Welcome to the Epoch of Reionization repository. This project leverages advanced Bayesian Convolutional Neural Networks (BCNNs) to identify and segment high-probability mass regions within large-scale galactic halo datasets. Developed to process astronomical simulation data with rigorous uncertainty quantification, this repository provides a scalable and robust framework for researchers studying cosmic structures.
Understanding the large-scale structure of the universe often requires precise segmentation of galactic halos from raw simulation data. This repository implements a Bayesian convolutional architecture that not only performs segmentation but also integrates uncertainty quantification—a crucial feature when dealing with the inherent noise and sparsity of cosmological data.
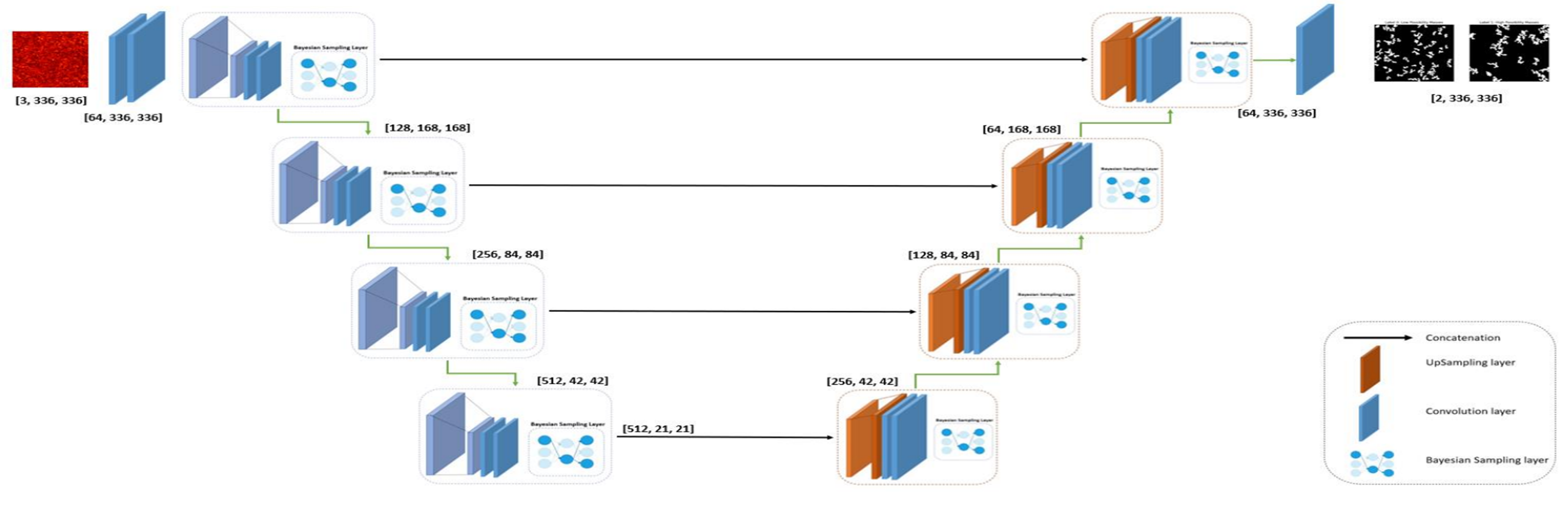
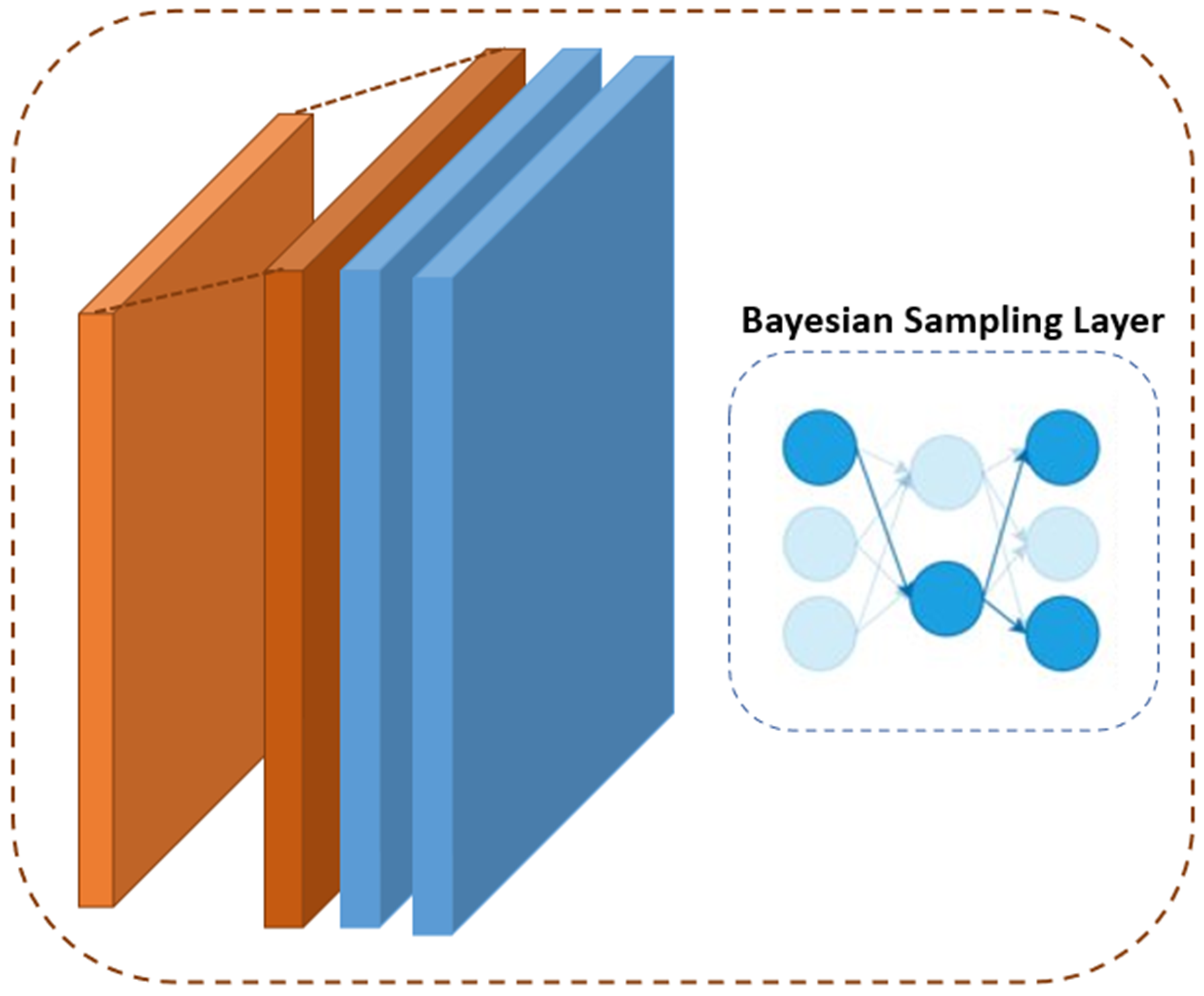
The diagram above illustrates the BCNN architecture used in this project. The network progressively downsamples and encodes the spatial information of the input map, passing through Bayesian sampling layers to capture probabilistic distributions of mass regions. Each layer of the network is carefully designed for optimal information retention and dimensional reduction, ultimately producing segmentation maps with pixel-wise uncertainty estimates.
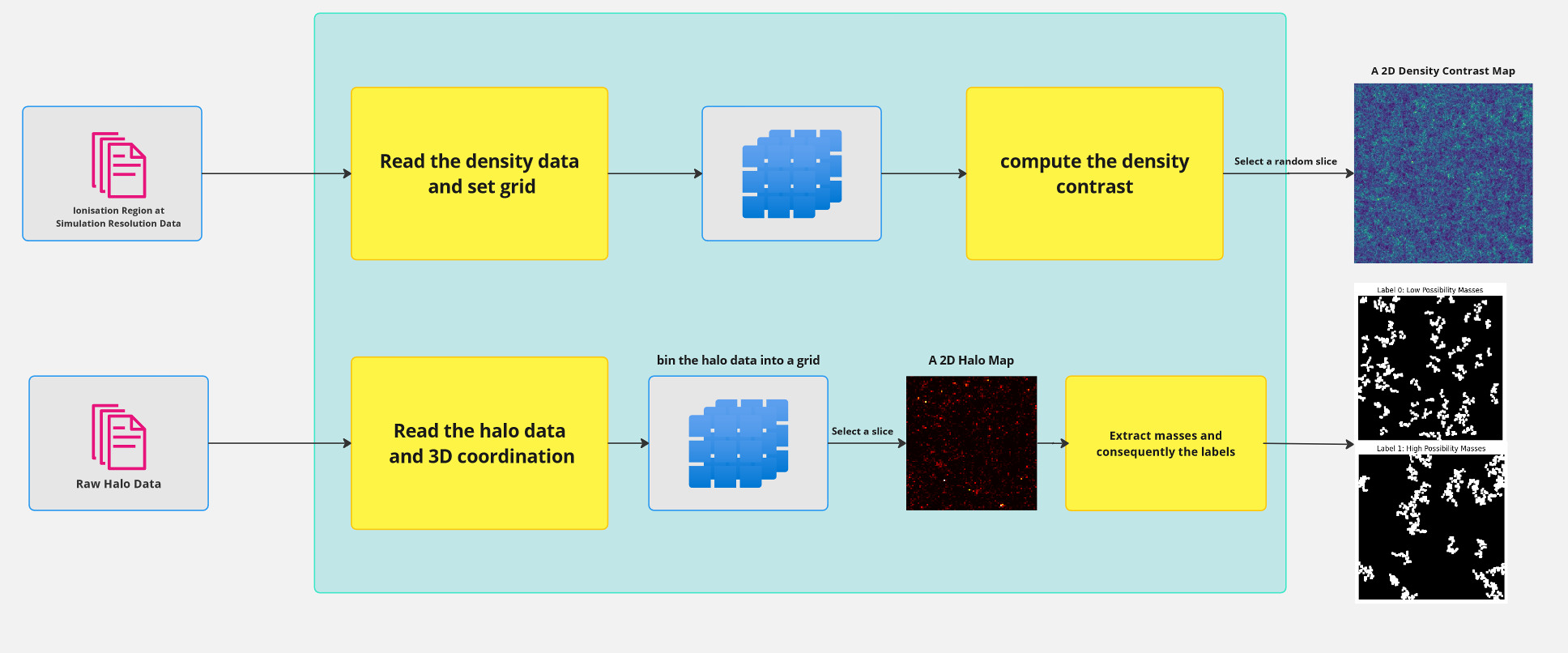
The dataset preparation pipeline involves:
- Density Contrast Calculation: Computes density contrast maps from raw ionisation data.
- Halo Data Binning: Halo data are binned into a 2D grid to generate corresponding 2D halo maps.
- Labelling: The maps are labelled to indicate high and low mass probability regions for training and validation.
The following flowchart provides an overview of this preprocessing sequence:
This workflow efficiently processes high-dimensional data to generate both density and halo maps, crucial for training the BCNN to distinguish between regions of high and low mass concentrations.
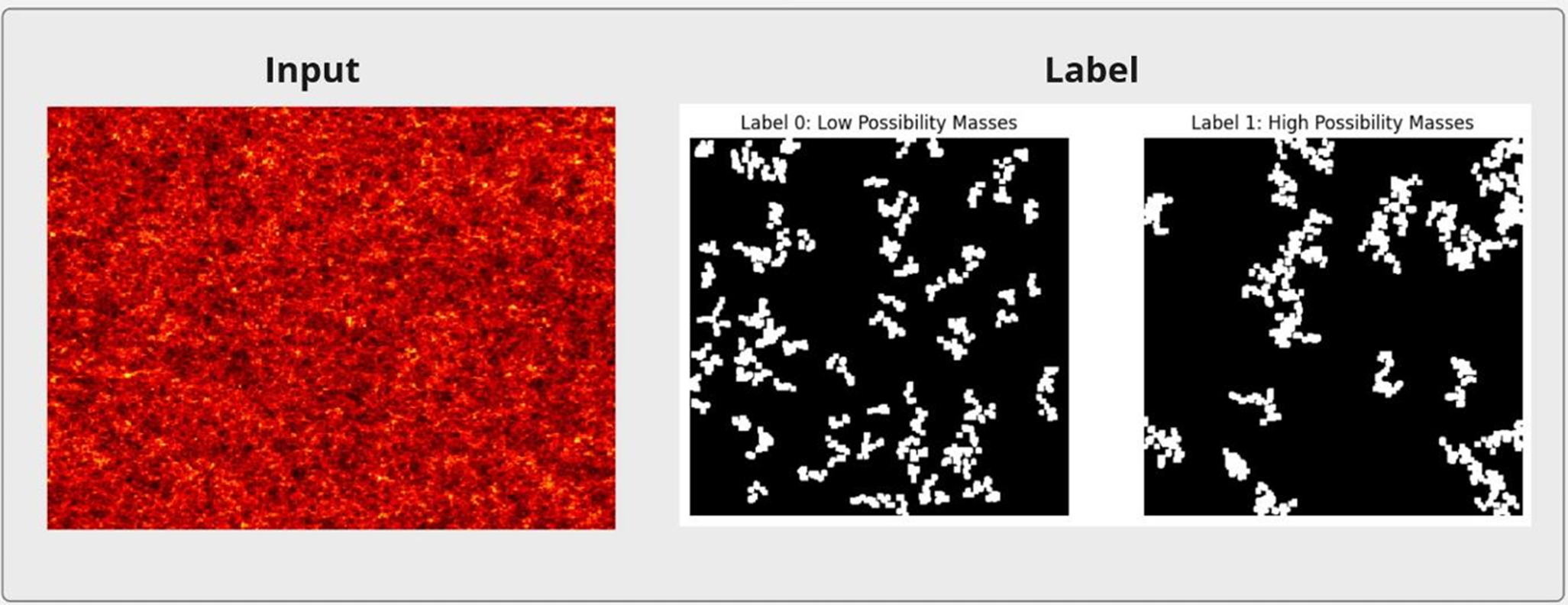
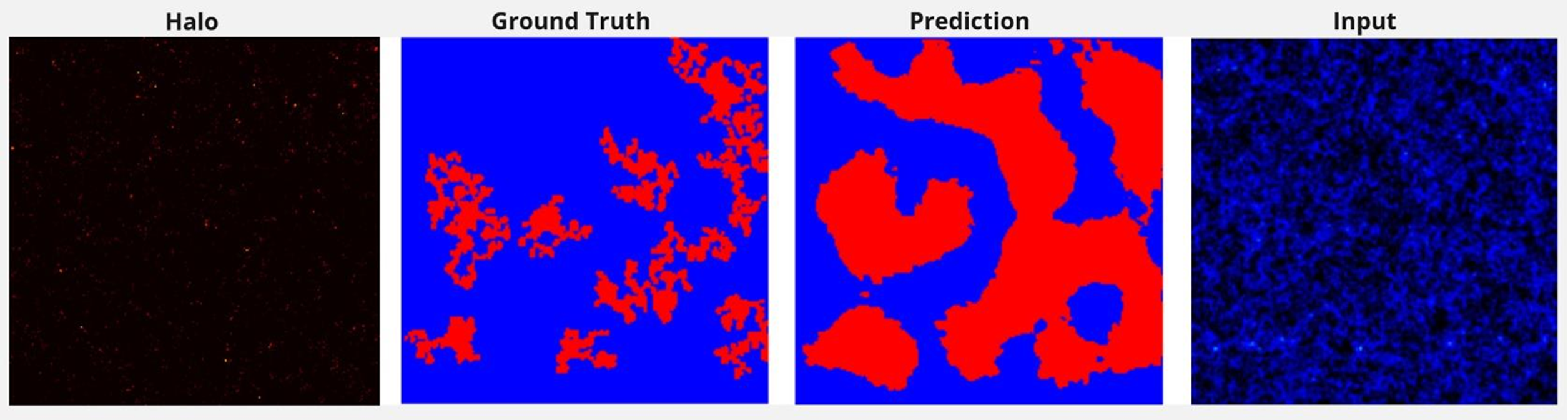
The input data consists of 2D halo and density contrast maps, while labels correspond to binary segmentation maps highlighting regions with high and low mass probability. Below is a sample input alongside ground truth and model-predicted outputs:
These input-label pairs provide a comprehensive training set that enables the network to generalise well on unseen regions of the simulation data, supporting accurate predictions in high-dimensional galactic datasets.
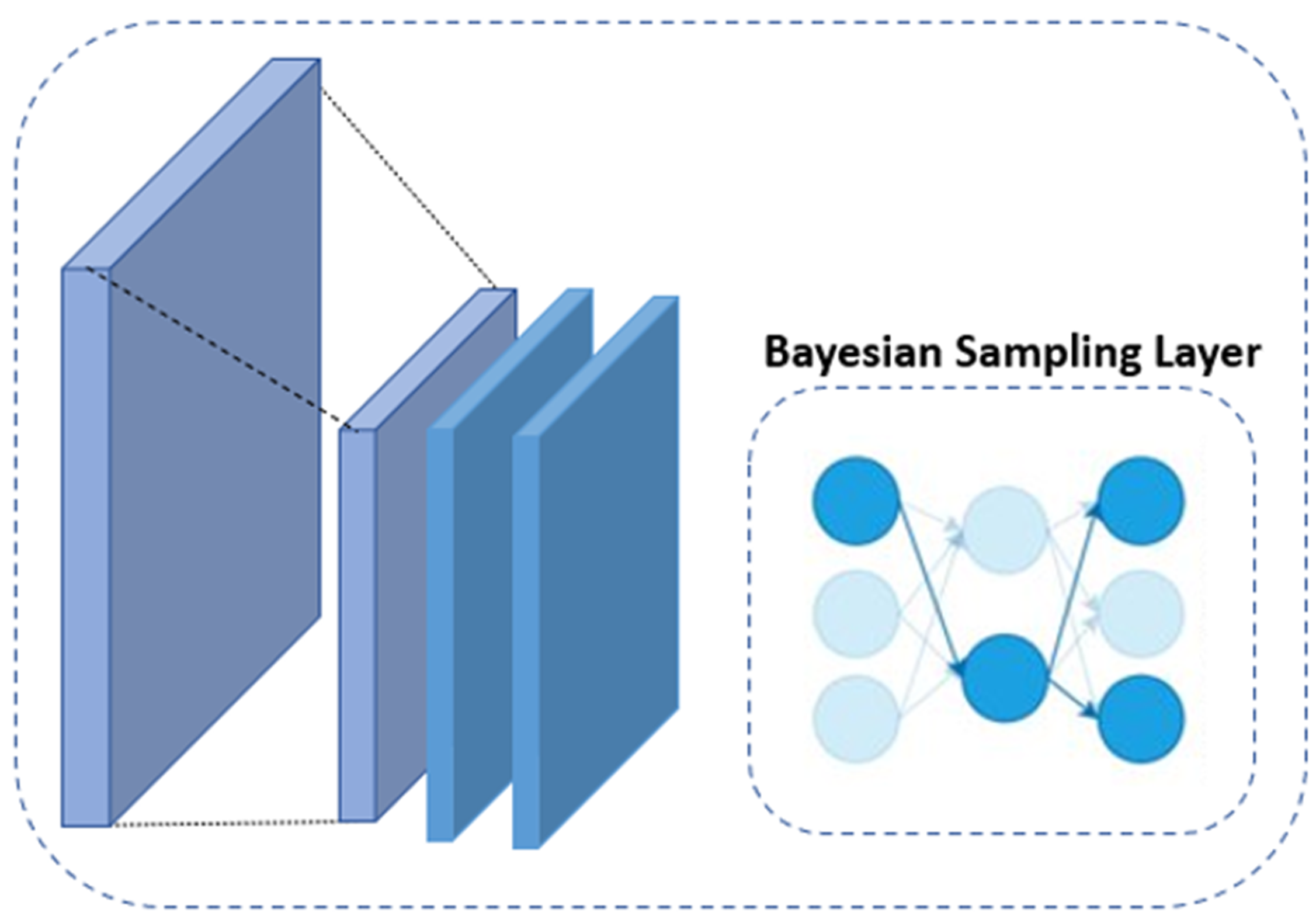
To address uncertainties in predictions, our BCNN integrates Bayesian Sampling Layers. These layers provide an interpretable framework to estimate the probability of high-mass regions, enhancing the reliability of segmentation outcomes. Below is an illustrative breakdown of the Bayesian Sampling mechanism within the network:
By incorporating these layers, the model captures a spectrum of possible outcomes, giving users confidence intervals for the segmented mass regions—ideal for scientific applications where precision and confidence are paramount.
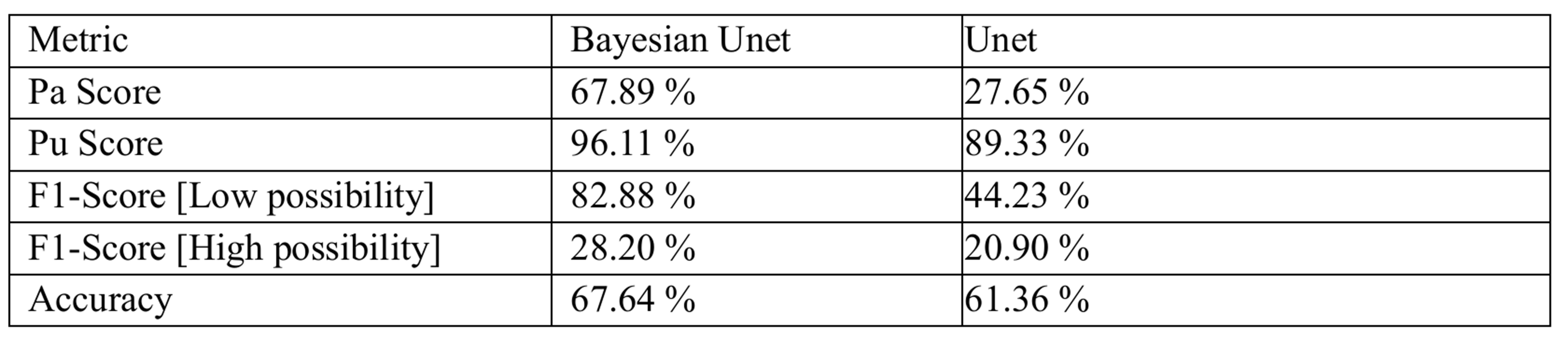
The network's predictive performance demonstrates promising results, achieving effective segmentation with minimal false positives. The following figure presents the Ground Truth versus Predictions, showcasing the model's accuracy and robustness across a random slice from the dataset:
The output predictions closely match the ground truth labels, verifying the efficacy of the Bayesian layers in mitigating uncertainties in cosmological datasets.
- Clone the Repository:
git clone https://github.com/your-repo-path/galactic-halo-segmentation.git