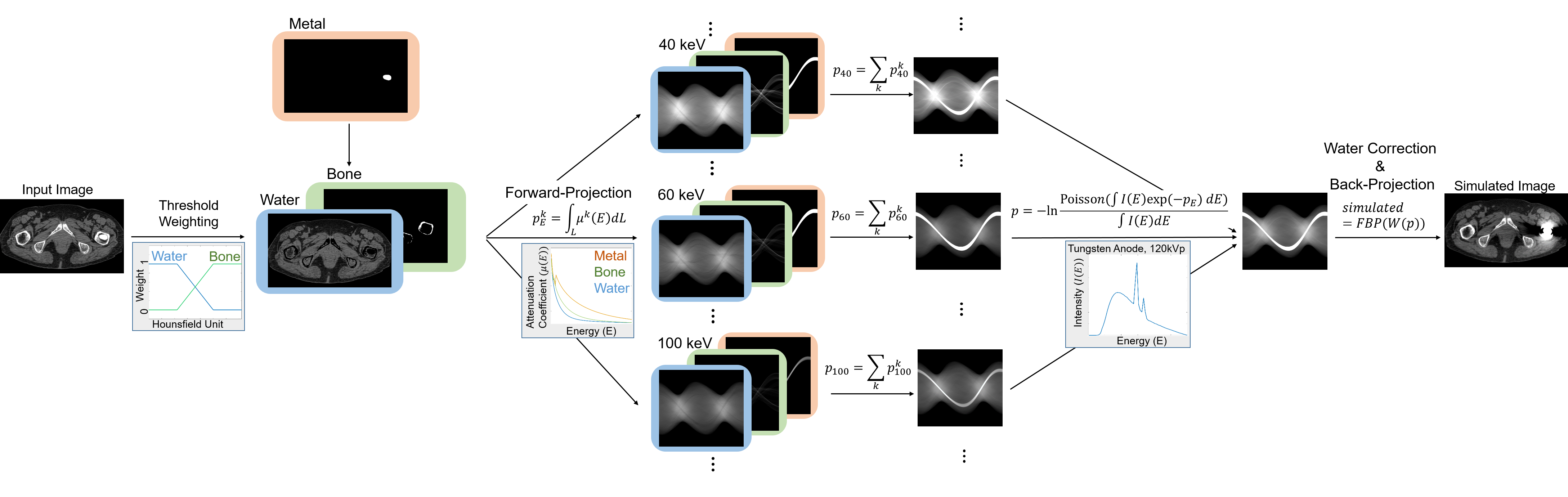
A MATLAB implementation of metal artifact simulation based on [1].
We also introduced a water-based beam hardening correction [2] to generate an image similar to that generated by common CT systems, where a built-in calibration linearizes the polychromatic x-ray projection.
If you use this code, please consider citing:
Sakamoto, M., Hiasa, Y., Otake, Y., Takao, M., Suzuki, Y., Sugano, N., & Sato, Y. (2019, March). Automated segmentation of hip and thigh muscles in metal artifact contaminated CT using CNN. In International Forum on Medical Imaging in Asia 2019 (Vol. 11050, p. 110500S). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
Mitsuki Sakamoto sakamoto.mitsuki.si2@is.naist.jp
Yoshito Otake otake@is.naist.jp
MATLAB (Image Processing Toolbox required).
We tested our code using MATLAB 2015a, 2018a and 2019a.
You can test metal artifact simulation by running "simulation_demo.m".
We prepared 2 images and corresponding metal labels of different parts in the "sample data" directory.
The input and output images will be saved in "outputs" directory.
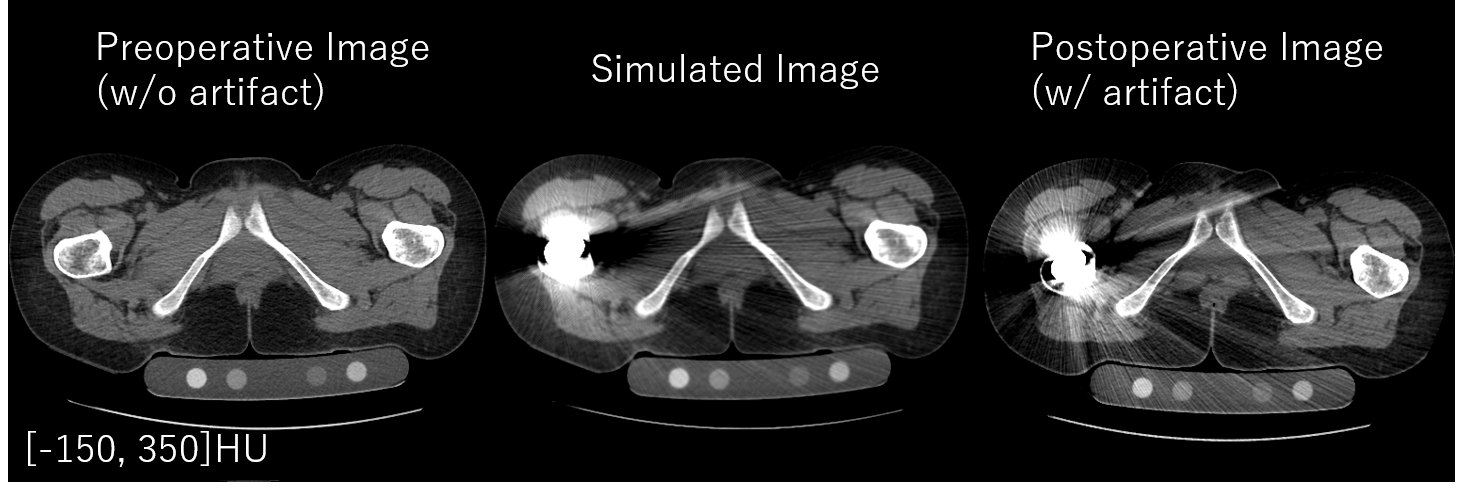
In "sample_1.mat", a CT image of the hip joint region and a corresponding metal label are stored.
Below is the simulation result obtained by using the default settings.
In addition to the preoperative (input) and the simulated (output) images, the postoperative CT image of the same patient is shown below.
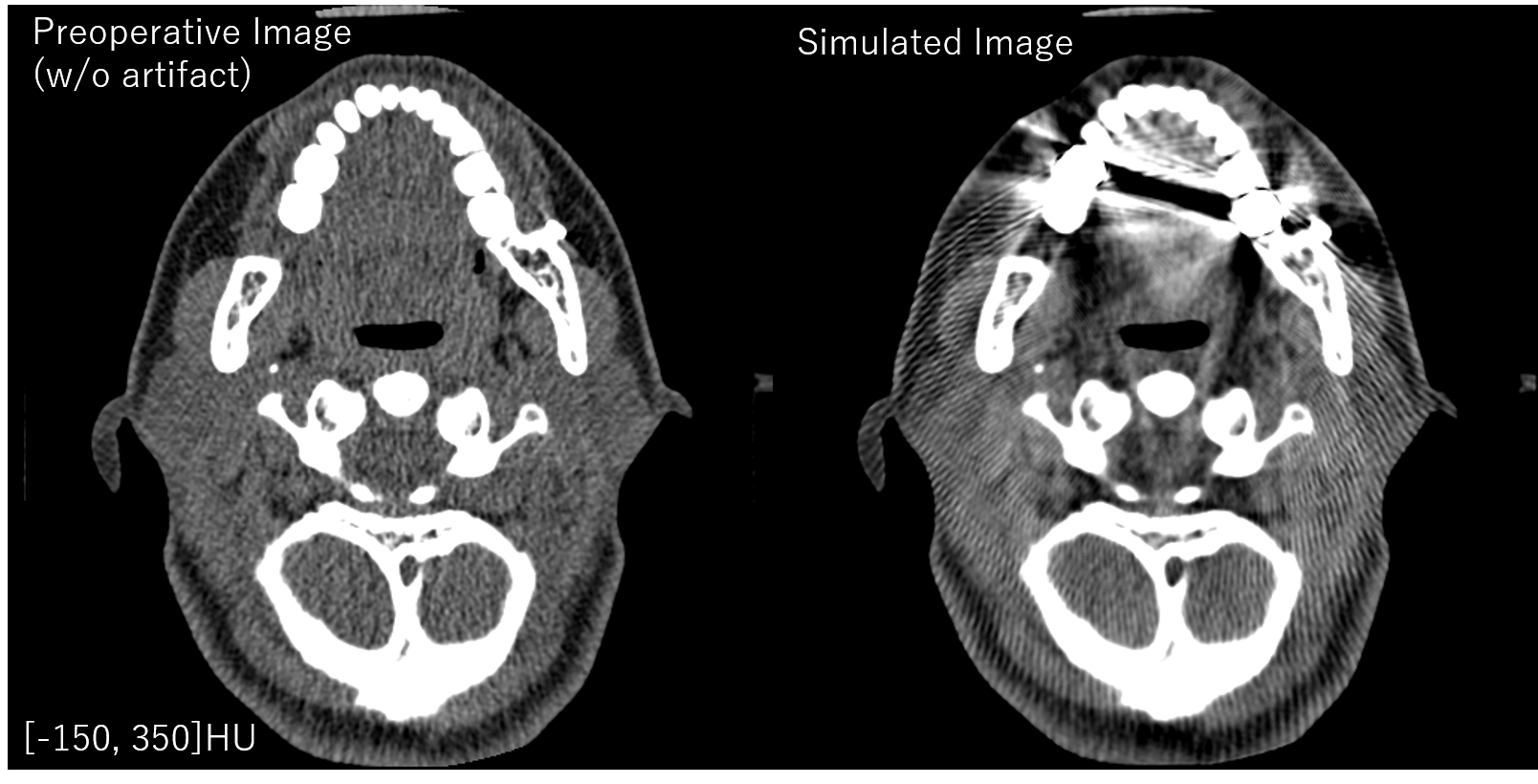
In "sample_2.mat", a CT image of the head with a corresponding metal label are stored.
Below is the simulation result obtained using the default settings.
This project is licensed under the MIT license.
-
Zhang, Y., & Yu, H. (2018). Convolutional neural network based metal artifact reduction in X-ray computed tomography. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 37(6), 1370-1381.
-
Herman, G. T. (1979). Correction for beam hardening in computed tomography. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 24(1), 81.