This repository looks into how one can use the Data Refinery service available on IBM Cloud to, as the name suggests, refine data through data cleansing, shaping and validation in addition anomaly detection and data visualization.
A lot of time is said to be spent cleansing, shaping and formatting data before doing any analysis. In fact, you might have heard people saying that data scientists can spend up to 80 percent of their time finding and preparing data. To address this, IBM built IBM Data Refinery, an intuitive cloud-based data preparation service, where you can quickly source, shape and share your data sets.
IBM Data Refinery, first released in November 2017, is part of the Watson Data Platform integrated environment and is a self-service data preparation client for data scientists, data engineers, and business analysts. With it, you can quickly transform large amounts of raw data into consumable, quality information that’s ready for analytics. IBM Data Refinery makes it easy to explore, prepare, and deliver data that people across your organization can trust. It provides:
- Ability to access data wherever it resides (in the cloud, on-premises, or on your desktop)
- Powerful shaping operations to clean, organize, fix, and validate data
- Scripting support for RStudio’s dplyr for the efficient and flexible manipulation of data sets
- Support for single- and multi-column operations and the creation of complex new columns from existing columns
- Ability to undo, redo, and delete steps in a data flow
- Monitoring of data preparation flows
- Interactive data validation and automatic detection of anomalies such as missing values, outliers, and duplicates
- Visualizations that provide insight into large amounts of data
When refining your data, the Data tab is where you can see a simple of how you data looks and see the result of any operation you select to do on your data. The Profile tab allows you to see a summary of some basic statistical analysis and can be used to find anomalies. The Visualizations tab helps with getting insights into your data.
An IBM Cloud account - A lite account, which is a free of charge account that doesn’t expire, can be created through going to IBM Cloud. Make sure to set the region to US South.
It is through the newly created Watson Studio service instance that we will be able to use the IBM Data Refinery service. You can skip this step if you already have Watson Studio service instance created.
- Select Catalog found at the top right of the page.
- Click on Watson from the menu on the left, which you can find under Platform services.
- Select Watson Studio.
- Enter the Service name or keep the default value and make sure to select the US South as the region/location and your desired organization, and space.
- Select Lite for the Plan, which you can find under Pricing Plans and is already selected. Please note you are only allowed one instance of a Lite plan per service.
- Click on Create.
- You will be taken to the main page of the service. Click on Get Started. This will take you to the Watson Studio platform. If this is your first time on this platform and you don't have an associated account, you will be asked to Confirm your IBM Cloud organization and space information.
- On the IBM Watson Watson main page, click on Refine data Under Get started with key tasks. If you don't have any projects previously created, you will be asked to Create Project. Otherwise, you will need to select one of your already existing projects or create a New project from the IBM Watson Watson main page.
- Enter a Name and Description for your new to-be-created project.
- Under Define storage, add a new IBM Cloud Object Storage instance by clicking on Add under Select storage service.
- In the new window that gets opened, select Lite as the Plan and click Create.
- Enter the Service name or keep the default value.
- Click on Confirm.
- Click on Refresh to see the newly created service instance and get it selected.
- You can select to Restrict who can be a collaborator under Choose project options if you wish to do so at this stage.
- Click on Create.
- You should be taken to a page showing an Overview of the project you just created.
- Click on Assets on the panel found under the name of your project at the top of the page.
- At the top right of the page, click on the icon that has zeros and ones (two of each).
- Click on Load and drag and drop the two files adult_person_info.csv and adult_org_info.csv, which can be found this GitHub repository under the folder Data sets.
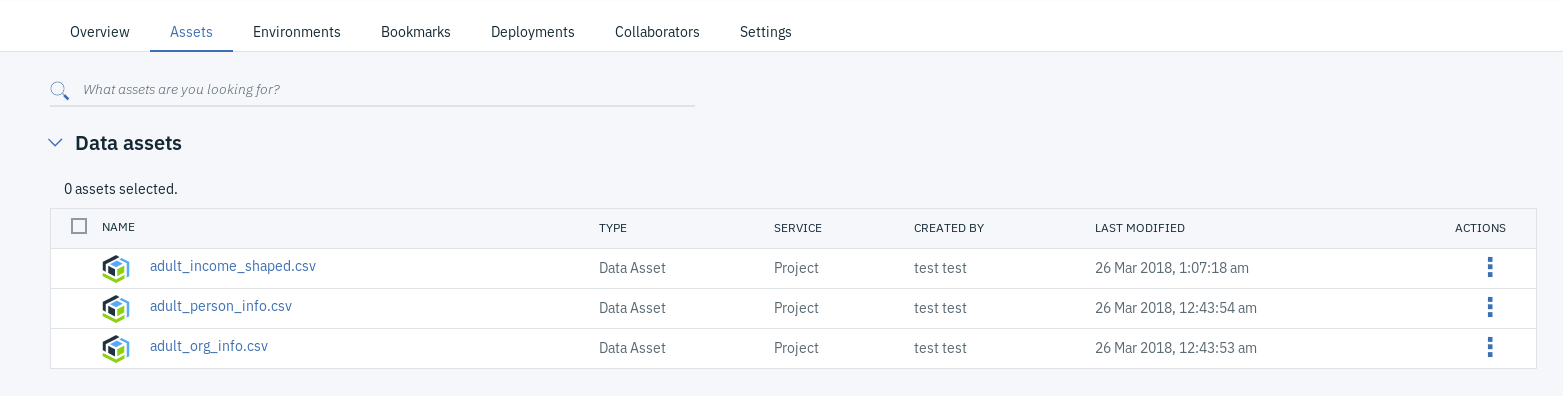
- You will notice that once the files are uploaded, they will be added under Data assets.
- Go to the triple dot menu next to next to adult_person_info.csv under Data assets and select Refine. This will open a page that shows a sample of the content, where you can start cleaning and reshaping the data set.
- On the panel on the right, you will find Details including the project the data asset belongs to, and description of the resulting data set we will get after the refining process. Close it for the time being.
- Click on Steps, which you can find right hand-side of the page. This is where you will see each operation you will define while transforming the data. It shows the data flow defining the operations to be done on the entire data set.
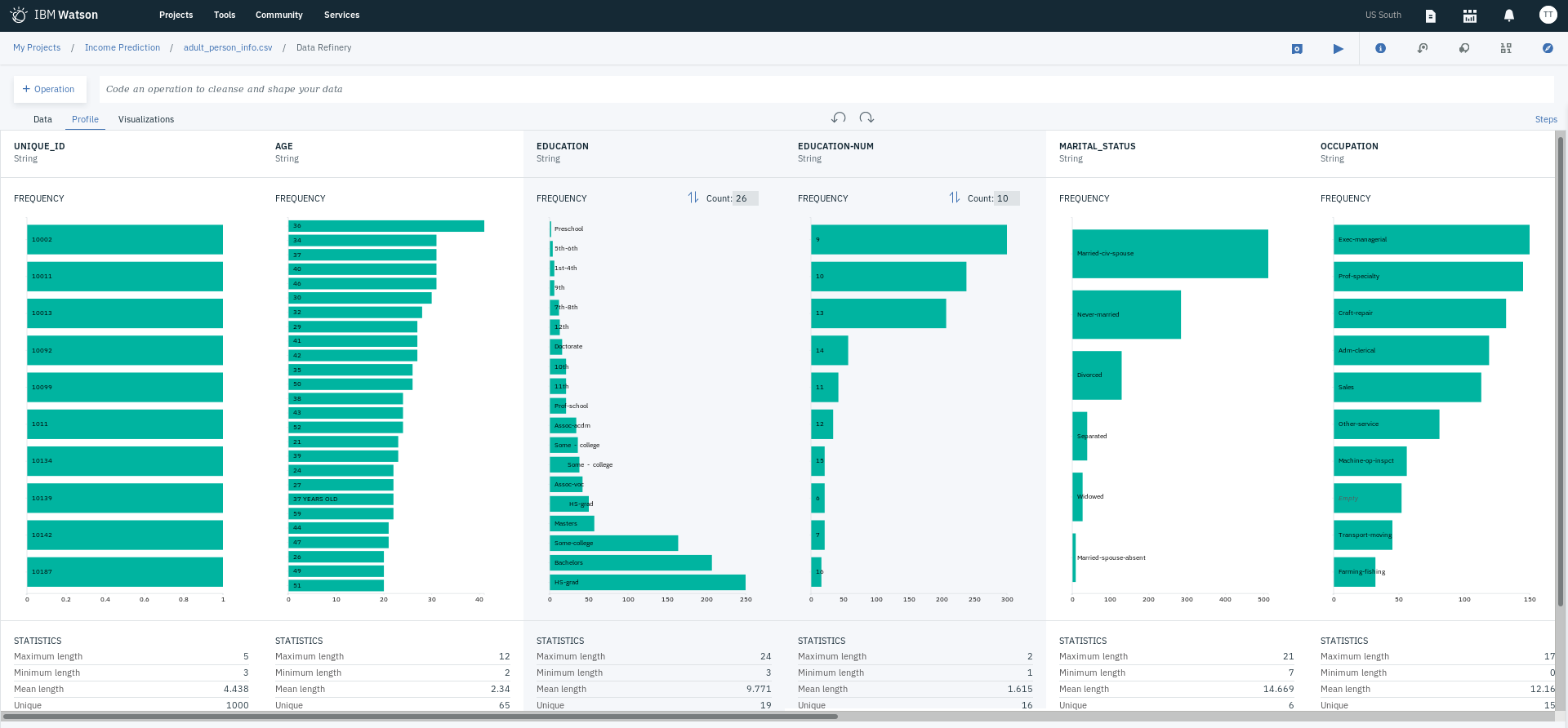
- Click on the Profile tab and talk quick look at data summary and get a feel of you data (do this after skimming through your data displayed in the Data tab). You will notice some weird values under FREQUENCY for some fields. For example, you will notice that some values under AGE contain additional string and there multiple values under SEX that seem to be meant to represent the value Male). You will also notice that, for the most part, EDUCATION and EDUCATION-NUM seem to have the similar frequency values. We will get back to this in a bit.
- Click on the Data tab to see a sample of your data.
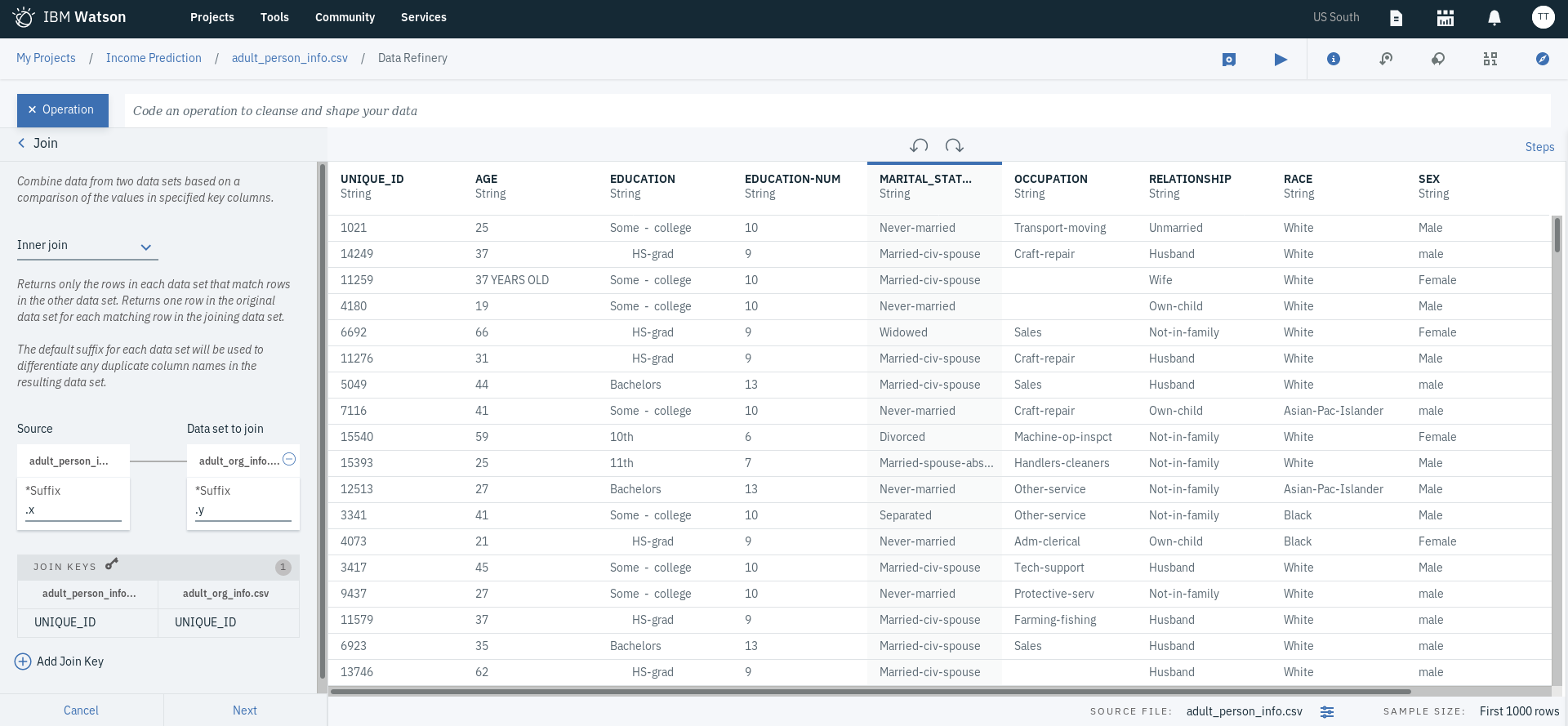
- Click on + Operation and then select Join, which you can find under ORGANIZE. This to join both the data assets we added namely the one we are currently refining, adult_person_info.csv, and adult_org_info.csv.
- Select Inner join as the method of how we want our data to be combined (Inner Join selects records that have matching column value(s) in both tables).
- By default, the Source is selected as the current data asset (adult_person_info.csv). type of joining choose adult_org_info.csv as the Data set to join.
- Modify the Suffix field as you desire, which is just a way for you to differentiate any duplicate fields resulted during the joining process. You can use the default values.
- For the JOIN KEYS, select UNIQUE_ID representing the employee ID, as the join key for both data sets and click Next
- Select all fields and click Apply.
- We will notice that there are 2 columns representing OCCUPATION, one coming from each of the data sets. Let's check to see if they contain the exact same values.
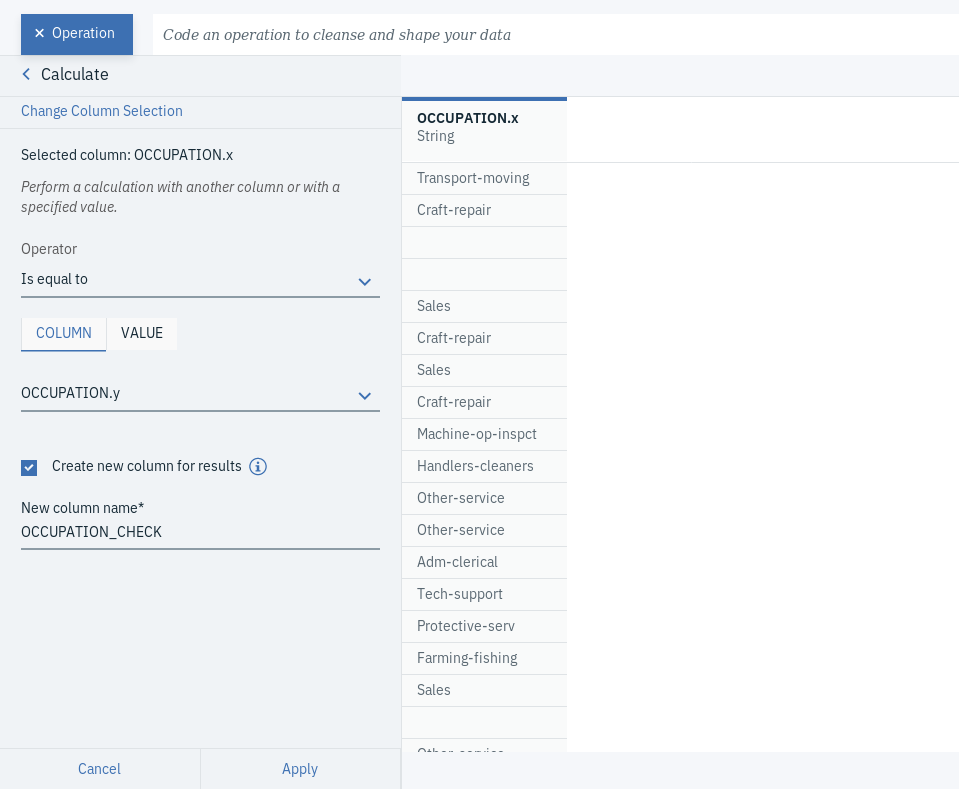
- Click on + Operation and select Calculate, which you can find under FREQUENTLY USED.
- Choose OCCUPATION.x as the Selected column, Is equal to as the Operation and OCCUPATION.y as the COLUMN.
- Select to Create new column for the results and enter the New column name.
- Click Apply. You will see the resulting column added at the right end of the table.
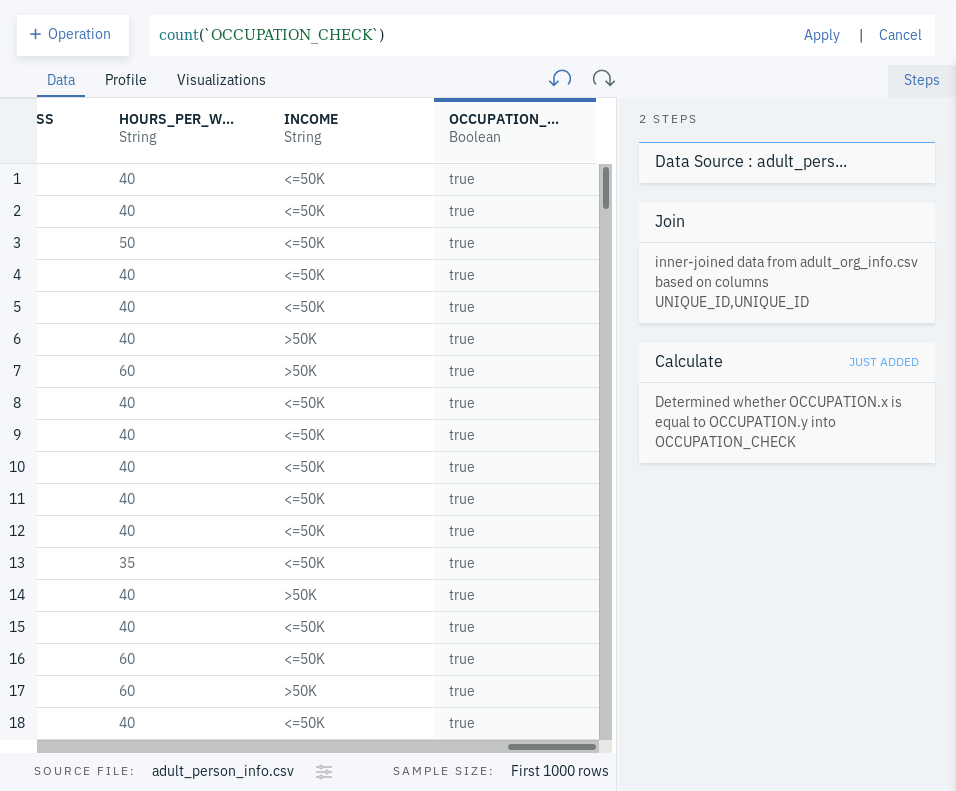
- In the space next to the + Operation button, place the cursor and select count.
- Click on the count that was added to the box and select count(
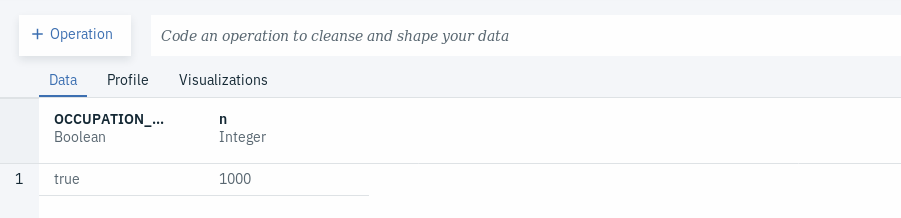
<column>). - Click on and choose the newly created column (we called it OCCUPATION_CHECK).
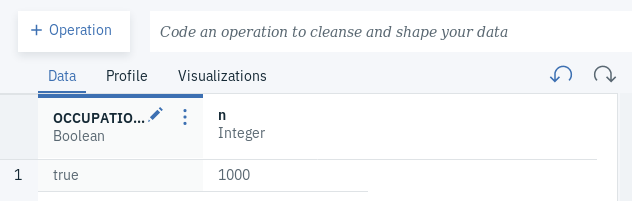
- In our case, we will see that all fields that had values were identical in both OCCUPATION.x and OCCUPATION.y, which is indicated as we can only see true as the only value with the newly created column. In other cases, we might see that some values are not identical due to one reason or the other. In such situations, what we can do is select the column we get from the data asset coming from the more trusted source.
- Go back 2 steps by either clicking on the Undo shaped button found at the top middle of the page or by going to the step added under Steps and clicking on the bin icon. Whichever way you select, you will need to do it twice.
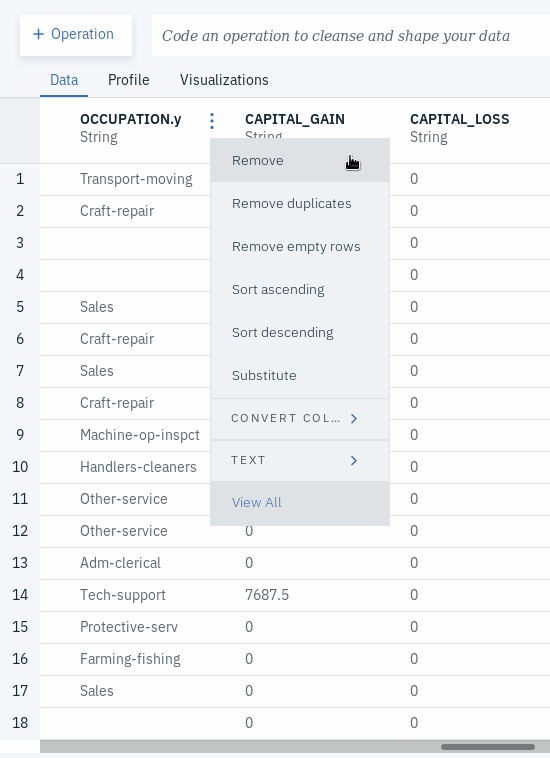
- Go to column called OCCUPATION.x and rename it to OCCUPATION by clicking on the pencil shaped icon next to the column name.
- Go to column called OCCUPATION.y and remove by clicking on the triple dot menu next to the column name and selecting Remove.
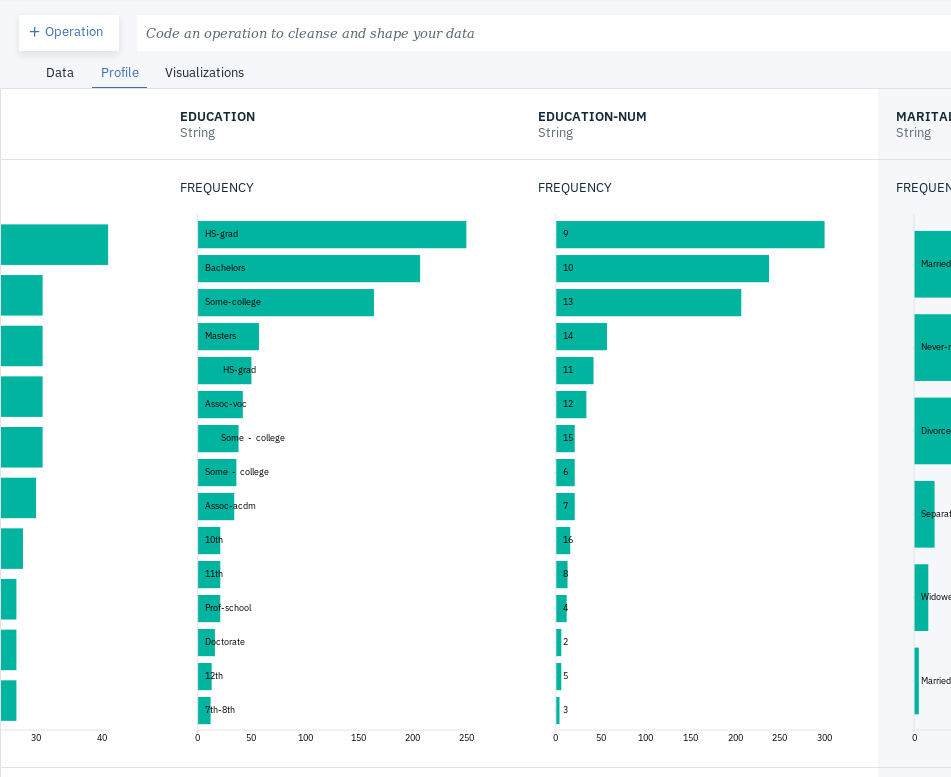
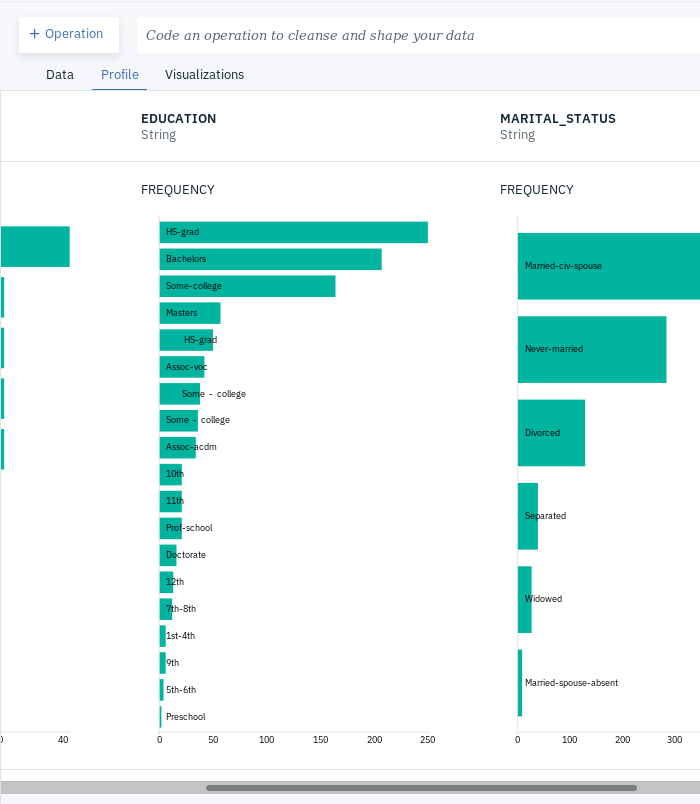
- Click on the Profile tab and take a closer look at the column EDUCATION and EDUCATION-NUM. You will notice they have the same frequencies.
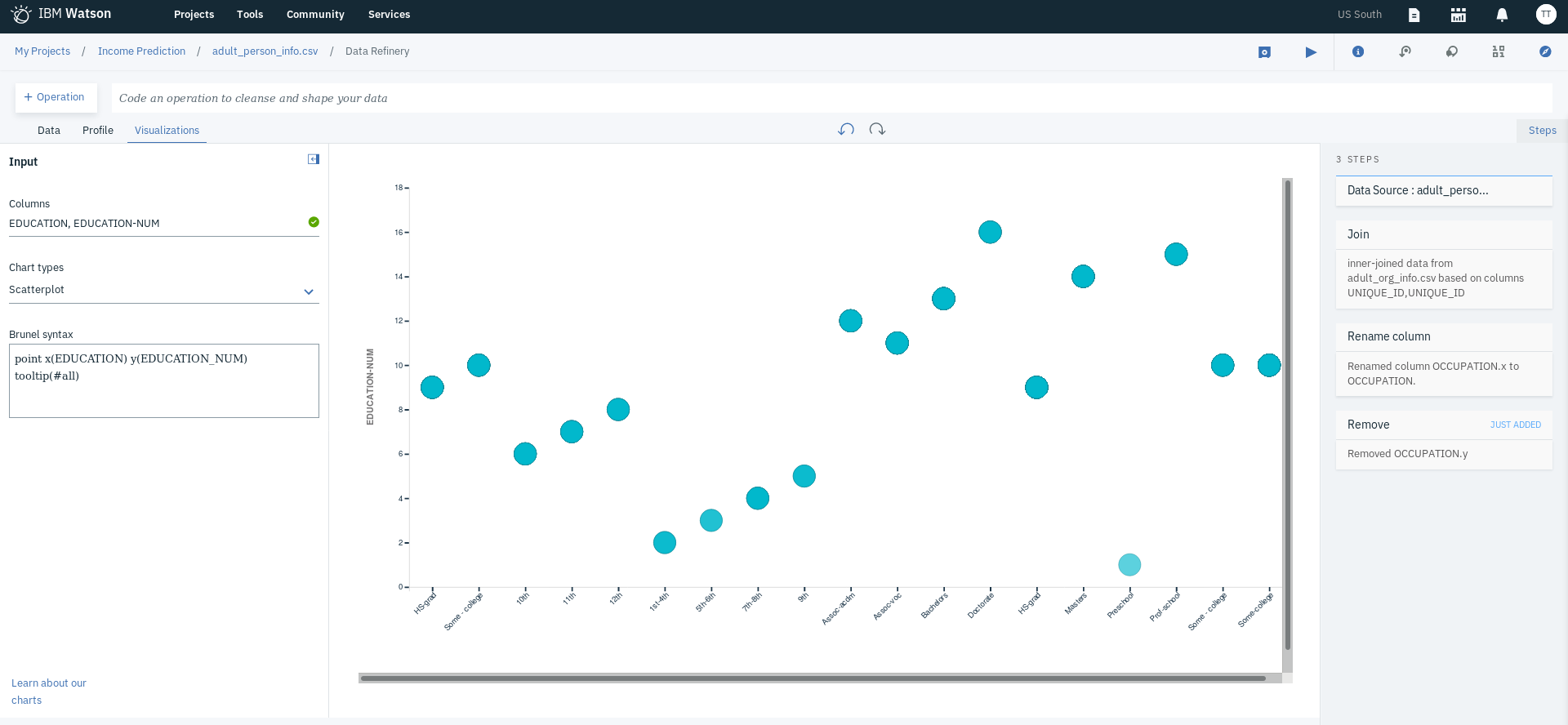
- Click on the Visualization tab to confirm this and select EDUCATION and EDUCATION-NUM as the Columns and Scatterplot as the Chart types.
- You will notice that each of the circles drawn correspond to a value from each column, confirming that they overlap and are indeed the same thing. Note that this might not be the ideal choice for the graph.
- Go back to the Data tab and remove the column EDUCATION-NUM the same way we did with OCCUPATION.y.
- Click on the Profile tab and take a closer look at the column EDUCATION. You notice there are some additional values with extra spaces at the beginning and possibly the end of the string.
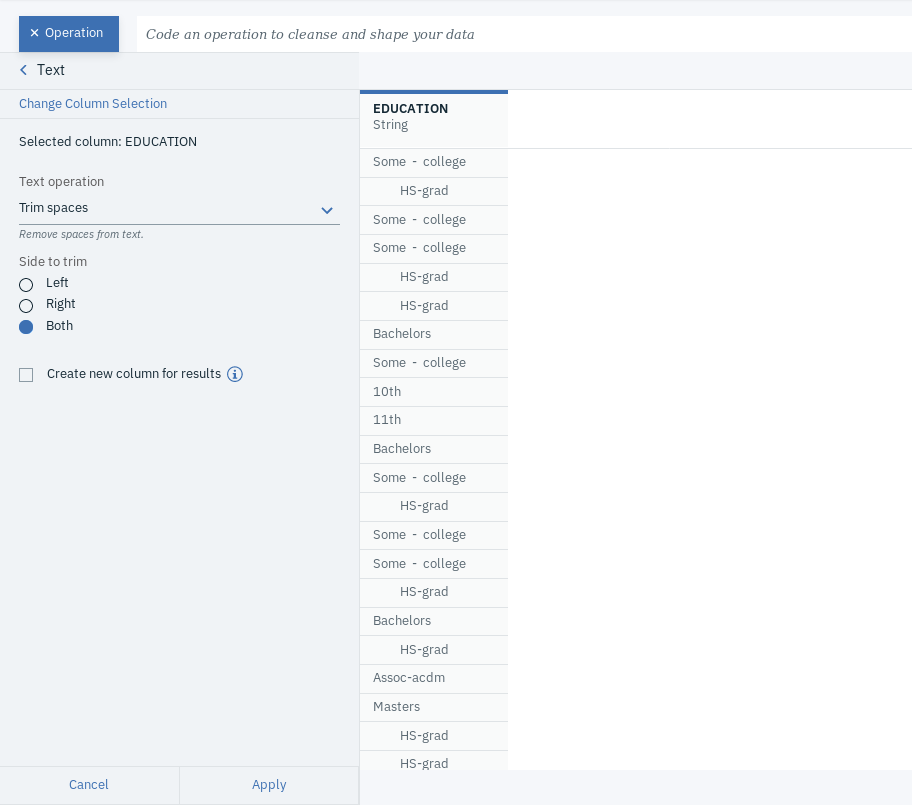
- Click on +Operation and select Text, which you can find under FREQUENTLY USED.
- Choose EDUCATION as the Selected column, Trim spaces as the Text Operation and Both as the Side to trim.
- Click Apply and go to the Profile tab again to check if all the additional values have been removing. You will notice the we still have Some - college as an additional value, which we want to harmonize and change to Some-college.
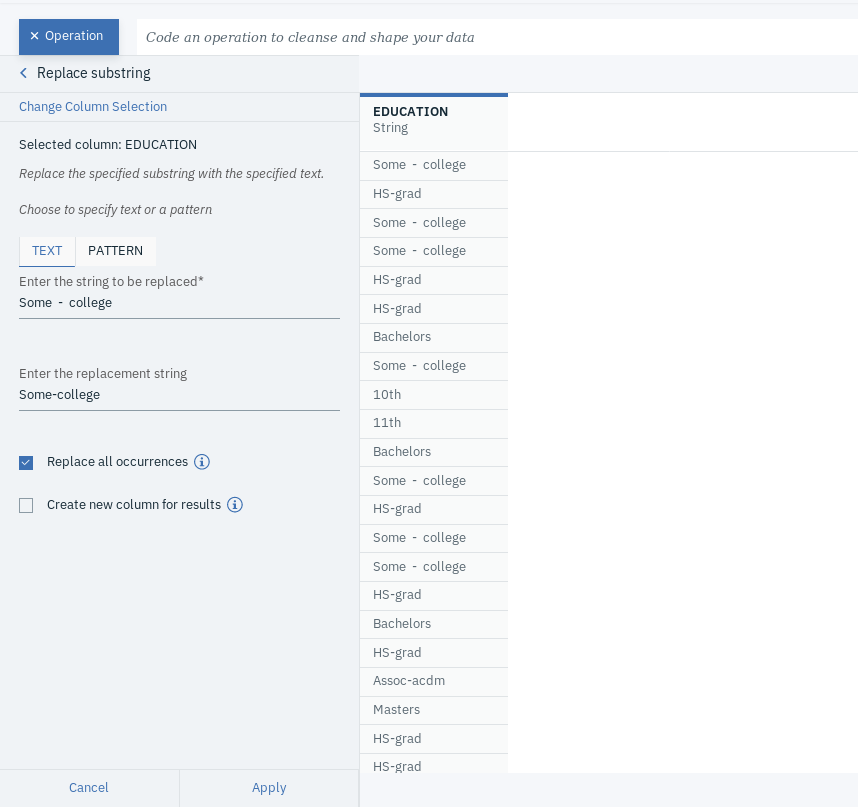
- Click on +Operation and select Replace substring, which you can find under CLEANSE.
- Choose EDUCATION as the Selected column. Under TEXT tab, type Some - college under Enter the string to be replaced and Some-college under Enter the string replace with. Make sure to select Replace all occurrences
- Click Apply.
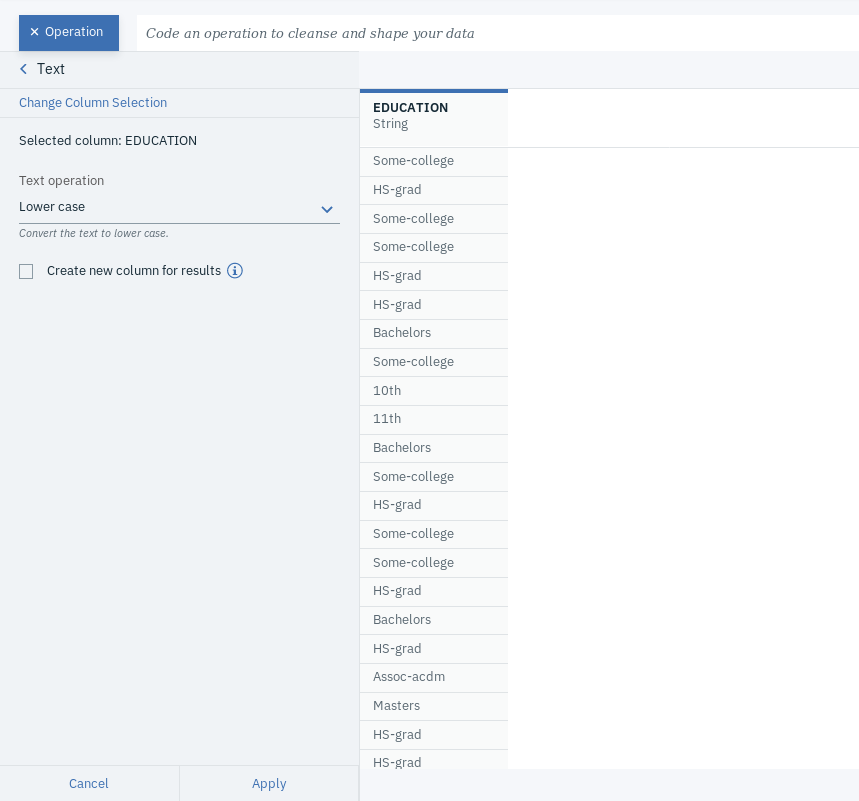
- We also want to convert all values in the EDUCATION column to lower case. So, click on +Operation and select Text, which you can find under FREQUENTLY USED.
- Choose EDUCATION as the Selected column, Lower case as the Text Operation.
- Click Apply and go to the Profile tab again to for a final check.
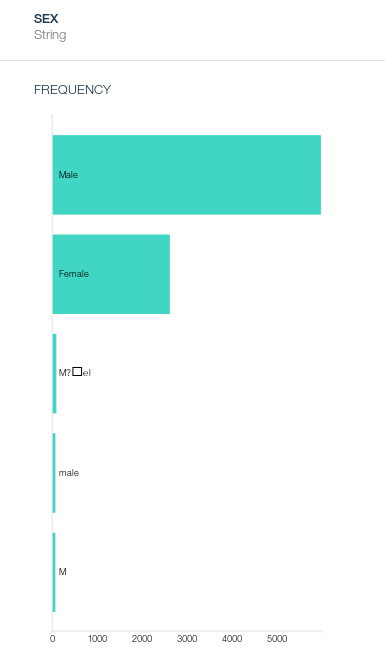
- Click on the Profile tab and take a closer look at the column SEX. You will notice some additional values other than Male and Female, mainly ones that we want to change to Male.
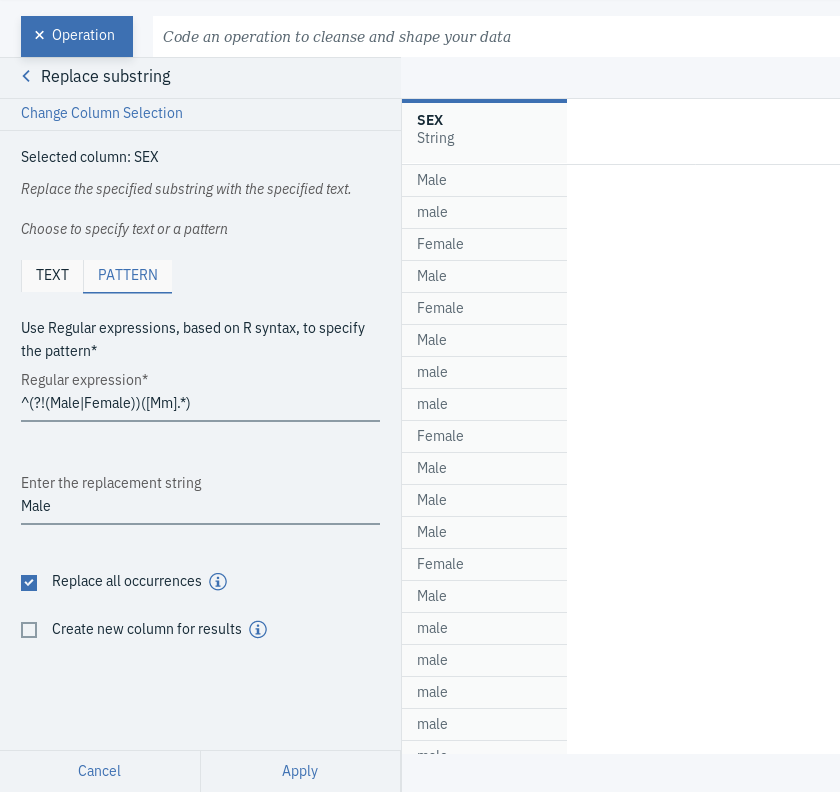
- Click on +Operation and select Replace substring, which you can find under CLEANSE.
- Choose SEX as the Selected column. Under PATTERN tab, type ^(?!(Male|Female))([Mm].*) under Regular expression and Male under Enter the string replace with. Make sure to select Replace all occurrences.
What is meant by ^(?!(Male|Female))([Mm].*) is to find any expression that doesn't start with Male or Female and starts with the letter M or m, which could be followed by any character.
- Click Apply and go to the Profile tab again to for a final check.
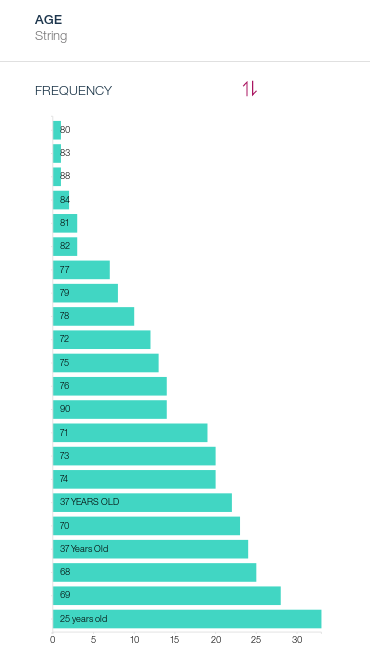
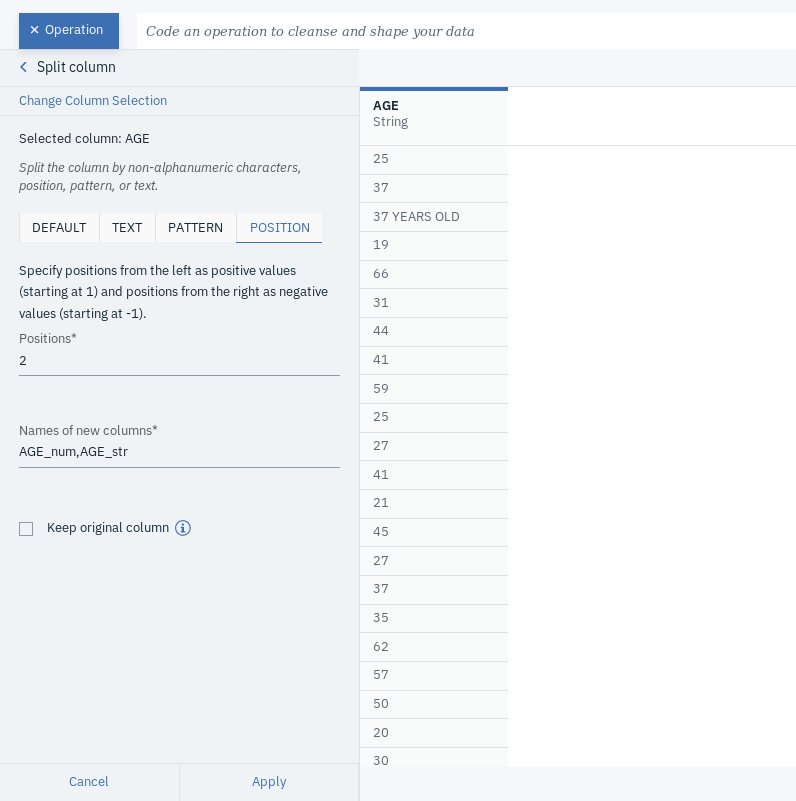
- Click on the Profile tab and take a closer look at the column AGE. You will notice some values with additional string such as years old. What we want is to just retain the numerical part, which can only be a two-digit number in our case (we know there are no additional characters that were added before the numerical part of the values or that the digits contain no weird characters).
- Click on +Operation and select Split column, which you can find under ORGANIZE.
- Choose AGE as the Selected column. Under POSITION tab, type 2 under Positions and AGE_num,AGE_str under the Names of new columns. Make sure to unselect Keep original column
- Click Apply.
Bear in mind that this is not the best approach to handle this. This is just provide an example of how to use the split column operation.
- Go to the Data tab and remove the newly created column called AGE_str, which only contain the string part of the age.
- Go to column called AGE_num and rename it to AGE.
- Go to the Profile tab again to for a final check.
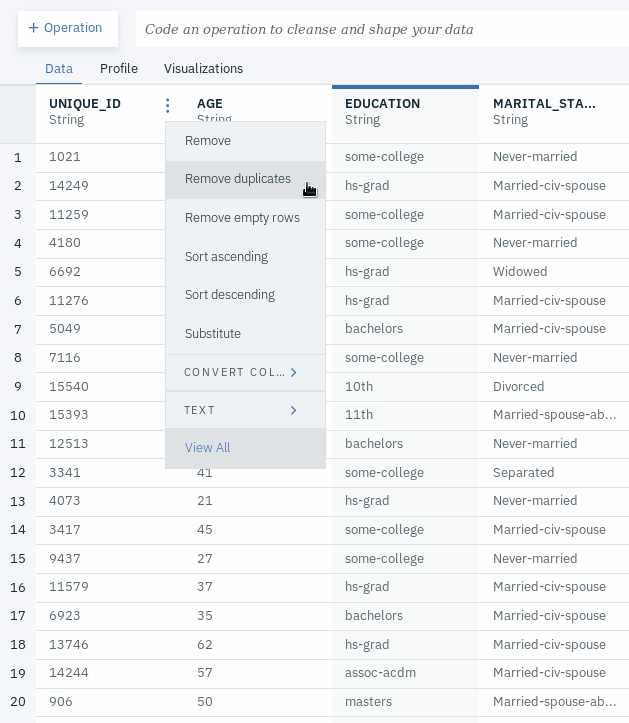
- Go to the Data tab.
- Go to the column called UNIQUE_ID and remove rows with any duplicate UNIQUE_ID values by clicking on the triple dot menu next to the column name and selecting Remove duplicates.
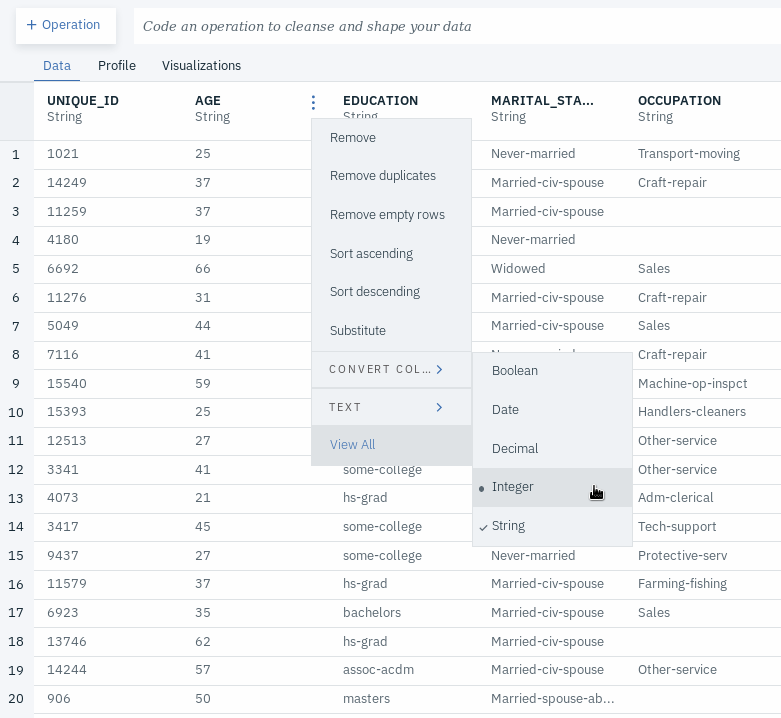
- Go to the Data tab.
- Go to the column called AGE and change its type to Integer by clicking on the triple dot menu next to the column name and selecting CONVERT TYPE followed by selecting Integer.
- In the same way, change the data type of HOURS_PER_WEEK to Integer, and CAPITAL_GAIN and CAPITAL_LOSS to Decimal.
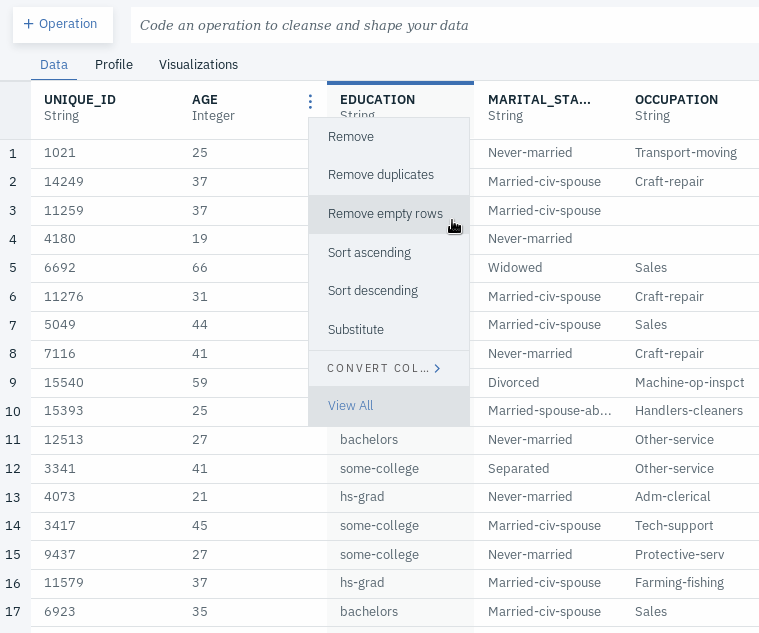
- Go to the Data tab.
- Go to the column called AGE and remove rows with any empty values by clicking on the triple dot menu next to the column name and selecting Remove empty rows. Do the same thing to all the other columns.
- Go to the Profile tab to check if all empty values have been remove. Note that you will typically try to understand the different reasons behind having missing values and act accordingly. Some of the techniques used in such situations may include:
- Using deletion methods such as:
- List-wise deletion
- pairwise deletion
- Single imputation methods such as:
- Mean/Mode substitution
- Regression Imputation
- Model-based methods such as:
- Maximum Likelihood
- Multiple Imputation
- Go to the Data tab.
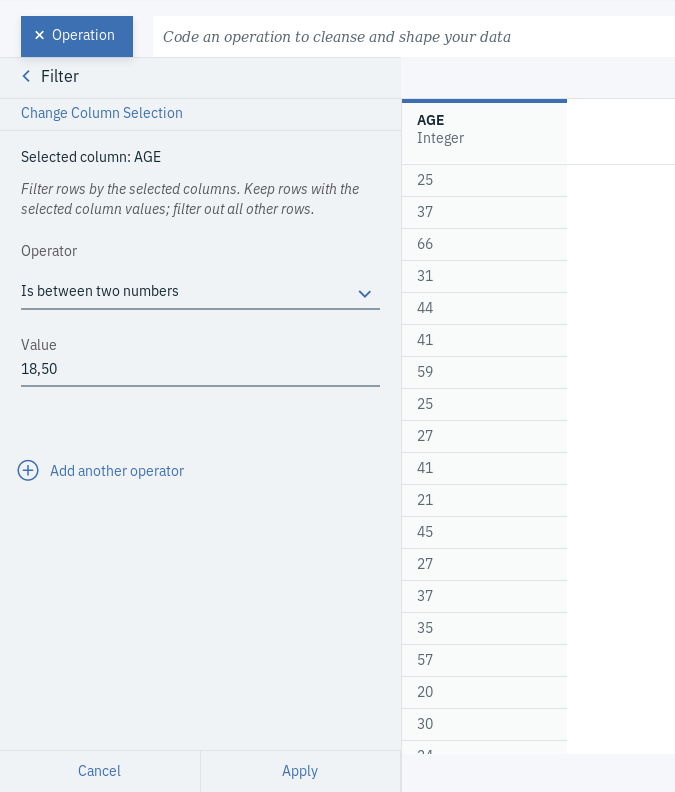
- Click on + Operation and select Filter, which you can find under FREQUENTLY USED.
- Choose AGE as the Selected column, Is between two numbers as the Operator and 18,50 as the Value. This will only keep the rows that have age values between 18 and 50.
- Click Apply.
- Go to the Data tab.
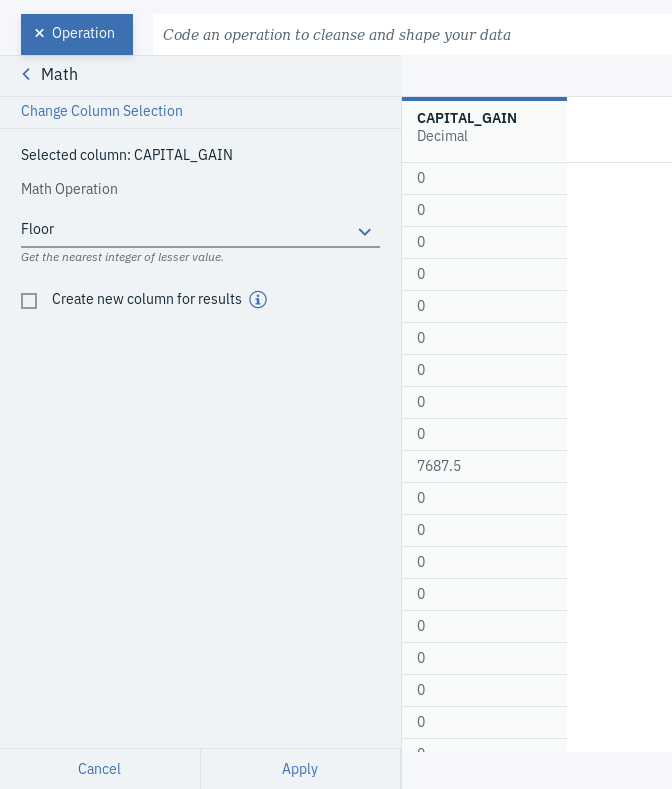
- Click on + Operation and select Math, which you can find under FREQUENTLY USED.
- Choose CAPITAL_GAIN as the Selected column and Floor as the Math Operation.
- Click Apply.
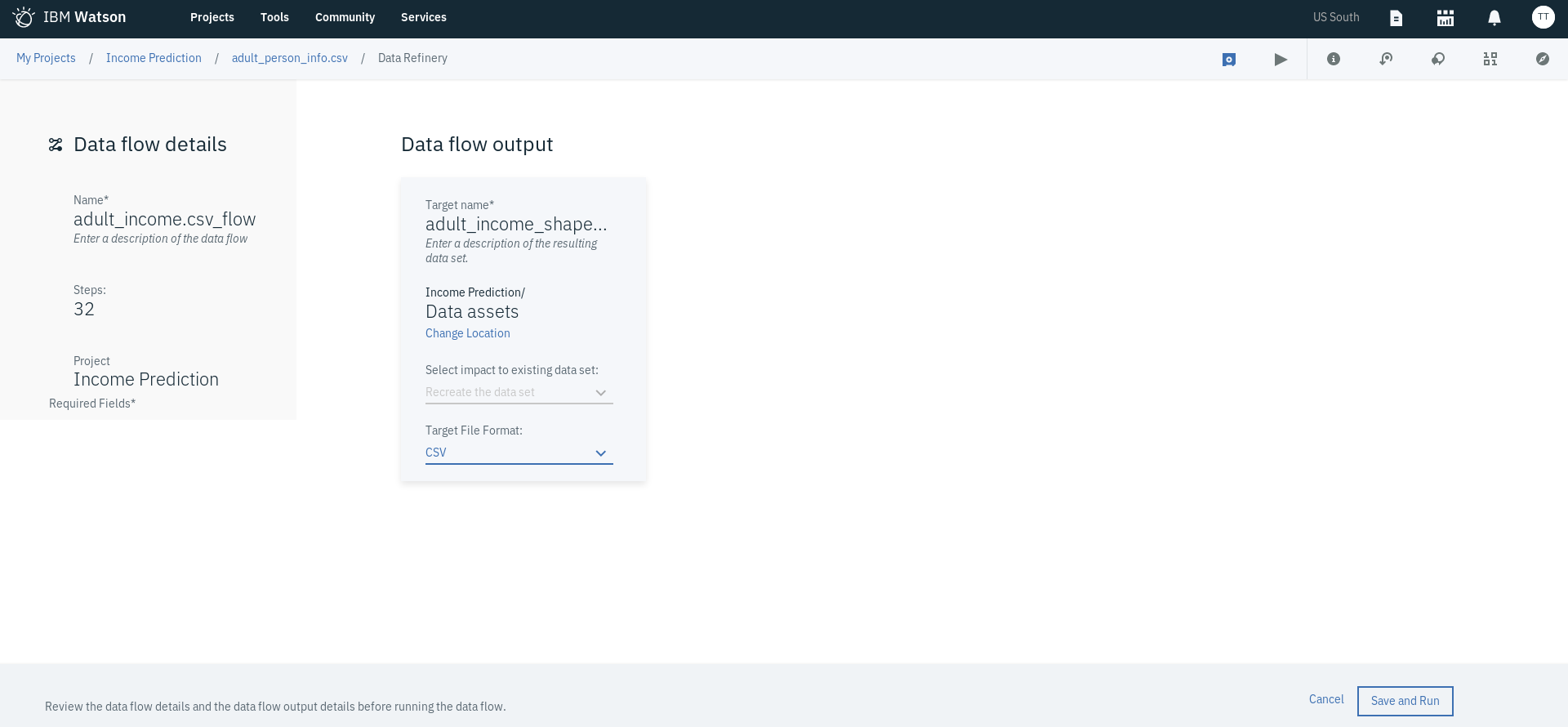
- At this point, you should have 32 Steps. The next step is to click on the play button to run the data flow as seen below.
- This will take you to a page where you will need to configure the Data flow details and Data flow output if you haven't already done so in the Details panel, which we mentioned earlier at the beginning of the Start refining the data section. Feel free to change the Name under Data flow details to adult_income.csv_flow and the Name under Data flow output to adult_income_shaped.csv.
- Click on Save and Run
- In the window that pops up, click on View Flow to track the progress of the running data flow.
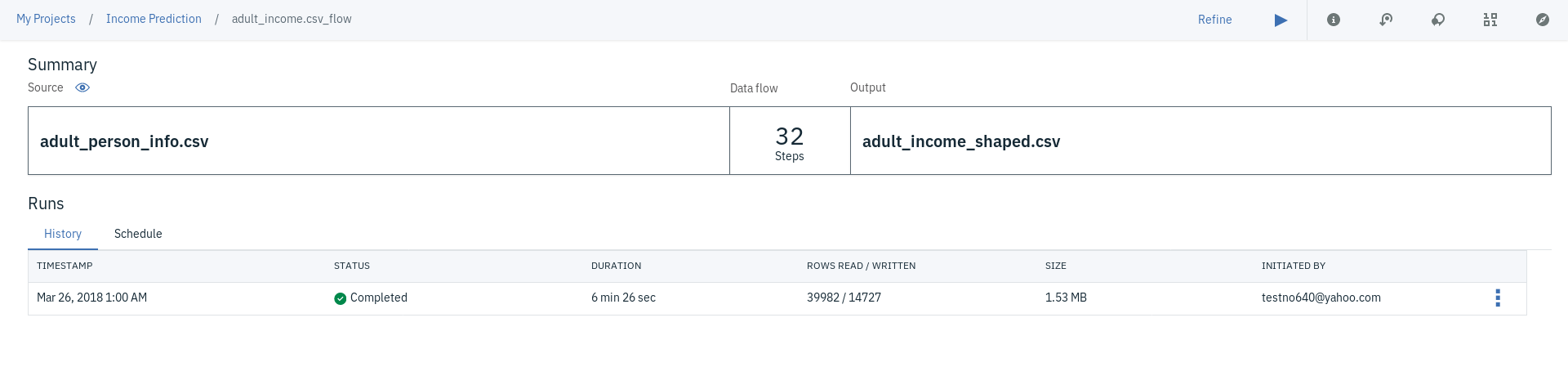
- The data flow should start running, executing each of the operations we defined. If things goes well, you should see the page similar to the one displayed below.
If you go back to the Assets page of your project, you will notice that the new csv file has been added as a new data asset.
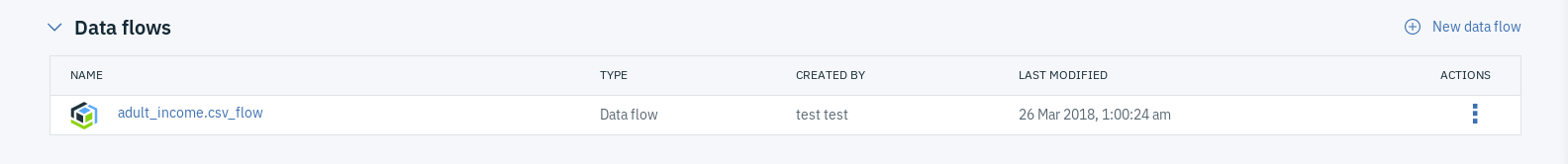
You can also find the data flow you created if you scroll down the same page, which can refine at any time by clicking on the triple dot menu next to the data flow name.
Aaaand that is it!!