The digital disruption of the sector has been one of the biggest changes in healthcare during the past ten years. This shift has led to the widespread storage, sharing, access, analysis, and use of health data across a wide range of digital platforms, including wearable technology, smartphone apps, and medical equipment. Big data banks may include hospital records, patient’s medical records, medical examinations, and hardware data from IOT (internet of things) devices which are built with the aim to improve upon or further elevate services provided by the health care industry.
These electronic health data sets are so enormously big and complicated that they are not only challenging to handle with conventional software or hardware, but also are not manageable using conventional or industry-grade specialized data management tools and procedures.
However, with the aid of modern technology, we can produce a lot of data, even to the point where it is now overwhelming. For all the pros that Big Data may bask in, it comes with its own set of cons, but with proper observation and application, we can outweigh the cons and Big Data can indisputably improve the health and medicine sector.
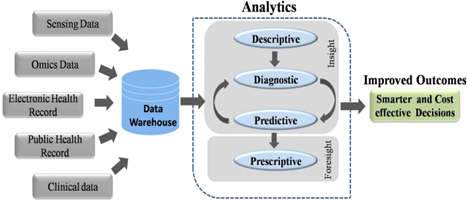
Fig:- Processing of Big data Analytics
Data warehouses hold enormous volumes of data that are produced from multiple resources. In order to produce more effective, innovative, and reasonably priced healthcare choices, these data sets are processed using analytic pipelines (Descriptive, Diagnostic, Predictive, Prescriptive).
In hospitals or clinics, medical personnel treat patients after reviewing the patient's medical history (information linked to diagnoses and prescriptions), medical and clinical data (such as information from imaging and lab results), and other private or confidential medical information. These reports were previously completed using a paper file system or handwritten notes. It used to take a lot of time to carry and manage all of these paper works, not to mention potential pitfalls like patients who wouldn't report in public. However, the digitalization of all clinical exams and medical records in healthcare systems has now become a regular and widely used practice thanks to the development of computer systems and its capabilities. Patients gain from it since they now enjoy the privacy to fill out forms as they wish from the comfort of their homes.
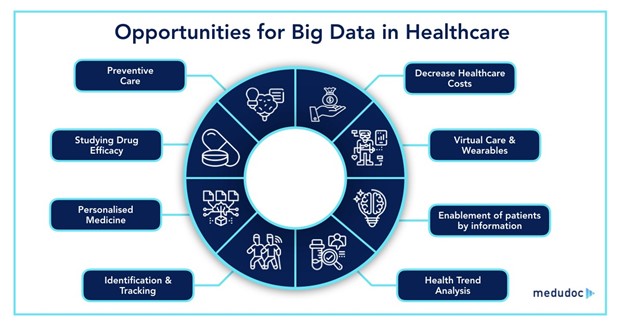
Big Data has a wide variety of possible advantages. We can identify diseases early thanks to it, first of all. In order to provide a more precise picture of how cancer may evolve in the future, for instance, genomic data is helpful. The fact that a disease can be treated more quickly and successfully if it is discovered early is another argument in its favor. Second, it can save costs and waste.
According to McKinsey, big data analytics can enable savings in U.S. healthcare of more than $300 billion annually, or around $920 per person. Using smart technologies and data analytics, clinicians can more easily identify patients who are prone to acquire a particular ailment, stop the disease from becoming worse, and predict epidemics before they start. This reduces the tedious work and mistake involved with manual data handling. Predictive modeling algorithms are a good example of this because they are used to predict the potential spread of viruses to prevent epidemics or to diagnose diseases like diabetes at a very early stage.
Furthermore, big data has also made it possible for doctors to monitor and consult with patients virtually, reducing the need for in-person exams and desk work. Additionally, it is simple for healthcare professionals to access patient records with a single click, which improves system efficiency and saves time. This is what makes the patient experience better overall. On top of that, big data can also be used in the healthcare industry to link many disciplines and conduct in-depth research on a disease.
Additionally, data from various experiments are needed in biomedical research labs or facilities to comprehend the biological processes. In order to continue providing patients with new, life-improving medications in a timely manner, pharmaceutical companies can improve their capacity for pharmaceutical analytics. Additionally, by managing the big data that was produced throughout all stages of pharmaceutical development, the price of pharmaceutical products will be customer friendly.
There are a lot of applications, software and devices that are used to extract data.
- Fitbit: It enables users to keep eyes on their heart rate and track their physical activities.
- ECG devices: Assist users in keeping track of their pulse rate, heart rate variability, breathing rate, temperature, and activity.
- Blood pressure monitors: These monitors make use of oscillometer technology to measure blood pressure.
- Electric Health Records (EHRs): It offers a wide range of information that supports advanced analytics and improves in clinical decision-making.
- Hadoop: Data sets can now be used by researchers because of Hadoop. Large datasets are processed and created using the MapReduce algorithm, which is implemented by Hadoop
- OCR: Optical Character Recognition is such a software that promotes digitization and can read both handwriting and computer fonts.
- Image Analytics: Visualization Toolkit is a well-liked piece of free software for the effective processing and analysis of 3D images from medical examinations. Another one is called SPM, and it has the ability to process and examine 5 different kinds of brain pictures (e.g., MRI, fMRI, PET, CT-Scan and EEG)
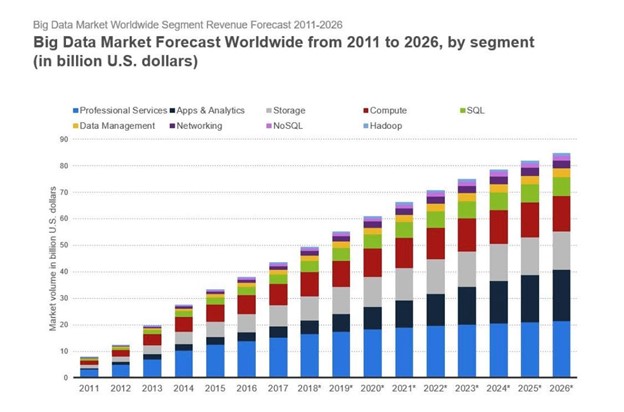
Figure 2: Applications and analytics for big data are expected to increase from $5.3 billion in 2018 to $19.4 billion in 2026, growing at a CAGR of 15.49%. From $16.5 billion in 2018 to $21.3 billion in 2026, the global market for big data, which includes professional services, is expected to rise.
The majority of hospital information systems and electronic medical records have trouble handling unstructured and untapped data. In most medical centers, data is neglected, forgotten, or abandoned for a long time because the majority of it is still unorganized and underutilized. They sometimes fall victim to corruption or damage.
Big Data is a term used to describe a collection of extremely large data sets that cannot be kept, handled, or examined without the required technology and software support and are therefore always subject to data leak. The patient may be misled by the poor quality of heterogeneous biological data.
Furthermore, measurement errors, missing data, or difficulties in interpreting the information hidden in textual reports can all have an impact on medical big data. The use of big data technologies entails keeping track of assets and patient data, organizing gathered data, and visualizing data on dashboards and reports.
Thus, it restricts the patient's freedom. The security of patients' sensitive personal data is a major concern for healthcare institutions since hackers frequently attempt to exploit huge data storages.
Considering how fast and simple the healthcare system has become, big data has the potential to advance the health business despite some of its downsides. It can get over its drawbacks as time goes on and technology advances. Researchers discovered that the growth of healthcare data is anticipated to be quicker than that of industry, financial services, or the media. Through 2025, healthcare data will expand at a 36% average annual growth rate (CAGR). 97.2% of firms are investing in big data and AI because they see its value and prevalence.
- What is Big Data in health industry https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/2047-2501-2-3
- Figure 1: Processing of Big data Analytics https://journalofbigdata.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s40537-019-0217-0#Fig1
- Benefits of Big Data and how it is liked with healthcare industry https://www.coursera.org/articles/big-data-in-healthcare
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/255970/global-big-data-market-forecast-by-segment/limitations-of-Big-Data-in-healthcare
- https://www.impactmybiz.com/blog/big-data-healthcare-explained/
- https://www.businesscompilerng.com/2022/05/big-data-analytics-in-healthcare.html#:~:text=One%20of%20the%20major%20drawbacks,the%20dashboard%20and%20the%20reports
Hello! I'm Abdus Salam. I'm a student currently studying Health Informatics in Deggendorf Institute of Technology. I love cycling, reading books, and sometimes writing. Matriculation Number: 22209351