Both the standalone app and AWS Lambda function will:
Fetch a list of all the repos under:
- Org name
- Team name
When fetchng the repo list, if the repo is either privarte or archived it will be excluded.
The stanalone App saves the repo data locally in the ./traffic_stats directory.
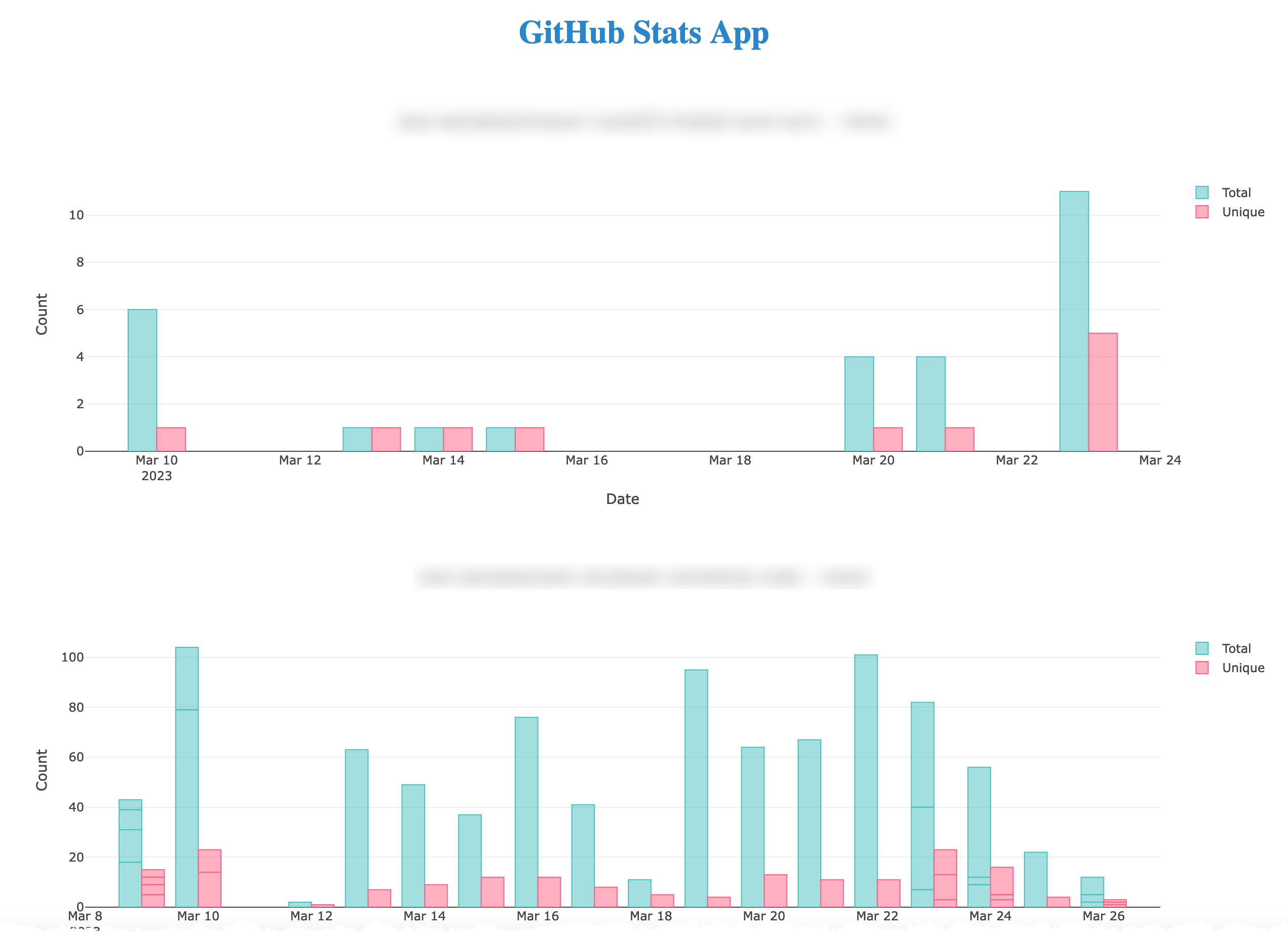
Running the app will start a Flask App and open a web page to the local Flask server:
Create a new Python virtual environment:
$ python3 -m venv .venv
Now activate the new virtual environment:
$ source ./.venv/bin/activate
The local requirements.txt file should be all you need:
$ pip install -r ./requirements.txt
If this doesn't work as expect4d for any reason. you can deactivate the virtual environment with the deactivate command.
Then, recreate a new virtual environment, activate it (source ./.venv/bin/activate) and manually install the Python packages with pip as below:
First, install Python as it's a pre-requsite for some of the other packages:
$ pip install Cython
$ pip install pip jnius dash dash_bootstrap_components gunicorn psutil requests pyyaml PyGithub --upgrade
The standalone app uses local environment details for:
- access_token = os.environ["GITHUB_TOKEN"]
- org_name = os.environ["GITHUB_ORG_NAME"]
- team_name = os.environ["GITHUB_TEAM_NAME"]
As such, these three environment variables will need to be available.
To create them:
export <environment variable> = <value>
i.e.: export GITHUB_ORG_NAME = "my-org-name"
The app takes the following command line arguments:
- [ --run| -r ] Runs the Flask App and opens a local browser
- [ --create | -c ] Creates a yaml file from the list of repos
- [ --update | -u ] Updates the repo list and stats
- [ --shutdown | -s" ] Shuts down the Flask App
- [ --list | -l ] List Repos
As the app runs in the background, to stop the app use the --shutdown (-s) flag.
The AWS Lambda function gathers the same stats via the same mechanism, however the CDK app also creates a DyamoDB table and stores data in the DyamoDB table. The DyamoDB table will be updaetd everytime the Lambda function runs.
The Lambda function is run on a period basis triggered by an Eventbridge schedule.
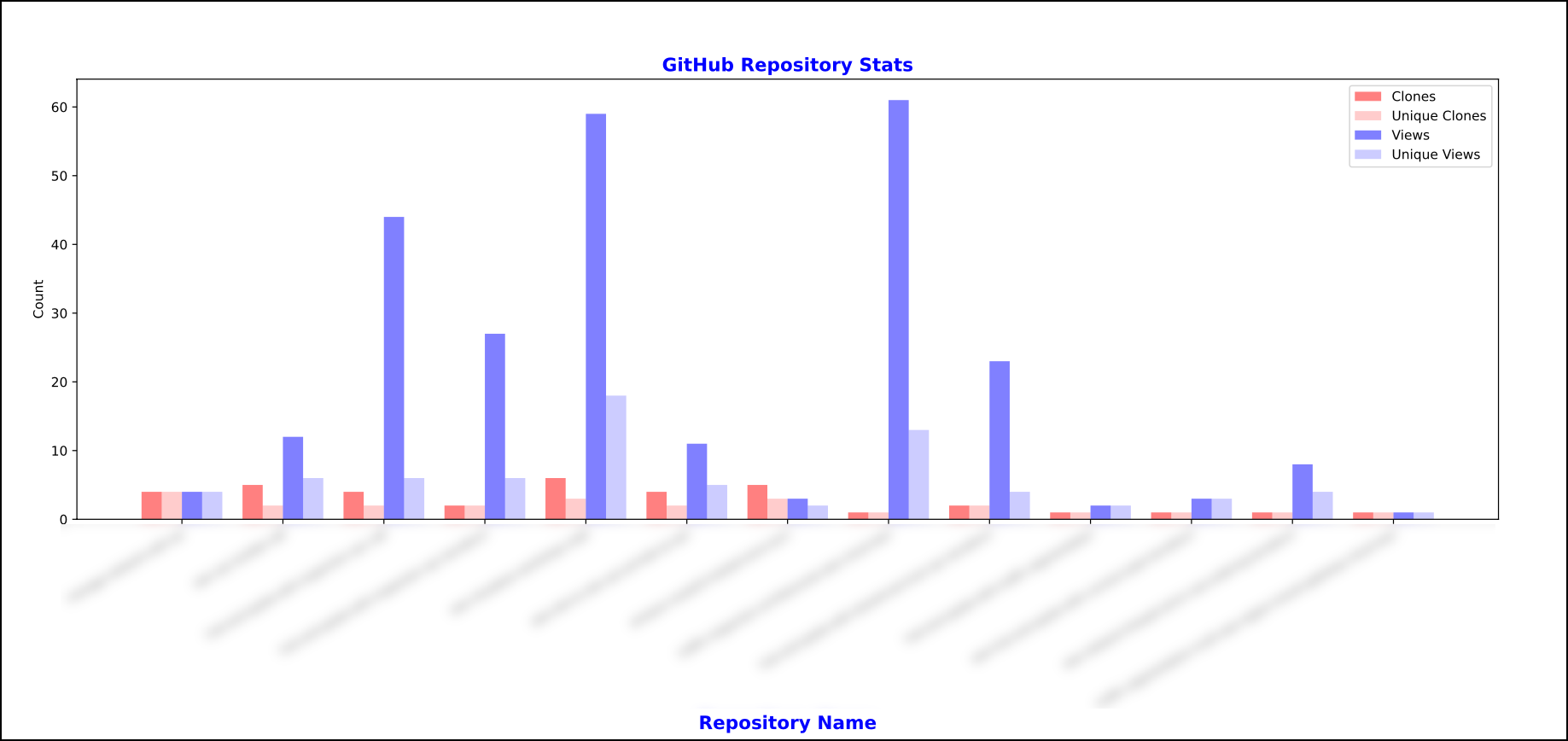
There is also a dbdata.py app in the ./graph_data folder which will fetch the data from the DynamoDB table and graph it, the graph will be saved as a pdf in the ./graph_data/data folder.
Command line options:
--list List the GitHub repositories
--update Invoke the Lambda function to update the statistics
--run Run the data visualization
--help Print this help message
The graphed data will show in a local browser and look similar to:
After cloning this project, first:
- Activate the Python virtual environment
$ source ./venv/bin/activate
- Install the required dependencies:
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
To add Python packages to the Lambda function layer (a layer is required to add additional Pyhon packages that aren't natively available):
$ pip3 install pip Cython PyGithub requests boto3 --upgrade --target ./lambda/layer
At this point you can now synthesize the CloudFormation template for this code.
$ cdk synth
Other useful CDK commands:
To add additional dependencies, for example other CDK libraries, just add
them to your setup.py file and rerun the pip install -r requirements.txt
command.
cdk ls list all stacks in the appcdk synth emits the synthesized CloudFormation templatecdk deploy deploy this stack to your default AWS account/regioncdk diff compare deployed stack with current statecdk docs open CDK documentation
To dploy the stack, run the following command:
$ cdk deploy
To clean up the stack, run the following command:
$ cdk destroy
In this example:
- We know the Lambda function name is "GitHubRepoStatsFunction"
- The region is "eu-west-1"
To run the Lambda function (synchronously), use the following command:
aws lambda invoke --function-name GithubStatsFunction \
--region eu-west-1 \
--cli-binary-format raw-in-base64-out \
--payload '{"key": "test"}' /dev/stdout
This should print out to standard output:
{
"statusCode": 200, "body": "\"Stats updated successfully.\""
}
{
"StatusCode": 200,"ExecutedVersion": "$LATEST"
}
If you want to test the Lambda function asynchronously, use the following command:
aws lambda invoke --function-name GithubStatsFunction \
--region eu-west-1 \
--invocation-type Event \
--cli-binary-format raw-in-base64-out \
--payload '{"key": "test"}' /dev/stdout
A successful response will look like this:
{
"StatusCode": 202
}