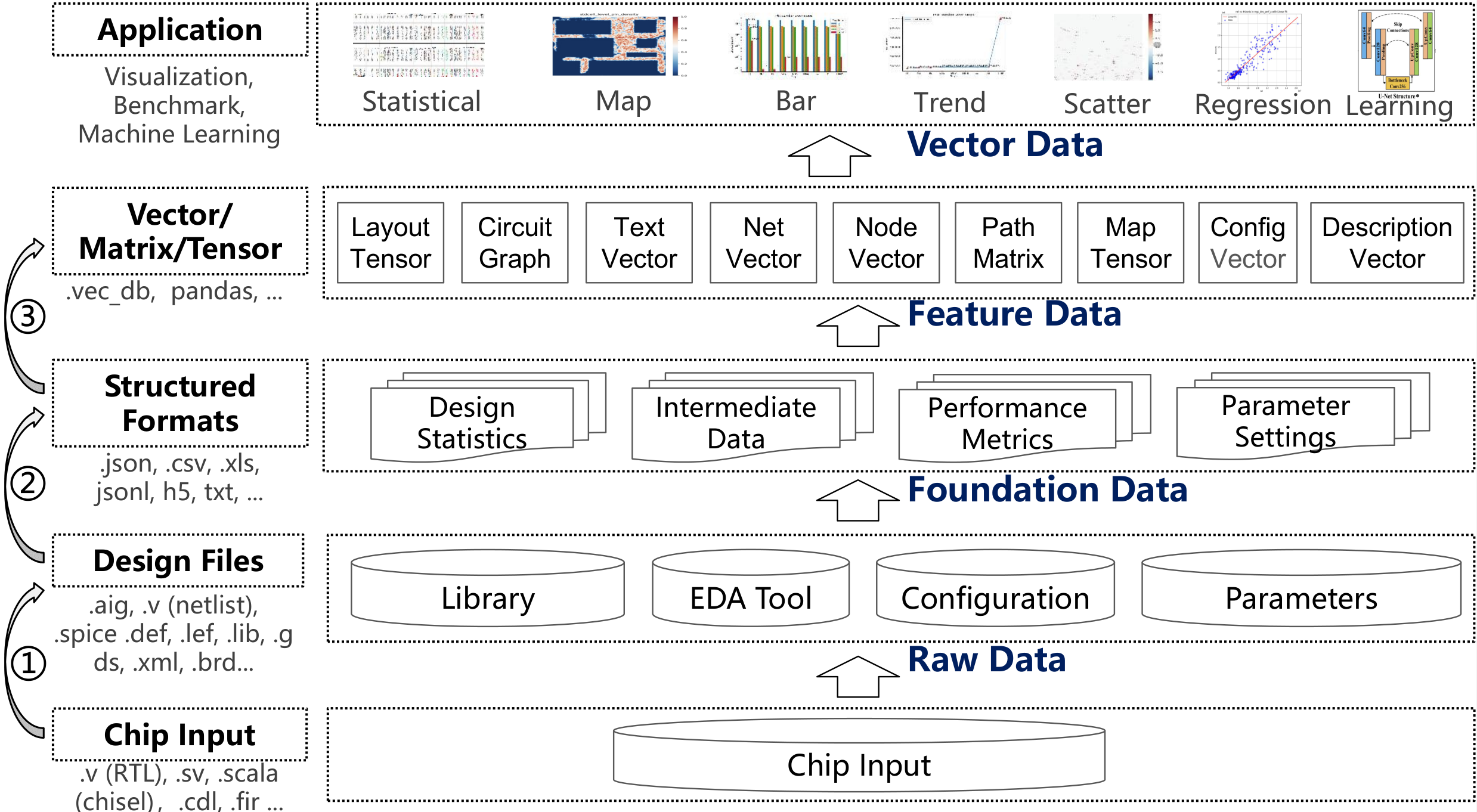
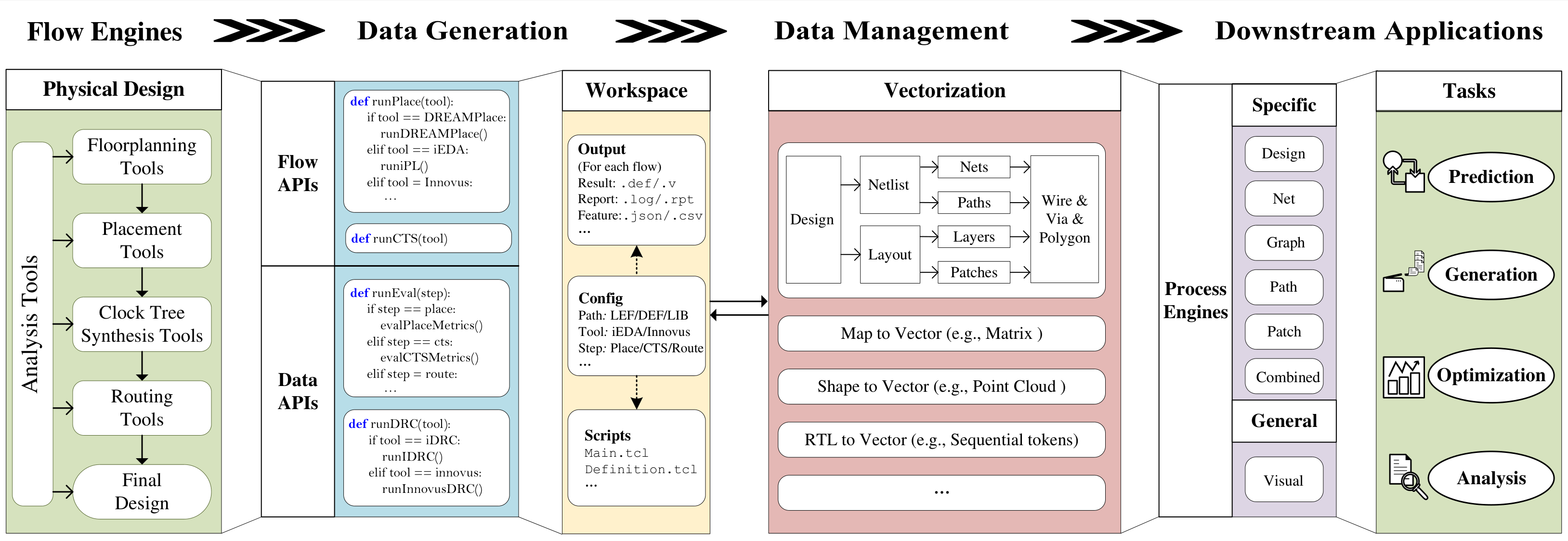
AiEDA is an open-source AI-native Electronic Design Automation (EDA) library that revolutionizes chip design workflows by introducing a unified design-to-vector methodology. Built on the open-source EDA infrastructures, it transforms diverse chip design data into standardized multi-level vector representations through modular engine integration, comprehensive data extraction frameworks, and hierarchical data management. AiEDA bridges traditional EDA tools with modern AI/ML techniques by providing complete physical design flows, programmatic data extraction capabilities, and standardized Python interfaces, establishing an AI-aided design (AAD) paradigm that enables seamless integration between EDA datasets and AI frameworks.
AiEDA adopts a layered modular architecture that seamlessly integrates traditional EDA tools with modern AI/ML technologies, providing a complete workflow from design input to result analysis. The overall architecture consists of seven core layers, each responsible for specific functional domains, collectively building a complete Design-to-Vector methodology.
AiEDA Architecture
├── AI Layer (aieda.ai) # AI model training and inference core layer
│ ├── Net Wirelength Prediction # TabNet-based wirelength prediction model
│ ├── Graph Delay Prediction # Graph delay prediction model
│ ├── Design Space Exploration # Automated design space exploration framework
│ ├── Patch Congestion Prediction # Placement congestion prediction model
│ └── Model Training Infrastructure# ML model training and inference infrastructure
├── Analysis Layer (aieda.analysis) # Multi-dimensional analysis tools layer
│ ├── Design-level Analysis # Design-level statistics and analysis
│ ├── Net Analysis # Net-level performance and distribution analysis
│ ├── Path Analysis # Timing path analysis and optimization
│ └── Patch Analysis # Grid feature and density analysis
├── EDA Integration Layer (aieda.eda)# EDA tools integration layer
│ ├── iEDA Tool Wrappers # 11+ open-source EDA tool wrappers
│ ├── Flow Management # Automated EDA flow management
│ └── Data Extraction # Design data extraction and transformation
├── Data Management Layer (aieda.data)# Data management and feature engineering layer
│ ├── Database Structures # EDA design data models
│ ├── Vector Generation # Design feature vectorization engine
│ ├── Feature Engineering # Feature extraction and engineering
│ └── Data I/O Utilities # Data reading/writing and conversion tools
├── Flow Management (aieda.flows) # Workflow management layer
│ ├── EDA Flow Orchestration # EDA toolchain orchestration
│ ├── Data Generation Workflows # Automated dataset generation workflows
│ └── Flow Configuration # Flow configuration and execution engine
├── Workspace Management (aieda.workspace)# Workspace management
│ ├── Project Organization # Project structure and file management
│ ├── Configuration Management # Design and tool configuration management
│ └── Path Management # File path and resource management
├── Utilities (aieda.utility) # Common utility library
│ ├── Logging System # Structured logging system
│ ├── JSON Parsing # Configuration file parser
│ └── Permission Management # File permission management
├── GUI Interface (aieda.gui) # Graphical user interface
│ ├── Layout Visualization # Chip layout visualization
│ ├── Data Visualization # Analysis result visualization
│ └── Workspace Management UI # Workspace management interface
└── Report Generation (aieda.report) # Report generation system
├── Data-driven Reports # Data-driven report generation
└── Visual Summary # Visual report summary
Key Components:
- Net Wirelength Prediction: TabNet-based models that accurately predict wire lengths between cells, enabling early-stage optimization of placement results.
- Graph Delay Prediction: Graph neural network models for predicting signal propagation delays across complex net structures and paths.
- Patch Congestion Prediction: Deep learning models that forecast potential congestion hotspots in the chip layout, allowing proactive design adjustments.
- Design Space Exploration (DSE): Automated frameworks for exploring vast design parameter spaces to identify optimal configurations efficiently.
- Model Training Infrastructure: Comprehensive support for training, validating, and deploying various ML models, with built-in utilities for data preprocessing, model evaluation, and hyperparameter tuning.
Key Submodules:
graph_delay_predict: Graph neural network implementations for delay predictionnet_wirelength_predict: TabNet models for wirelength predictionpatch_congestion_predict: CNN-based models for congestion predictiondesign_parameter_optimization: Algorithms for automated parameter tuning
Key Components:
- Design Analysis: Statistical evaluation of overall design characteristics, including cell type distribution, core area usage, pin distribution patterns, and design rule compliance metrics.
- Net Analysis: Detailed examination of net structures, wire distributions, net length statistics, and their correlation with performance metrics.
- Path Analysis: Critical path identification, delay analysis, stage composition analysis, and timing constraint verification.
- Patch Analysis: Grid-based analysis of local design features, including wire density, cell density, congestion patterns, and feature correlation heatmaps.
Key Classes:
DesignAnalyzer: Comprehensive design-level analysis engineNetAnalyzer: Specialized for net structure and distribution analysisPathAnalyzer: Focused on timing path evaluation and optimizationPatchAnalyzer: Grid-based local feature and density analysis
Supported EDA Tools:
- iEDA Tool Integration: Wrappers for 11+ EDA tools
- Placement (iPL): standard cell placement
- Clock Tree Synthesis (iCTS): Clock distribution network design and optimization
- Routing (iRT): Global and detailed routing
- Static Timing Analysis (iSTA): Comprehensive timing verification and analysis
- Design Rule Checking (iDRC): Verification of manufacturing design rules
- Power Network Synthesis (iPDN): Power grid design and optimization
- And more ...
- More EDA tool wrappers will continue to be open source
Key Features:
- Standardized Python interfaces for all EDA tools
- Automatic configuration management
- Seamless toolchain integration
- Real-time progress monitoring
- Result extraction and formatting
Key Components:
- Database Structures: Comprehensive data models that represent EDA design features, analysis results, and optimization parameters in a structured format.
- Vector Generation: Advanced engines for extracting and transforming design features into numerical vectors suitable for machine learning algorithms.
- Feature Engineering: Tools for creating, selecting, and transforming features to improve model performance and interpretability.
- Data I/O Utilities: Robust handlers for reading and writing various EDA file formats, configuration files, and analysis results.
- Parameters Management: Systems for defining, validating, and managing EDA tool parameters across different design stages.
Key Submodules:
database: Data models and storage mechanismsio: File format handlers and convertersvectors: Feature extraction and vectorization engines
Key Components:
- iEDA Flow Management: Frameworks for defining, configuring, and executing complete EDA toolchains, from design input to final verification.
- Data Generation Workflows: Automated pipelines for generating large datasets from design variations, supporting ML model training and validation.
- Flow Configuration: Flexible systems for defining custom flow sequences, dependencies, and parameter passing between stages.
- Flow Execution Engine: Robust infrastructure for executing flows with error handling, progress tracking, and result collection.
Key Classes:
DbFlow: Base class for all database-backed flowsRunIEDA: Flow for executing iEDA toolchainsDataGeneration: Flow for automated dataset creation
Key Components:
- Project Organization: Frameworks for creating and managing standardized project structures, ensuring consistency across different designs and users.
- Configuration Management: Systems for defining, storing, and accessing project-specific and tool-specific configuration settings.
- Path Management: Utilities for managing file paths, resource locations, and output directories in a consistent manner.
- Workspace Initialization: Tools for setting up new workspaces with predefined structures and default configurations.
Key Classes:
Workspace: Core class for workspace creation and managementConfigs: Configuration management systemPathsTable: Path and resource management utilities
Key Components:
- Logging System: Comprehensive logging infrastructure with configurable verbosity levels, log rotation, and formatted output.
- JSON Parsing: Robust parsers for configuration files and data exchange formats, with validation and error handling.
- Permission Management: Utilities for managing file and folder permissions, ensuring secure access to project resources.
- File System Operations: Helper functions for common file and directory operations, such as creation, deletion, and copying.
Key Classes:
Logger: Custom logger with formatted output and verbosity controlJsonParser: Enhanced JSON handling with validation capabilitiesFolderPermission: Utilities for managing file system permissions
Key Components:
- Layout Visualization: Interactive displays of chip layouts, including cells, nets, paths, and other design elements with zoom and pan capabilities.
- Data Visualization: Charts, graphs, and heatmaps for visualizing analysis results, performance metrics, and optimization trends.
- Workspace Management UI: Interfaces for creating, configuring, and managing design workspaces and projects.
- Chip Visualization: Detailed views of chip components, layers, and physical characteristics.
- Patch Visualization: Grid-based visualization of local design features and density maps.
Key Classes:
LayoutViewer: Interactive layout visualization componentChipViewer: Detailed chip structure visualizationWorkspaceManagerUI: Workspace management interfacePatchesViewer: Grid-based patch visualization
Key Components:
- Data-driven Reports: Automated generation of comprehensive reports with embedded visualizations, statistics, and insights.
- Visual Summary: Creation of concise visual summaries that highlight key findings and recommendations.
- Customizable Templates: Support for user-defined report templates to meet specific documentation requirements.
- Export Formats: Generation of reports in various formats for easy sharing and integration with other tools.
Key Classes:
ReportGenerator: Core engine for creating data-driven reportsReportModule: Base class for specialized report componentsVisualSummary: Utilities for creating visual report elements
The AiEDA data flow follows this pattern:
- Design Input → Workspace creation with design files
- EDA Processing → EDA tools process the design through various stages
- Data Extraction → Feature extraction and vectorization from EDA results
- AI Analysis → ML models analyze extracted features
- Optimization → AI-guided parameter optimization and design improvements
- Validation → Results validation and iteration
Design Files → Workspace → EDA Tools → Feature Extraction → AI Models → Analyse → Results
↑ ↓
└──── Feedback Loop (Optimization) ─────┘
-
Clone the repository with submodules:
git clone <repository-url> cd AiEDA git submodule update --init --recursive
-
Install Python Dependencies and AiEDA library:
We support multiple Python package managers (conda, uv, etc.). We recommend UV for its efficiency.
# Use the provided build script (recommended) # The script builds the AiEDA library by default ./build.sh # You can also skip the AiEDA library build using --skip-build # (recommended for development) ./build.sh --skip-build # Or install manually # Install UV pip install uv # Create and activate virtual environment uv venv source .venv/bin/activate # Install aieda using one of the following options: # Option 1: Development mode (recommended for development) uv pip install -e . # Option 2: Regular installation uv build uv pip install dist/aieda-0.1.0-py3-none-any.whl
-
Compile iEDA:
mkdir build cd build cmake .. make -j32 ieda_pyNote:
- When compiling iEDA, you need to switch to the AiEDA directory (i.e., ~/AiEDA/), not the iEDA directory (i.e., ~/AiEDA/aieda/third_party/iEDA/).
- Building ieda_py requires sudo privileges to download additional system libraries.
-
Run Tests:
uv run python test/test_sky130_gcd.py
Docker provides a containerized environment with all dependencies pre-configured, including Python/C++ dependencies, AiEDA library, and source code.
- Docker installed on your system
- At least 20GB of available disk space (this will be optimized in future versions)
-
Clone the repository with submodules:
git clone <repository-url> cd AiEDA git submodule update --init --recursive
-
Build the Docker image:
docker build -t aieda:latest . -
Run the container:
# Test the installation docker run --rm aieda:latest python3 test/test_sky130_gcd.py # Run in detached mode for interactive use docker run -dit --name myaieda aieda:latest bash # Enter the running container docker exec -it myaieda bash
Note: For detailed Docker instructions, refer to the build script and Dockerfile in the repository.
# Test the fullflow (Recommended)
python test/test_sky130_gcd.py
# or
uv run python test/test_sky130_gcd.py
# Test physical design flow using iEDA
python test/test_ieda_flows.py
# or
uv run python test/test_ieda_flows.py
# Test vector generation
python test/test_ieda_vectors.py
# or
uv run python test/test_ieda_vectors.pyimport aieda
from aieda.workspace import workspace_create
from aieda.flows import RunIEDA, DataGeneration
from aieda.analysis import CellTypeAnalyzer
from aieda.ai import TabNetTrainer
# Create workspace
workspace = workspace_create(directory="./my_design", design="gcd")
# Run EDA flow
run_ieda = RunIEDA(workspace)
run_ieda.run_flow()
# Generate training data
data_gen = DataGeneration(workspace)
data_gen.generate_vectors()
# Perform analysis
analyzer = CellTypeAnalyzer()
analyzer.analyze()
# Train AI model
trainer = TabNetTrainer()
trainer.train()- AI-Native Design: Built from ground up with AI/ML integration
- Comprehensive EDA Integration: Support for 11+ EDA tools via iEDA
- Automated Workflows: End-to-end automation from design to optimization
- Extensible Architecture: Modular design for easy extension and customization
- Production Ready: Proven with 4+ successful tape-outs
- Open Source: Fully open-source with active community support
As a key outcome of the AiEDA library, we are proud to introduce iDATA, a large-scale, open-source dataset specifically designed to facilitate AI-aided design (AAD) research. The iDATA dataset is generated using AiEDA's design-to-vector methodology and data management capabilities, providing structured, vectorized data for a variety of AI-EDA tasks.
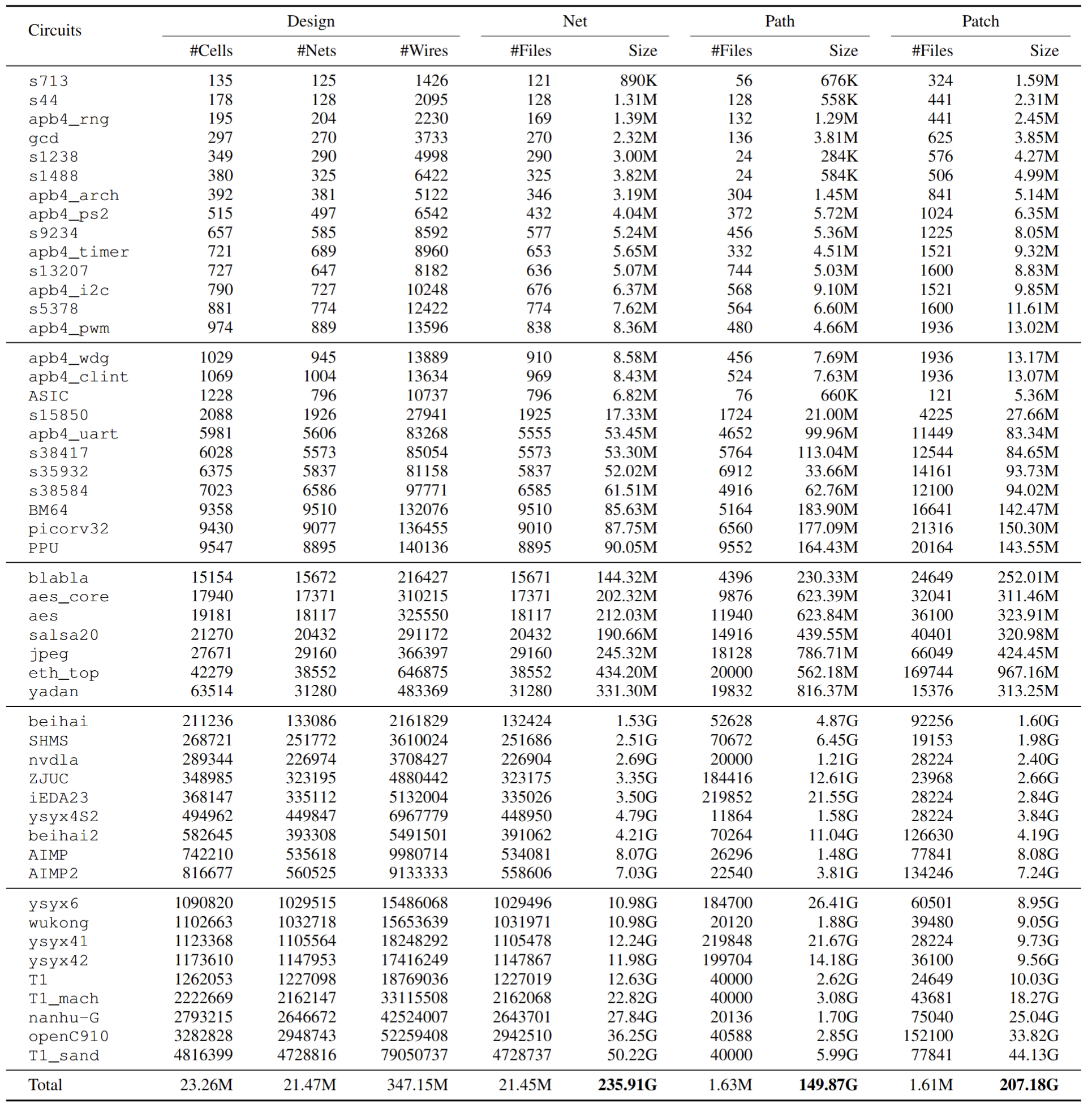
- Data Source: The iDATA dataset is derived from 50 real-world chip designs, covering a diverse range of applications including digital signal/image processors (DSP/ISP), peripheral/interface circuits, functional modules, memories, CPUs, GPUs, and SoCs. These designs are sourced from open repositories such as OSCPU, OSCC, OpenLane, ISCAS89, and CHIPS Alliance, as well as internal projects. All designs are synthesized using 28nm technology and processed through complete physical design flows using Innovus, with data extraction performed via iEDA tools.
- Data Scale and Statistics: The complete iDATA dataset amounts to 600 GB of structured data (excluding original raw design files). It includes vectorized representations at multiple levels: design-level, net-level, graph-level, path-level, and patch-level. The dataset captures a wide spectrum of design complexities, with cell counts ranging from 135 to 4,816,399, net counts from 125 to 4,728,816, and wire counts from 1,426 to 79,050,737. Detailed statistics are summarized in the table below.
- Purpose and Availability: iDATA serves as a ready-to-use resource for researchers to train and validate AI models for tasks such as prediction, generation, and optimization in EDA workflows. The full dataset will be open-sourced as soon as possible, providing a foundation for future AI-EDA research.
- Accessible Data Samples: To provide a concrete understanding of our data structure, we have included vectorized data samples in our GitHub repository. This data, located at https://github.com/OSCC-Project/AiEDA/tree/master/example/sky130_gcd/output/iEDA/, was generated by running the open-source iEDA toolchain on the gcd netlist. Regarding the full iDATA dataset, its release is a more complex process due to its large size and the need for data anonymization.
- AiEDA2.0: An Open-source AI-Aided Design (AAD) Library for Design-to-Vector, ISEDA, 2025
- iEDA: An Open-source infrastructure of EDA, ASPDAC, 2024
- iPD: An Open-source intelligent Physical Design Tool Chain, ASPDAC, 2024
We welcome contributions! Please see our contributing guidelines and feel free to submit issues and pull requests.
This project is open-source. Please refer to the LICENSE file for details.
For questions and support, please visit our documentation (https://ieda.oscc.cc/en/aieda/library/) and the deepwiki (https://deepwiki.com/OSCC-Project/AiEDA) or contact us (https://ieda.oscc.cc/en/publicity/connection.html)