I explored 4 questions using several publically available datasets from Yelp. This was part of a homework assignment for GA's Data Science Immervise, so I my goal was to exercise a wide set of new skills, instead of creating accurate models.
Question Predict whether a business resides in las vegas using only keywords from customer reviews. What are the most significant predictors for classifying a business as being based in Las Vegas?
Results I attempted to do some feature engineering, and used random forest to create a model to predict whether the business was located in las vegas. My baseline precision was 0.62, and my model had a 5 fold cross validated precision of 0.66. Test precision was 0.67 and recall was 0.93.
The top 10 features (by magnitude of coefficient) were as follows:
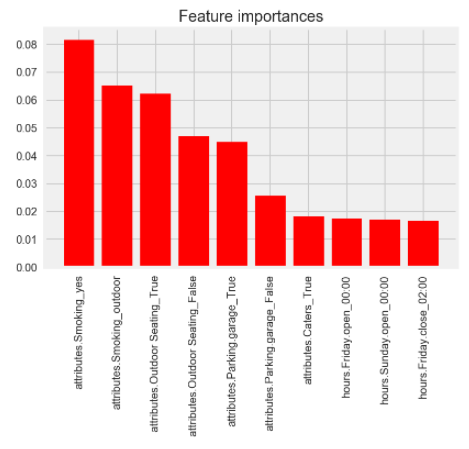
Conclusion The largest factor to a business' location being classified as Las Vegas is 'mMoking' == yes, which in a way makes sense. Outdoor seating, outdoor smoking, and having a parking garage were also big factors for las vegas, which also makes sense - a lot of people expect to be able to smoke wherever in vegas, and the high density of shops/casinos/businesses on the strip means you need a lot of parking garages.
We decided to move on from this question after putting in around 6 hours, but if I were to move forward I would do some more feature engineering. In particular I would see which businesses are open late during weekdays, because I think vegas businesses would be more likely to be open all hours, and I would create a feature for 24_hour_business, or late_night_business.
Question I wanted to use Yelp data to investigate if there were two groups of users: users who rated a restaurant based on the service they received, and users who did not base their ratings on service. If it turned out that service significantly affected the reviews of a particular group of users, then advertising could be more specifically personalized to them.
To test this, I first identified users who mentioned service in their reviews, and those who did not, and split them up into two groups: a "service oriented" user group, and a non-service oriented user group. I then created a multi-class logistic regression model to predict the number of stars each group would give for a certain restaurant. If there was a difference between the two groups, I would be able to see that in the feature weights; service oriented features should have significantly higher weights for the service-oriented user group. And the most important features for non-service oriented users should not be service related features.
Results I first used linear regression to create a model to predict if a user was a 'service-oriented' user.
The top 10 features (by magnitude of coefficient) were as follows:
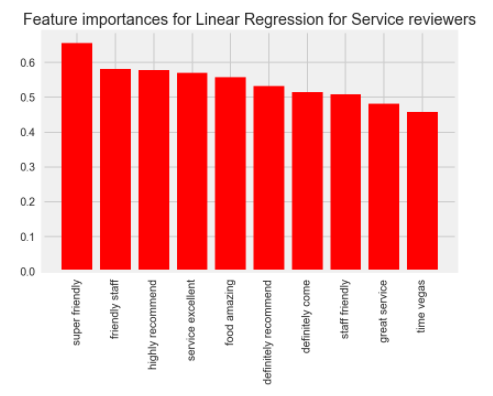
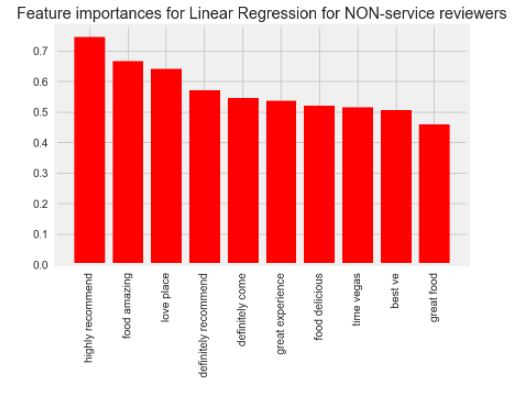
We also used Multi class logistic regression to predict 'service-oriented' users.
The top 10 features (by magnitude of coefficient) were as follows:
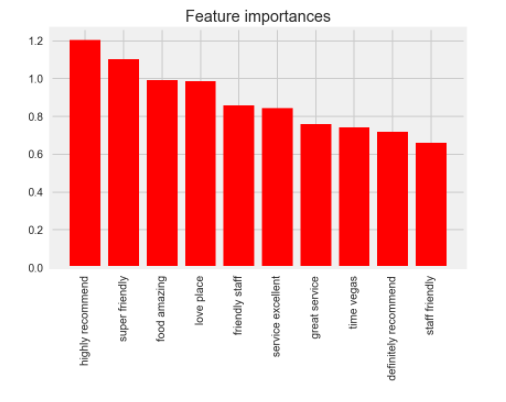
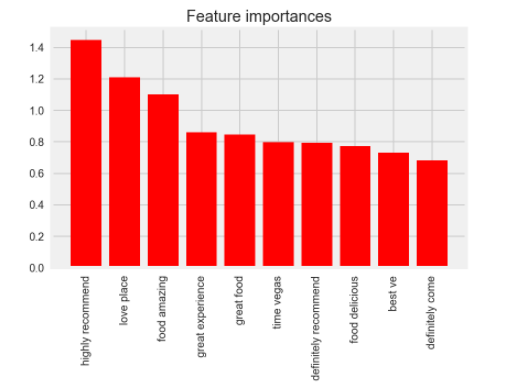
Conclusion After the model was fit and validated (zero one loss of 51.6%), service features represented 5 out of the top 10 features in predicting 5 stars for 'service' oriented customers.
For non-service oriented customers, service features represented 0 out of the top 10 features in predicting 5 star ratings. Each feature was found to statistically significant.
The results strongly suggested the two user groups really are different. In other words, the most important factors that determine how a user is going to rate a restaurant are significantly different between the customers who mention service in their reviews, and those customers who do not.
To further investigate the question, I would ask whether, for the same business, non-service oriented customers reviews significantly differed from service oriented customer reviews, and perform the t-test aggregated over a large number of businesses. This would tell me if the two groups of users actually rated businesses differently. The results would inform advertising strategy - if the two groups have different scores for the same businesses on average, it's important to target the two groups with different strategies.