 epochs.
- Training weights are present here
- evaluation logs:
- training logs
- Inference results
This is trained using the frozen weights from the bbox model.
!python main.py --batch_size 1 --masks --epochs 25 --lr_drop 15 --data_path ../coco_panoptic/ --coco_panoptic_path ../coco_panoptic/annotations/ --dataset_file coco_panoptic --frozen_weights /gdrive/MyDrive/EVA6/CAPSTONE/output/checkpoint.pth --output_dir output/segm_model
-
The coco_eval seems to need the "segmentation" key in the coco json. which is missing in the current dataset.
File "/content/detr/datasets/coco_eval.py", line 227, in evaluate self._prepare() File "/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/pycocotools/cocoeval.py", line 104, in _prepare _toMask(gts, self.cocoGt) File "/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/pycocotools/cocoeval.py", line 92, in _toMask rle = coco.annToRLE(ann) File "/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/pycocotools/coco.py", line 422, in annToRLE segm = ann['segmentation'] KeyError: 'segmentation'As for now setting cocoEvaluator to None.
-
After complete training for 25 epochs the results were not good and the panoptic evaluation results looked like this
| PQ | SQ | RQ | N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 3.0 | 14.7 | 3.2 | 95 |
| Things | 4.9 | 15.8 | 5.2 | 47 |
| Stuff | 1.1 | 13.6 | 1.3 | 48 |
There was another bug, we need to change the value of "is_thing_map" based on the categories for out dataset. This improved the evaluation logs manifold. after epoch 5 of new training:
| PQ | SQ | RQ | N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | 14.3 | 47.7 | 17.3 | 95 |
| Things | 25.1 | 64.0 | 31.4 | 47 |
| Stuff | 3.4 | 41.8 | 3.9 | 48 |
This training is still in progress and the current results are not good.
- Training weights are present here
- training logs
- Inference results
-
- While combining segmentation for custom classes, if there were multiple segments of the same object, that was considered as a single segment. This should be fixed to get better predictions.
- After the bug fix in creating ground truth, it would have been ideal to traing the bounding box model from scratch for better results.
- An algorithm like RICAP can help the model look at multiple segments from different classes in a single image.