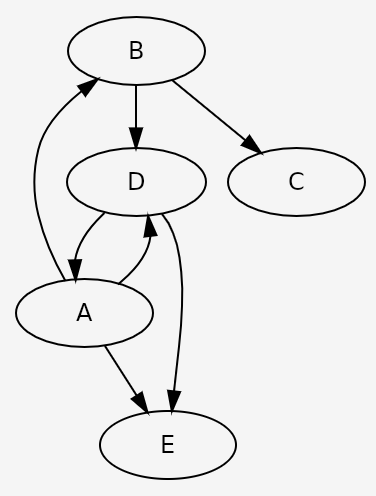
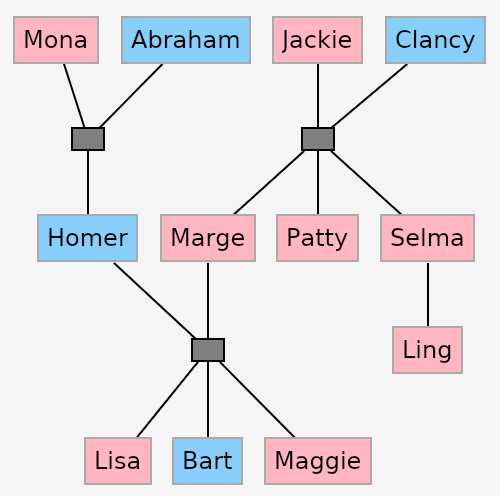
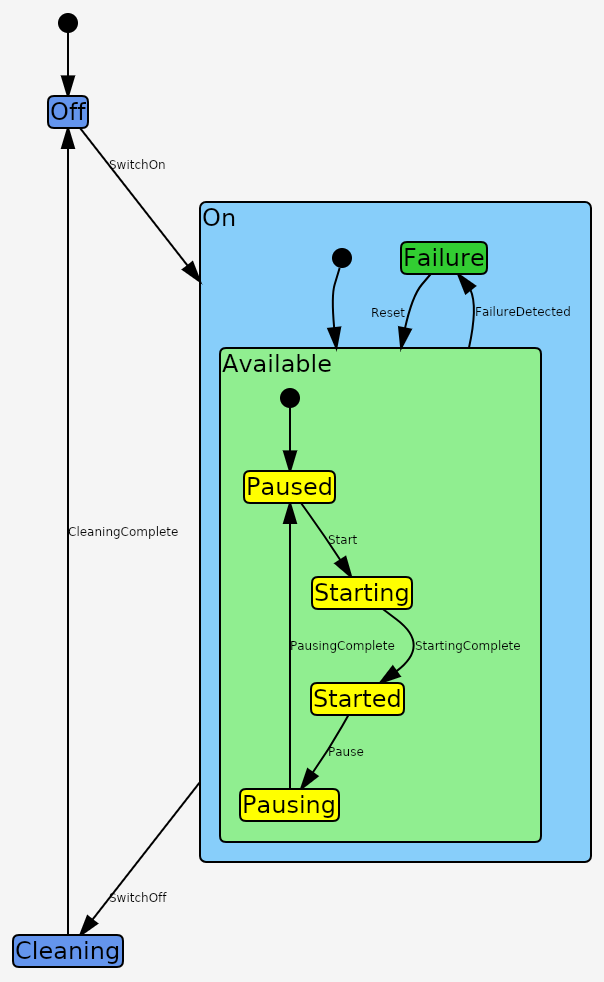
A graph layout panel for AvaloniaUI
Each individual graph is displayed through the GraphPanel control included in the assembly
<Window xmlns:agc="clr-namespace:AvaloniaGraphControl;assembly=AvaloniaGraphControl">
<agc:GraphPanel Graph="{Binding MyGraph}" LayoutMethod="SugiyamaScheme" />
</Window>The layout is internally implemented with MSAGL (Microsoft Automatic Graph Layout).
The following layout methods are available in MSAGL and can be set in the GraphPanel control independently of the graph model:
- SugiyamaScheme
- MDS
- Ranking
- IncrementalLayout
The GraphPanel control and the MSAGL assemblies are bundled in a nuget package. The existing MSAGL nuget packages are dedicated to the .NET Framework and do not include any netstandard assembly.
The GraphPanel control leverages the MVVM pattern used by AvaloniaUI. Each node of the graph view can be customized according to the underlying view model in the graph definition.
<Window xmlns:agc="clr-namespace:AvaloniaGraphControl;assembly=AvaloniaGraphControl">
<agc:GraphPanel Graph="{Binding MyGraph}" LayoutMethod="SugiyamaScheme" />
<agc:GraphPanel.DataTemplates>
<DataTemplate DataType="{x:Type local:StandardItem}">
<agc:TextSticker Text="{Binding Name}" Shape="Ellipse" Padding="30,10" />
</DataTemplate>
<DataTemplate DataType="{x:Type local:InteractiveItem}">
<ToggleButton Content="{Binding Name}" Padding="20,5" />
</DataTemplate>
</agc:GraphPanel.DataTemplates>
</agc:GraphPanel>
</Window>As shown in the demo, this graph panel can be used in cross-platform AvaloniaUI applications. It was successfully tested on Linux Desktop, Windows Desktop, Android and Browser (web assembly) environments.
public static Graph MyGraph
{
get
{
var graph = new Graph();
graph.Edges.Add(new Edge("A", "B"));
graph.Edges.Add(new Edge("A", "D"));
graph.Edges.Add(new Edge("A", "E"));
graph.Edges.Add(new Edge("B", "C"));
graph.Edges.Add(new Edge("B", "D"));
graph.Edges.Add(new Edge("D", "A"));
graph.Edges.Add(new Edge("D", "E"));
return graph;
}
}