SFuzz
Implementation(Source code) of paper:
SFuzz: Slice-based Fuzzing for Real-Time Operating Systems. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (ACM CCS 2022).
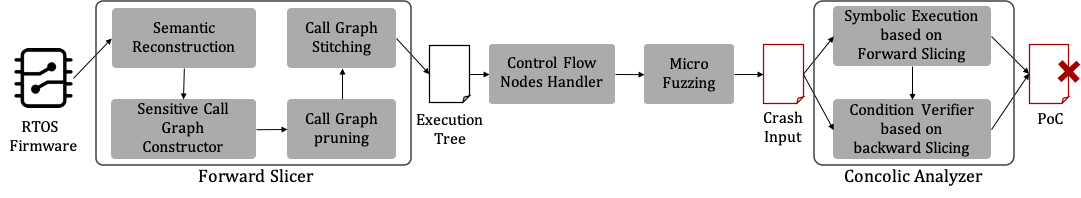
Overview of SFuzz
Setup
To get the docker image directly, go to: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1gSw9QFLuntsqoQlI_KjzoI8bej8ZT-E7/view?usp=share_link
Static Analysis
Perform taint analysis on the specified firmware, slice and patch the program for the taint analysis results.
This part uses the firmware collection in the evaluation_set folder as input.
Instructions for running this tool
- Download Ghidra (we use version 9.2.3).
- Change MAXMEM=2G to MAXMEM=4G in the analyzeHeadless file in the support directory of Ghidra folder.
sudo apt install openjdk-11-jdk- Place each file in a specific directory according to run.sh or modify run.sh according to the file location.
- Run run.sh for a single firmware or run run_all.py for the entire firmware set.
Directories
├── README.md
├── findbase # Tool to discover the base address for firmware loading
├── unstrip # Tool for recovering the symbols of a specific function in unsigned binary
├── unstrip_from_log # Tools for recovering function symbols based on information in the log function
├── statistics_script# Scripts for supporting statistics
├── evaluation_set # Unpacked firmware collection
├── findtrace_output # Static analysis results for firmware in evaluation_set
├── findtrace.py # Ghidra script that performs taint analysis and outputs slices and patches
├── run.sh # Shell scripts for processing individual firmware
├── run_all.py # Python script for batch processing of multiple firmware
└── setbase.py # Ghidra script for setting the base address for firmware loading
Run
For processing individual firmware
Be sure to modify run.sh according to the actual file location before you run it
sudo ./run.sh firmware_path arch base_addr
example:
sudo ./run.sh evaluation_set/DIR-100/30_DIR100 MIPS:BE:32:default 0x80000100
For batch processing of multiple firmware
sudo python3 run_all.py
Output
Most of the files end with an underscore and a number, which represents the number of the call tree corresponding to the current file.
30_DIR100_result/
├── call_checksum_0 # Address of checksum function calls
├── .......
├── call_checksum_7
├── calltrace_0 # Results of call trace in call tree
├── ........
├── calltrace_7
├── cbranch_info_0 # Jumping information at the branch
├── ........
├── cbranch_info_7
├── dict_0 # String information on the call tree (used to add to the AFL dictionary)
├── ........
├── dict_7
├── exec_0 # Contextual information used for fuzzing (source address and sink address, etc.)
├── ........
├── exec_7
├── patch_0 # Patch results for function calls or branches
├── ........
├── patch_7
├── sink_buf_0 # Information about the sink function address and its corresponding buffer
├── ........
├── sink_buf_7
├── stack_retaddr_0 # Return address information on the stack
├── ........
├── stack_retaddr_7
├── summary # Statistical Information
├── summary.json
├── xalloc_0 # Cross-reference information for the alloc function
├── ........
└── xalloc_7
Dynamic Analysis
Dynamic analysis includes fuzzing and concolic solving.
This project relies on the output of the static analysis as input.
Running environment configuration
apt-get install -y libc6-armel-cross gcc-arm-linux-gnueabi libc6-mipsel-cross gcc-mipsel-linux-gnu
apt-get install -y build-essential python3-dev automake cmake git flex bison libglib2.0-dev libpixman-1-dev python3-setuptools python python-setuptools
apt-get install -y lld llvm llvm-dev clang
apt-get install -y gcc-$(gcc --version|head -n1|sed 's/\..*//'|sed 's/.* //')-plugin-dev libstdc++-$(gcc --version|head -n1|sed 's/\..*//'|sed 's/.* //')-dev
apt-get install -y python3-pip
git clone https://github.com/AFLplusplus/AFLplusplus.git
cd AFLplusplus
make all && make install
git clone https://github.com/Battelle/afl-unicorn
cd afl-unicorn/unicorn_mode
wget https://bootstrap.pypa.io/ez_setup.py -O - | python
sed -i '120,122d' ./build_unicorn_support.sh
wget https://github.com/unicorn-engine/unicorn/archive/refs/tags/1.0.3.zip
unzip 1.0.3.zip && rm 1.0.3.zip && mv unicorn-1.0.3 unicorn
./build_unicorn_support.sh
pip3 install --upgrade "pip<21.0.0"
pip3 install pwntools==4.8.0
pip3 install angr==9.2.6
pip3 install tqdmThere are also minor modifications to the dependent projects.
https://amusing-aluminum-be0.notion.site/d0de68137f884c1984d4ae7c762b566f
Also, AFL requires: if in a docker environment, execute with root privileges outside the docker environment, otherwise execute the following statements directly with root privileges.
echo core > /proc/sys/kernel/core_patternbuild fuzz loader
in ./dynamic_analysis dir (in ./uniFuzzGo dir in docker):
make or make "UFDBG=-DUF_DEBUG -g"
run
in ./dynamic_analysis dir (in ./uniFuzzGo dir in docker):
(in tmux session)
python3 ./hybrid_all.py <device findtrace output dir> <device firmware path>
./clean.sh
python3 count.py <binary name>example:
python3 ./hybrid_all.py ~/findtrace_output/2834_AC11_result ~/evaluation_set/Tenda_AC11/2834_AC11
./clean.sh
python3 count.py 2834_AC11