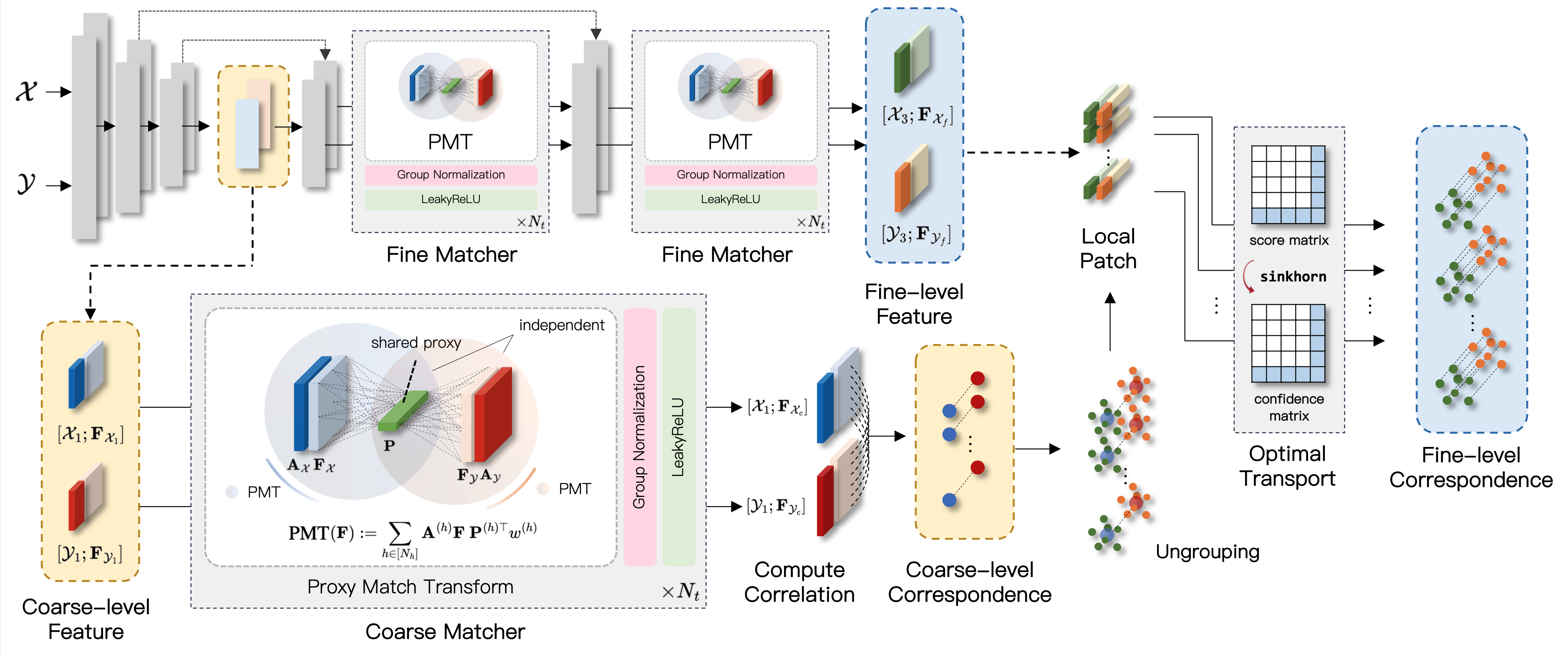
This is the implementation of the paper "3D Geometric Shape Assembly via Efficient Point Cloud Matching" by Nahyuk Lee, Juhong Min, Junha Lee, Seungwook Kim, Kanghee Lee, Jaesik Park and Minsu Cho. Implemented on Python 3.8 and Pytorch 1.10.1.
For more information, check out project [website] and the paper on [arXiv].
- Python 3.8
- PyTorch 1.10.1
- PyTorch Lightning 1.9
Conda environment settings:
conda create -n pmtr python=3.8 -y
conda activate pmtr
pip install torch==1.10.1+cu111 torchvision==0.11.2+cu111 torchaudio==0.10.1 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu111/torch_stable.html
pip install pytorch-lightning==1.9
pip install einops trimesh wandb open3d
python setup.py build install
pip install git+https://github.com/KinglittleQ/torch-batch-svd
pip install git+'https://github.com/otaheri/chamfer_distance'
pip install "git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/pytorch3d.git@stable"
To use the Breaking Bad dataset, follow the instructions in this repository to download both the everyday and artifact subsets.
- Note: We used the volume constrained version for both training and evaluation.
Additional arguments can be found in main.py.
# Single-GPU Training for pairwise assembly
python main.py --data_category {everyday, artifact} --fine_matcher {pmt, none} --logpath {exp_name}
# Multi-GPU Training (ex. 4 GPUs) for pairwise assembly
python main.py --data_category {everyday, artifact} --fine_matcher {pmt, none} --logpath {exp_name} --gpus 0 1 2 3
Additional arguments can be found in test.py.
python test.py --data_category {everyday, artifact} --fine_matcher {pmt, none} --load {ckp_path}
Checkpoints for both everyday and artifact subsets are available on our [Google Drive].
If you use this code for your research, please consider citing:
@article{lee2024pmtr,
title={3D Geometric Shape Assembly via Efficient Point Cloud Matching},
author={Lee, Nahyuk and Min, Juhong and Lee, Junha and Kim, Seungwook and Lee, Kanghee and Park, Jaesik and Cho, Minsu},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.10542},
year={2024}
}The codebase is largely built on GeoTransformer (CVPR'22) and HSNet (ICCV'19).