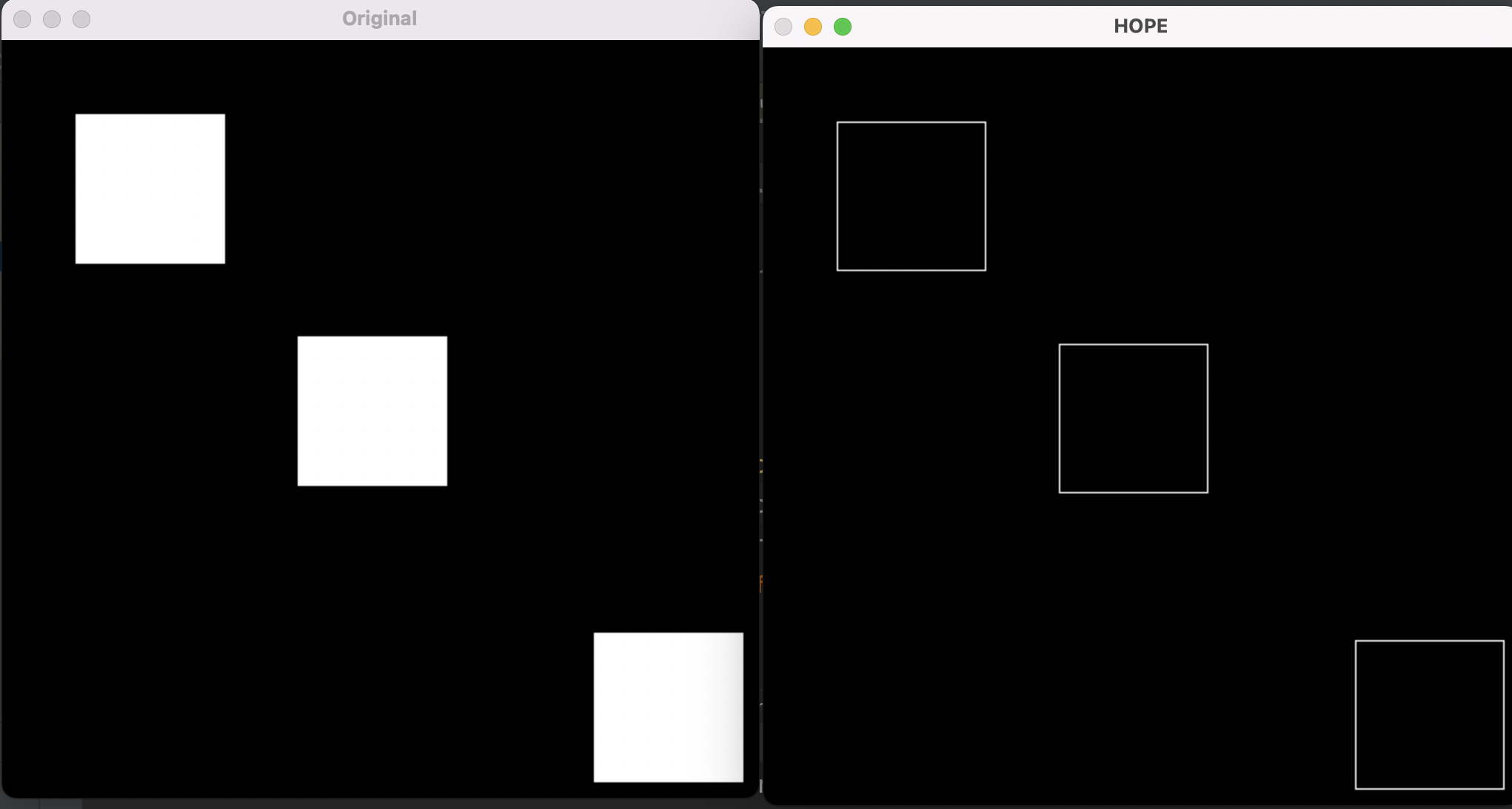
The border tracing algorithm is used to extract the contours of the objects (regions) from an image. When applying this algorithm it is assumed that the image with regions is either binary or those regions have been previously labeled.
is the starting pixel of the region border. Define a variable dir which stores the direction of the previous move along the border from the previous border element to the current border element.
Assign :
(a) dir = 0 if the border is detected in 4-connectivity
(b) dir = 7 if the border is detected in 8-connectivity
beginning the neighborhood search at the pixel positioned in the direction
(a) (dir + 3) mod 4
(b) (dir + 7) mod 8 if dir is even or (dir + 6) mod 8 if dir is odd
The first pixel found with the same value as the current pixel is a new boundary element Pn. Update the dir value.
the previous border element Pn-1 is equal to Po, stop. Otherwise repeat step (2).
5. after detecting the first object, it's removed from the original image , then the algorithm starts again with the image after removing the object , and detects the boundary for the next object , then we delete it from the original image , and so on so forth.
# Installing Dependencies
pip install numpy as np
pip install opencv-python
# clone the rebo
# Running the application
python3 boundaryTracing.pyThe circle Hough Transform (CHT) is a basic feature extraction technique used in digital image processing for detecting circles in imperfect images. The circle candidates are produced by “voting” in the Hough parameter space and then selecting local maxima in an accumulator matrix.