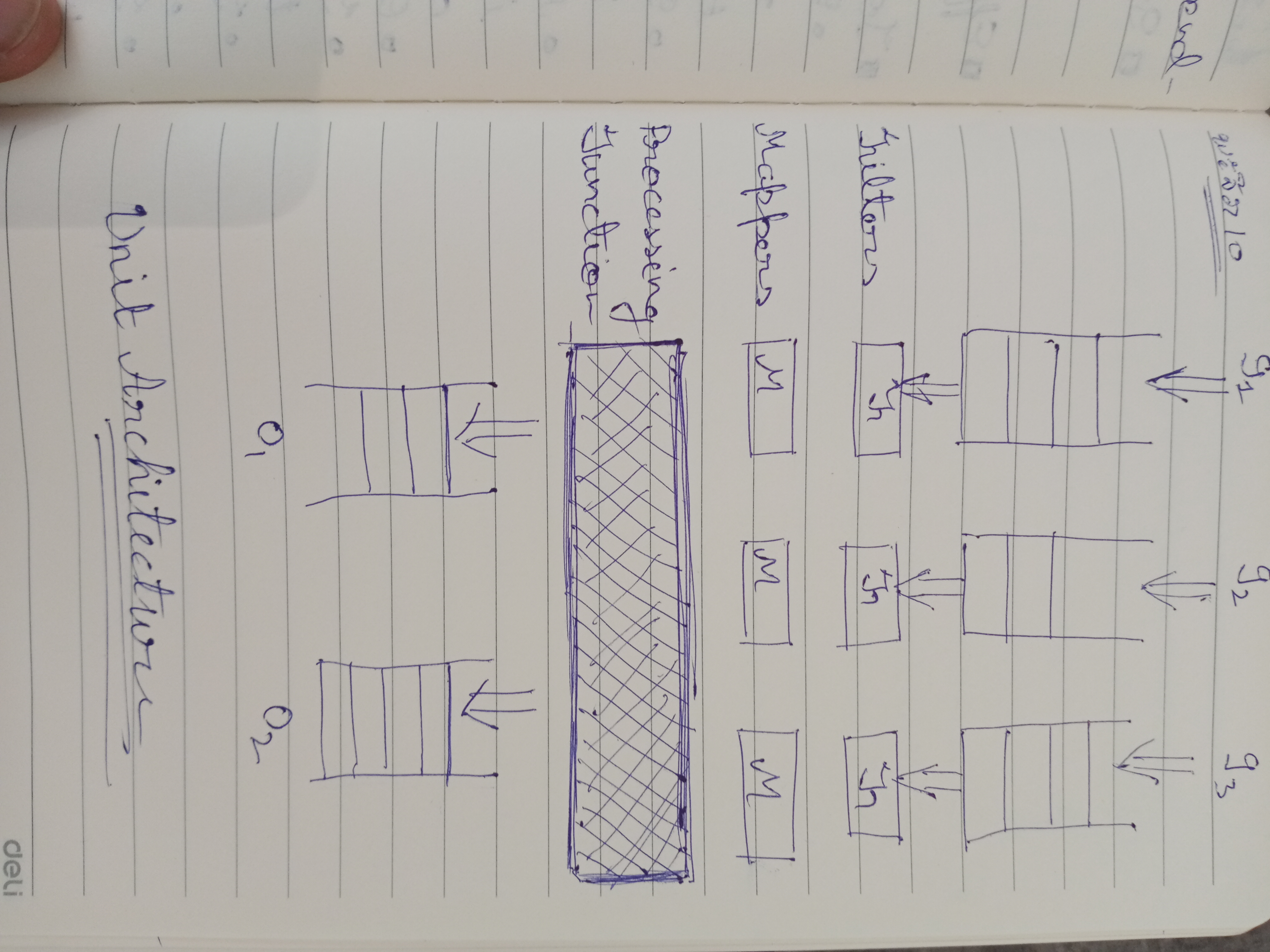
We introduce Unit, the primary asynchronous computation entity. A unit is a collection of channels. It applies the fun. It has configurable input or output queues. It is possible to have a queueless unit. A unit applies a function over input data elements. The results are queued to the outputs.
Several units are connected to form a Network. The connections are established through next() operation. next() sends a message to input queues. Typically, a network has a START unit and a FINAL unit. The START unit receives the network inputs. The Final unit emits the network output. Network flow is depicted graphically in:
Unit {
name
channels = {
channel1: {provider: {unit: 'name', channel: 'name'}},
channel2: {}
channel3: {provider: {unit: unitRef, channel: 'name'}}
}
functions: [
{
channels: ['channel1', 'channel2'],
func: ([c1, c2]) => {
return {channel3: c1 + c2}
}
}
]
start()
next({channel: data})
stop()
}Network {
name
channels = {
channel1: {provider: {unit: 'name', channel: 'name'}},
channel2: {}
channel3: {provider: {unit: unitRef, channel: 'name'}}
}
functions: [
{
channels: ['channel1', 'channel2'],
func: ([c1, c2]) => {
return {channel3: c1 + c2}
}
}
],
units: {
unit1: {
channels: {
u1channel: {provider: {unit: 'network', channel: 'channel1'}},
u2channel: {provider: {unit: 'network', channel: 'channel2'}},
},
functions: [
{
channels: ['u1channel'],
func: v => {
return {u2channel: v * 2}
}
}
]
}
}
start()
next({channel: data})
stop()
}The network and units together is a collection of nodes connected through predefined routes. Functions represent nodes and the channel associations are the predefined routes. A network of cities connected through highways is a close approximation. A trip from one city to another starts with route resolution. Map applications serve exactly that purpose. For our network, we introduce the concept of routes. A route is a description of nodes (unit-channel) that a request will follow. A route element has an associated request. A node processes its associated request.
Route {
stack
chain
next()
append(...elements)
copy()
merge(route)
}