okd-upi-install
This repository provides the configurations in order to install OKD through KVM (libvirt).
Prerequisites - Variables
In order to perform Day2 specific actions regarding authentication and persistent storage for the internal image register, it will therefore be necessary to inject environment variables. It's best to reference all the variables so you don't forget anything.
Here is below the exhaustive list:
CLUSTER_NAME: name of the cluster [caas]HTPASSWD_SECRET: htpasswd secret [base64]HTPASSWD_SECRET_NAME: name of the secretREGISTRY_PV_NAME: name of the persistent volumeNFS_MONITORING_SIZE: size of the storage used by the monitoring stack [XXGi]STORAGE_CLASS: storage class name
OpenShift 4 Install - User Provisioned Infrastructure (UPI)
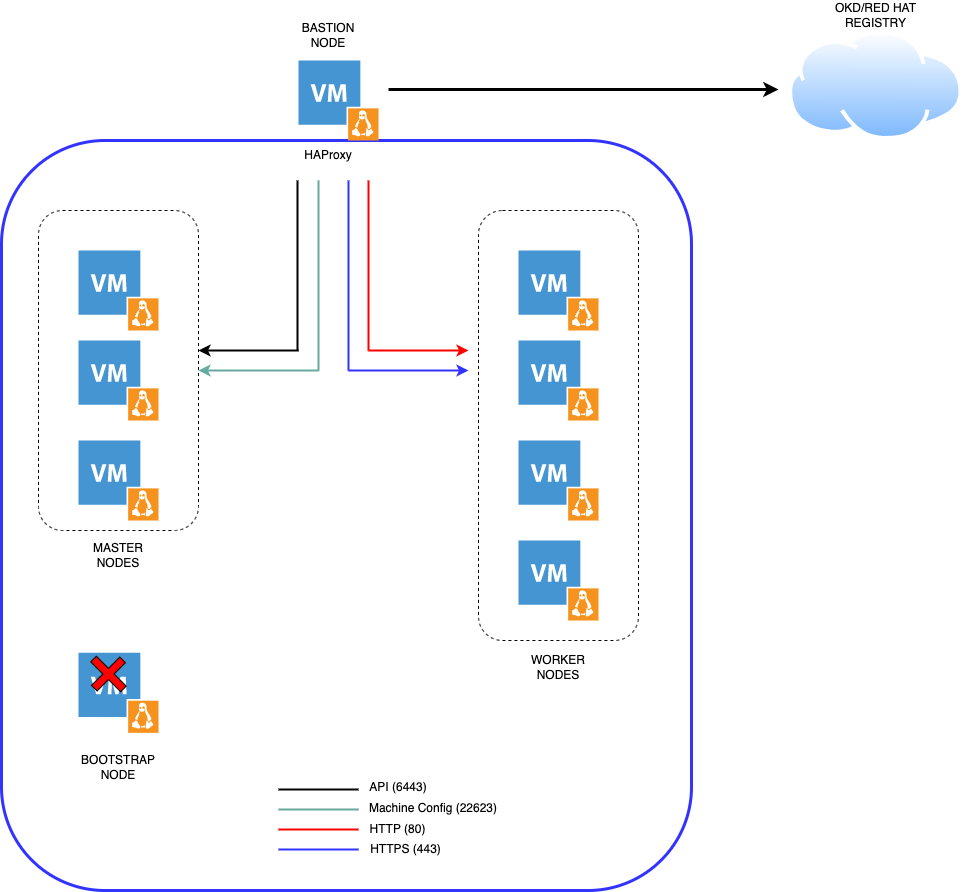
Architecture diagram
Information
- Cluster name: caas
- Base Domain: eazytraining.lab
OKD VMs
| VM | CPU | Memory | OS | IP Address | Disk (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bastion | 4 | 4 | Alma Linux 8.7 | 192.168.110.9 | 450 |
| Master-[1-3] | 6 | 10 | Fedora CoreOS 37 | 192.168.110.[111-113] | 60 |
| Worker-[1-4] | 8 | 12 | Fedora CoreOS 37 | 192.168.110.[114-117] | 60 |
| Bootstrap | 4 | 8 | Fedora CoreOS 37 | 192.168.110.110 | 40 |
Download Software
-
Download Alma Linux 8.7 for installing the bastion node
-
Download the following files
-
Login to Red Hat OpenShift Cluster Manager to download the Pull Secret
-
Select 'Create Cluster' from the 'Clusters' navigation menu
-
Select 'RedHat OpenShift Container Platform
-
Select 'Run on Bare Metal'
-
Download the Pull Secret
Prepare the environment for installing OKD 4.10
In KVM Hypervisor
All the below commands should be performed by using the root account.
- Install the KVM Hypervisor
Install all the dependencies
dnf install qemu-kvm libvirt libvirt-python3 jq libguestfs-tools virt-install vim git curl wget firewalld NetworkManager-tui -yEnable and start the service
systemctl enable libvirtd && systemctl start libvirtd && systemctl status libvirtd
systemctl enable firewalld && systemctl start firewalld && systemctl status firewalld- Create the ocpnet network in KVM
mkdir ~/ocp && cd ocp
cat <<EOF | tee ocpnet.xml
<network>
<name>ocpnet</name>
<forward mode='nat' dev='enp4s0'/>
<bridge name='ocpnet'/>
<ip address='192.168.110.1' netmask='255.255.255.0'>
</ip>
</network>
EOFvirsh net-define ocpnet.xml
virsh net-list --all
virsh net-autostart ocpnet
virsh net-start ocpnet
virsh net-list --all
virsh net-destroy default
virsh net-undefine default
systemctl restart libvirtd- Configure the network interfaces and the firewall
nmcli connection modify ocpnet connection.zone internal
nmcli connection modify 'System enp4s0' connection.zone public
firewall-cmd --get-active-zones
firewall-cmd --zone=internal --add-masquerade --permanent
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-masquerade --permanent
firewall-cmd --reload
firewall-cmd --list-all --zone=internal
firewall-cmd --list-all --zone=public- Download the Alma Linux 8.7 iso image to the dedicated pool on the host server.
mkdir -p /var/lib/libvirt/pool/ssd/iso && cd /var/lib/libvirt/pool/ssd/iso
wget http://mirror.almalinux.ikoula.com/8.7/isos/x86_64/AlmaLinux-8.7-x86_64-minimal.iso- Create the Bastion node server and install Alma Linux 8.7
Clone the repository
cd ~ && git clone https://github.com/ObieBent/okd-upi-install.gitCopy the required Kickstart file to the / directory
cp ~/okd-upi-install/ks.cfg /To create an encrypted password, you can use python:
python3 -c 'import crypt,getpass;pw=getpass.getpass();print(crypt.crypt(pw) if (pw==getpass.getpass("Confirm: ")) else exit())'The encrypted password should be added in the kickstart file.
Install the Bastion server
sh ~/okd-upi-install/deployBastion.shProvide the basic server installation for the Bastion server
mkdir -p ~/ansible/{roles,playbook} && cd ~/ansible/rolesClone the basic-server and basic-user ansible role
git clone https://github.com/ObieBent/basic-server.git
git clone https://github.com/ObieBent/basic-user.gitInstall ansible
dnf install -y epel-release
dnf install -y ansibleConfirm ansible installation
ansible --versionDefine the ansible.cfg file
cat <<EOF | tee ~/ansible/ansible.cfg
[defaults]
inventory = hosts
roles_path = ./roles
gathering = smart
host_key_checking = False
[diff]
always = True
EOFDefine the hosts file
cat <<EOF | tee ~/ansible/hosts
[all]
bastion ansible_host=192.168.110.9
gitlab ansible_host=192.168.110.99
EOFDeploy the basic configuration to the Bastion server
cp manifests/basic-server.yaml ~/ansible/playbookModify the playbook
basic-server.yaml. Line 32 should contain the public ssh-key of the user that will have the sudo rights on the server
cd ~/ansible
ansible-playbook playbook/basic-server.yaml -l bastion -u root -k -v Configure Environmental Services
-
SSH to the Bastion server
-
Update the OS and install required dependencies
dnf update
dnf install -y bind bind-utils dhcp-server httpd haproxy nfs-utils chrony vim jq wget git- Download Client and Installer tools
mkdir -p ~/ocp && cd ocp
wget https://github.com/okd-project/okd/releases/download/4.10.0-0.okd-2022-07-09-073606/openshift-client-linux-4.10.0-0.okd-2022-07-09-073606.tar.gz -O openshift-client-linux.tar.gz
wget https://github.com/okd-project/okd/releases/download/4.10.0-0.okd-2022-07-09-073606/openshift-install-linux-4.10.0-0.okd-2022-07-09-073606.tar.gz -O openshift-install-linux.tar.gz- Extract Client and Installer tools and move them to /usr/local/bin
# Client tools
tar xvf openshift-client-linux.tar.gz
mv oc kubectl /usr/local/bin
# Installer
tar xvf openshift-install-linux.tar.gz
mv openshift-install /usr/local/bin- Confirm Client and Installer tools are working
kubectl version --client --short
oc version
openshift-install version- Download config files for each of the services
cd ~
git clone https://github.com/ObieBent/okd-upi-install.git- Setup the mirroring registry for OKD (Air-gapped installation)
mkdir -p /shares/registry/{auth,certs,data}Install podman and httpd-tools
dnf -y install podman httpd-tools skopeoPrepare the csr answers
cd /shares/registry
cat <<EOF | tee /shares/registry/csr-answers
[req]
default_bits = 4096
default_md = sha256
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
x509_extensions = v3_ca
prompt = no
[req_distinguished_name]
C = FR
ST = Paris
L = Paris
O = Eazytraining
OU = Eazytraining Lab
CN = local-registry.caas.eazytraining.lab
[v3_ca]
subjectKeyIdentifier = hash
authorityKeyIdentifier = keyid:always,issuer:always
basicConstraints = CA:true
keyUsage = digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment, keyAgreement, keyCertSign
issuerAltName = issuer:copy
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
DNS.1 = local-registry.caas.eazytraining.lab
DNS.2 = ocp-svc.eazytraining.lab
EOFGenerate the self-signed certificate for the mirroring registry
openssl req -newkey rsa:4096 -nodes -sha256 -keyout /shares/registry/certs/caas-eazytraining-lab.key -x509 -days 365 -out /shares/registry/certs/caas-eazytraining-lab.crt -config csr-answersTrust the certificate
cp certs/caas-eazytraining-lab.crt /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/
update-ca-trust
trust list | grep -i 'local-registry.caas.eazytraining.lab'Generate credentials for accessing to the registry
htpasswd -bBc /shares/registry/auth/htpasswd evreguser2 esbc_reg2099Start the registry
podman run --name eazyregistry \
-p 5000:5000 \
-v /shares/registry/data:/var/lib/registry:z \
-v /shares/registry/auth:/auth:z \
-e "REGISTRY_AUTH=htpasswd" \
-e "REGISTRY_HTTP_SECRET=fetnmqf981la0eqoof3" \
-e "REGISTRY_AUTH_HTPASSWD_REALM=Registry Realm" \
-e "REGISTRY_AUTH_HTPASSWD_PATH=/auth/htpasswd" \
-v /shares/registry/certs:/certs:z \
-e "REGISTRY_HTTP_TLS_CERTIFICATE=/certs/caas-eazytraining-lab.crt" \
-e "REGISTRY_HTTP_TLS_KEY=/certs/caas-eazytraining-lab.key" \
-e "REGISTRY_COMPATIBILITY_SCHEMA1_ENABLED=true" \
-d \
docker.io/library/registry:latestAllow some firewall rules
firewall-cmd --add-port=5000/tcp --zone=internal --permanent
firewall-cmd --add-port=5000/tcp --zone=public --permanent
firewall-cmd --reloadVerify access to the registry
curl -u evreguser2:esbc_reg2099 https://local-registry.caas.eazytraining.lab:5000/v2/_catalog Log in to the registry with podman
podman login -u evreguser2 local-registry.caas.eazytraining.lab:5000Your credentials will be Base64 encoded into /run/containers/0/auth.json, the content of this file should be added to your pull secret file.
Configure the mirroring
cp -a ~/okd-upi-install/mirroring ~/Download your pull secret from Red Hat and place it into the ~/mirroring folder. Don't forget to add the content of the registry authentication file (/run/containers/0/auth.json)
sh ~/mirroring/mirror.shCreate the systemd unit file that can be used to control the container registry
podman generate systemd --new --files --name eazyregistryThis command will create a systemd unit file located in the current directory. The systemd unit file will ensure that the container is still running even after reboot of the server.
# container-eazyregistry.service
# autogenerated by Podman 4.2.0
[Unit]
Description=Podman container-eazyregistry.service
Documentation=man:podman-generate-systemd(1)
Wants=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
RequiresMountsFor=%t/containers
[Service]
Environment=PODMAN_SYSTEMD_UNIT=%n
Restart=on-failure
TimeoutStopSec=70
ExecStartPre=/bin/rm -f %t/%n.ctr-id
ExecStart=/usr/bin/podman run \
--cidfile=%t/%n.ctr-id \
--cgroups=no-conmon \
--rm \
--sdnotify=conmon \
--replace \
--name eazyregistry \
-p 5000:5000 \
-v /shares/registry/data:/var/lib/registry:z \
-v /shares/registry/auth:/auth:z \
-e REGISTRY_AUTH=htpasswd \
-e REGISTRY_HTTP_SECRET=fetnmqf981la0eqoof3 \
-e "REGISTRY_AUTH_HTPASSWD_REALM=Registry Realm" \
-e REGISTRY_AUTH_HTPASSWD_PATH=/auth/htpasswd \
-v /shares/registry/certs:/certs:z \
-e REGISTRY_HTTP_TLS_CERTIFICATE=/certs/caas-eazytraining-lab.crt \
-e REGISTRY_HTTP_TLS_KEY=/certs/caas-eazytraining-lab.key \
-e REGISTRY_COMPATIBILITY_SCHEMA1_ENABLED=true \
-d docker.io/library/registry:latest
ExecStop=/usr/bin/podman stop --ignore --cidfile=%t/%n.ctr-id
ExecStopPost=/usr/bin/podman rm -f --ignore --cidfile=%t/%n.ctr-id
Type=notify
NotifyAccess=all
[Install]
WantedBy=default.targetInstall the generated systemd unit file
cp /root/container-eazyregistry.service /etc/systemd/system
systemctl enable container-eazyregistry.service
systemctl is-enabled container-eazyregistry.serviceRestart the registry container
systemctl restart container-eazyregistry.service- Configure BIND DNS
Apply configuration
cp -f ~/okd-upi-install/dns/named.conf /etc/named.conf
cp -R ~/okd-upi-install/dns/zones /etc/namedConfigure the firewall for DNS
firewall-cmd --add-port=53/udp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reloadEnable and start the service
systemctl enable --now named
systemctl start named
systemctl status namedConfirm dig now sees the correct DNS results by using the DNS server running locally
dig eazytraining.lab @127.0.0.1
dig -x 192.168.110.9 @127.0.0.1Change the nameserver configured in the /etc/resolv.conf by 127.0.0.1
- Configure DHCP
Copy the conf file to the correct location for the DHCP service to use
cp ~/okd-upi-install/dhcp/dhcpd.conf /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.confConfigure the firewall
firewall-cmd --add-service=dhcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reloadEnable and start the service
systemctl enable --now dhcpd
systemctl start dhcpd
systemctl status dhcpd- Configure the Apache Web Server
Change default listen port to 8080 in httpd.conf
sed -i 's/Listen 80/Listen 0.0.0.0:8080/' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confConfigure the firewall for Web Server traffic
firewall-cmd --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reloadEnable and start the service
systemctl enable --now httpd
systemctl start httpd
systemctl status httpdMaking a GET request to localhost on port 8080 should now return the default Apache webpage
curl localhost:8080- Configure HAProxy
Copy HAProxy config
cp -f ~/okd-upi-install/haproxy/haproxy.cfg /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfgConfigure the firewall
firewall-cmd --add-port=9000/tcp
firewall-cmd --add-port=6443/tcp --zone=public --permanent # kube-api-server on control plane nodes
firewall-cmd --add-port=22623/tcp --zone=public --permanent # machine-config server
firewall-cmd --add-service=http --zone=public --permanent # web services hosted on worker nodes
firewall-cmd --add-service=https --zone=public --permanent # web services hosted on worker nodesEnable and start the service
setsebool -P haproxy_connect_any 1 # SELinux name_bind access
systemctl enable --now haproxy
systemctl start haproxy
systemctl status haproxy- Configure NFS for the OpenShift persistent storage. It is a requirement to provide storage to the Registry, empyDir can be specified if necessary.
Create the Share
Check available disk and its location df -h
dnf install nfs-utils -y
chown -R nobody:nobody /shares/
chmod -R 777 /shares/Export the Share
echo "/shares 192.168.110.0/24(rw,sync,root_squash,no_subtree_check,no_wdelay)" > /etc/exports
exportfs -rvSet firewall rules
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service mountd --permanent
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service rpc-bind --permanent
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service nfs --permanent
firewall-cmd --reloadEnable and start the NFS related services
systemctl enable --now nfs-server rpcbind
systemctl start nfs-server rpcbind nfs-mountd- Configure NTP Server Set the NTP server
vim /etc/chrony.conf
# comment below line
# pool 2.almalinux.pool.ntp.org iburst
# add below lines
# Europe NTP servers
server 0.europe.pool.ntp.org
server 1.europe.pool.ntp.org
server 2.europe.pool.ntp.org
server 3.europe.pool.ntp.org
# Modify below line
# Allow NTP client access from local network
allow 192.168.110.0/24Enable and start the NTP service
systemctl enable --now chronyd
systemctl start chronyd
systemctl status chronydVerify NTP Server
chronyc sourcesAllow remote access to NTP server
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=ntp
firewall-cmd --reloadGenerate and host install files
- Generate an SSH key pair
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -N "" -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa- Create an install directory
mkdir ~/ocp-install- Setup the install-config.yaml required for the installation
export CLUSTER_NAME=caas
export PULL_SECRET=$(cat /root/mirroring/pull-secret.json)
export SSH_KEY=$(cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub)
export REGISTRY_CERTIFICATE=$(awk '{printf(" %s\n", $0)}' /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/*.crt)cat ~/okd-upi-install/manifests/install-config.yaml.tpl | envsubst > ~/ocp-install/install-config.yaml- Check if the install-config yaml is populated as expected
vim ~/ocp-install/install-config.yaml- Generate Kubernetes manifest files
openshift-install create manifests --dir ~/ocp-installAbove warning message says that master nodes are schedulable, it means we can have workload on control planes (control planes will also work as worker nodes). If you wish to disable this then run following sed command,
sed -i 's/mastersSchedulable: true/mastersSchedulable: false/' ~/ocp-install/manifests/cluster-scheduler-02-config.ymlGenerate the Ignition config and Kubernetes auth files
openshift-install create ignition-configs --dir ~/ocp-install/- Create a hosting directory to serve the configuration files for the OpenShift booting process
mkdir -p /var/www/html/ocp4- Copy all generated install files to the new web server directory
cp -R ~/ocp-install/*.ign /var/www/html/ocp4/- Move the Fedora Core OS image to the web server directory
mkdir -p /var/www/html/okd4-image
wget https://builds.coreos.fedoraproject.org/prod/streams/stable/builds/37.20230205.3.0/x86_64/fedora-coreos-37.20230205.3.0-live-kernel-x86_64 -O /var/www/html/okd4-image/fcos-37-vmlinuz
wget https://builds.coreos.fedoraproject.org/prod/streams/stable/builds/37.20230205.3.0/x86_64/fedora-coreos-37.20230205.3.0-live-initramfs.x86_64.img -O /var/www/html/okd4-image/fcos-37-initramfs.img
wget https://builds.coreos.fedoraproject.org/prod/streams/stable/builds/37.20230205.3.0/x86_64/fedora-coreos-37.20230205.3.0-live-rootfs.x86_64.img -O /var/www/html/okd4-image/fcos-37-rootfs.img- Create the .treeinfo file which will be used as a helper for installing the OS
cat <<EOF > /var/www/html/okd4-image/.treeinfo
[general]
arch = x86_64
family = Fedora CoreOS
platforms = x86_64
version = 37
[images-x86_64]
initrd = fcos-37-initramfs.img
kernel = fcos-37-vmlinuz
EOF- Change ownership and permissions of the web server directory
# OS
chcon -R -t httpd_sys_content_t /var/www/html/okd4-image
chown -R apache: /var/www/html/okd4-image
chmod 744 -R /var/www/html/okd4-image/
# Ignition files
chcon -R -t httpd_sys_content_t /var/www/html/ocp4/
chown -R apache: /var/www/html/ocp4/
chmod 744 -R /var/www/html/ocp4/- Confirm you can see all files added to the /var/www/html/ocp4/ and /var/www/htlm/okd4-image/ dirs through Apache
curl localhost:8080/ocp4/
curl localhost:8080/okd4-image/Deploy OpenShift
- Deploy the bootstrap host and the control plane hosts
From the KVM Hypervisor
Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/ObieBent/okd-upi-install.gitOpen four terminal
cd okd-upi-install1st terminal
sh fcos/control-plane/deployBootstrap.sh2nd terminal
sh fcos/control-plane/deployMaster01.sh3rd terminal
sh fcos/control-plane/deployMaster02.sh4th terminal
sh fcos/control-plane/deployMaster03.shMonitor the Bootstrap Process
From the Bastion host
- You can monitor the bootstrap process from the ocp-svc host at different log levels (debug, error, info)
openshift-install --dir ~/ocp-install wait-for bootstrap-complete --log-level=debug- Once bootstrapping is complete the ocp-bootstrap node can be removed
Remove the Boostrap Node
- Remove all references to the ocp-bootstrap host from the /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg file
# Two entries
vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
# Restart HAProxy
systemctl reload haproxy- The ocp-bootstrap host can now be safely shutdown and deleted.
sh ~/okd-upi-install/cleanup-bootstrap.sh Wait for installation to complete
- Collect the OpenShift Console address and kubeadmin credentials from the output to the install-complete event
openshift-install --dir ~/ocp-install wait-for install-complete --log-level=debug- Continue to join the worker nodes to the cluster in a new tab whilst waiting for the above command to complete
Join Worker Nodes
- Setup 'oc' and 'kubectl' clients on the Bastion machine
export KUBECONFIG=~/ocp-install/auth/kubeconfig
echo 'export OC_EDITOR="vim"' >> ~/.bashrc
echo 'export KUBE_EDITOR="vim"' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
# Test auth by viewing cluster nodes
oc get nodesOpen again four terminal
cd ~/okd-upi-install1st terminal
sh fcos/workers/deployWorker01-fcos.sh2nd terminal
sh fcos/workers/deployWorker02-fcos.sh3rd terminal
sh fcos/workers/deployWorker03-fcos.sh4th terminal
sh fcos/workers/deployWorker04-fcos.sh- View and approve pending CSRs
# View CSRs
oc get csr
# Approve all pending CSRs
oc get csr -o go-template='{{range .items}}{{if not .status}}{{.metadata.name}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}{{end}}' | xargs oc adm certificate approve
# Wait for kubelet-serving CSRs and approve them too with the same command
oc get csr -o go-template='{{range .items}}{{if not .status}}{{.metadata.name}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}{{end}}' | xargs oc adm certificate approve- Watch and wait for the Worker Nodes to join the cluster and enter a 'Ready' status
This can take 5-10 minutes
watch -n5 oc get nodesConfigure storage for the Image Registry
- Clone the CSI driver repository required in order to consume NFS volumes
mkdir ~/ocp/nfs -p && cd ~/ocp/nfs
git clone https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/nfs-subdir-external-provisioner.git k8s-csi-nfs
cd k8s-csi-nfs - Create namespace for NFS Storage provisioner
oc create namespace openshift-nfs-storage- Add monitoring label to namespace
oc label namespace openshift-nfs-storage "openshift.io/cluster-monitoring=true"- Configure deployment and RBAC for NFS
Switch project
oc project openshift-nfs-storageChange namespace on deployment and rbac YAML file
NAMESPACE=`oc project -q`
sed -i'' "s/namespace:.*/namespace: $NAMESPACE/g" ./deploy/rbac.yaml
sed -i'' "s/namespace:.*/namespace: $NAMESPACE/g" ./deploy/deployment.yamlCreate RBAC
oc create -f deploy/rbac.yaml
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user hostmount-anyuid system:serviceaccount:$NAMESPACE:nfs-client-provisionerConfigure deployment
vim ~/ocp/nfs/k8s-csi-nfs/deploy/deployment.yamlapiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: openshift-nfs-storage
spec:
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
serviceAccountName: nfs-client-provisioner
containers:
- name: nfs-client-provisioner
image: quay.io/external_storage/nfs-client-provisioner:latest
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-client-root
mountPath: /persistentvolumes
env:
- name: PROVISIONER_NAME
value: storage.io/nfs
- name: NFS_SERVER
value: 10.10.51.9 # Change this (NFS IP Server )
- name: NFS_PATH
value: /mnt/nfs_shares/okd # Change this (NFS mount path)
volumes:
- name: nfs-client-root
nfs:
server: 10.10.51.9 # Change this (NFS IP Server)
path: /mnt/nfs_shares/okd # Change this (NFS mount path)Configure Storage Class
vim ~/ocp/nfs/k8s-csi-nfs/deploy/class.yamlapiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: managed-nfs-storage
provisioner: storage.io/nfs # or choose another name, must match deployment's env PROVISIONER_NAME'
parameters:
archiveOnDelete: "false"Deploy Deployment and Storage Class
oc create -f ~/ocp/nfs/k8s-csi-nfs/deploy/class.yaml
oc create -f ~/ocp/nfs/k8s-csi-nfs/deploy/deployment.yamlVerify Deployment
oc get pods -n openshift-nfs-storage- Create the 'image-registry-storage' PVC by updating the Image Registry operator config by updating the management state to 'Managed' and adding 'pvc' and 'claim' keys in the storage key:
oc edit configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.iomanagementState: Managedstorage:
pvc:
claim: # leave the claim blank- Confirm the 'image-registry-storage' pvc has been created and is currently in a 'Pending' state
oc get pvc -n openshift-image-registry- Create the persistent volume for the 'image-registry-storage' pvc to bind to
export REGISTRY_SIZE=100
export REGISTRY_PV_NAME=registry-pv
cat ~/okd-upi-install/manifests/registry-pv.yaml | envsubst | oc create -f -- After a short wait the 'image-registry-storage' pvc should now be bound
oc get pvc -n openshift-image-registry- Set default storageclass
oc patch storageclass managed-nfs-storage -p '{"metadata": {"annotations": {"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class": "true"}}}'- Check clusteroperator status. Wait until Availability become True.
oc get clusteroperator image-registryAccess the OpenShift Console
- Wait for the 'console' Cluster Operator to become available
There will be a redeployment of the following cluster operators: kube-apiserver & openshift-apiserver
oc get clusteroperators- Append the following to your local workstations /etc/hosts file:
From your local workstation If you do not want to add an entry for each new service made available on OpenShift you can configure the ocp-svc DNS server to serve externally and create a wildcard entry for *.apps.caas.eazytraining.lab
# Open the hosts file
sudo vi /etc/hosts
# Append the following entries:
192.168.110.9 bastion api.caas.eazytraining.lab console-openshift-console.apps.caas.eazytraining.lab oauth-openshift.apps.caas.eazytraining.lab downloads-openshift-console.apps.caas.eazytraining.lab alertmanager-main-openshift-monitoring.apps.caas.eazytraining.lab grafana-openshift-monitoring.apps.caas.eazytraining.lab prometheus-k8s-openshift-monitoring.apps.caas.eazytraining.lab thanos-querier-openshift-monitoring.apps.caas.eazytraining.lab- Navigate to the OpenShift Console URL and log in as the 'username' user
You will get self signed certificate warnings that you can ignore If you need to login as kubeadmin and need to the password again you can retrieve it with: cat ~/ocp-install/auth/kubeadmin-password
Day 2 Gestures
Create the first Admin user
- Apply the
oauth-htpasswd.yamlfile to the cluster
export HTPASSWD_SECRET_NAME=htpasswd-secret
export HTPASSWD_SECRET=`htpasswd -n -B -b <username> <password> | base64 -w0`
cat ~/okd-upi-install/manifests/01-oauth-htpasswd.yaml | envsubst | oc apply -f -
cat ~/okd-upi-install/manifests/02-oauth-htpasswd.yaml | envsubst | oc replace -f - - Assign the new user admin permissions
export USER=<username>
cat ~/okd-upi-install/manifests/rbac-user-admin.yaml | envsubst | oc create -f - - Wait until the cluster operator
authenticationbecome available
watch -n5 oc get clusteroperators authentication-
Log in to the Web Console with the username provided in Step 1
-
Remove the kubeadmin user
oc delete secrets kubeadmin -n kube-system/!\ If you follow this procedure before another user is a cluster-admin, then the cluster must be reinstalled. It is not possible to undo this command.
Infra Nodes Configuration
- Adding the label
node-role.kubernetes.io/infra
oc label node ocp-worker-01.caas.eazytraining.lab node-role.kubernetes.io/infra=
oc label node ocp-worker-02.caas.eazytraining.lab node-role.kubernetes.io/infra=
oc label node ocp-worker-03.caas.eazytraining.lab node-role.kubernetes.io/infra=- Define the machine config pool configuration dedicated to the Infra Nodes
mkdir ~/ocp/infra-nodes cat <<EOF | sudo tee ~/ocp/infra-nodes/mcp.yaml
apiVersion: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/v1
kind: MachineConfigPool
metadata:
name: infra
spec:
machineConfigSelector:
matchExpressions:
- {key: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/role, operator: In, values: [worker,infra]}
nodeSelector:
matchLabels:
node-role.kubernetes.io/infra: ""
EOF- Apply the machine config pool configuration
oc apply -f ~/ocp/infra-nodes/mcp.yaml- Check the machine config pool
infrastatus
watch -n2 oc get mcp- Schedule the ingress controller pods on infra nodes
oc edit ingresscontrollers.operator.openshift.io -n openshift-ingress-operatorspec:
nodePlacement:
nodeSelector:
matchLabels:
node-role.kubernetes.io/infra: ""Verify if ingress controller pods are running on infra nodes
oc get pod -n openshift-ingress -o wide- Schedule the image registry pods on infra nodes
oc edit configs.imageregistry.operator.openshift.iospec:
nodeSelector:
node-role.kubernetes.io/infra: ""Verify if image registry pods are running on infra nodes
oc get po -n openshift-image-registry -owide- Remove label node-role.kubernetes.io/worker
oc label node ocp-worker-01.caas.eazytraining.lab node-role.kubernetes.io/worker-
oc label node ocp-worker-02.caas.eazytraining.lab node-role.kubernetes.io/worker-
oc label node ocp-worker-03.caas.eazytraining.lab node-role.kubernetes.io/worker-Monitoring
- Define the scheduling of the monitoring stack pods on Infra Nodes at the cluster level and the required size on the storage
export CLUSTER_NAME=caas
export NFS_MONITORING_SIZE=20Gi
export STORAGE_CLASS=`oc get sc -o jsonpath='{.items[?(@.metadata.annotations.storageclass\.kubernetes\.io/is-default-class=="true")].metadata.name}'`
cat ~/okd-upi-install/manifests/monitoring-cluster.yaml | envsubst | oc apply -f - - Enable monitoring for user-defined projects on Infra Nodes
oc apply -f ~/okd-upi-install/manifests/monitoring-user.yamlAuthentication operator
Removing of the Self-Provisioner
oc patch clusterrolebinding.rbac self-provisioners -p '{"subjects": null}'ETCD Encryption
oc edit apiserverAdd these lines
spec:
encryption:
type: aescbcThe encryption will create the update of some cluster operators
Check the encryption process
oc get openshiftapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'oc get kubeapiserver -o=jsonpath='{range .items[0].status.conditions[?(@.type=="Encrypted")]}{.reason}{"\n"}{.message}{"\n"}'Get the encryption key for openshift-apiserver
echo $(oc get secrets/encryption-config -n openshift-apiserver -o=jsonpath='{.data.encryption-config}') | base64 -d | jq .Get encryption key for openshift-kube-apiserver:
echo $(oc get secrets/encryption-config -n openshift-kube-apiserver -o=jsonpath='{.data.encryption-config}') | base64 -d | jq .Build the Operators Catalog Source
Required tool:
Disable the default OperatorHub sources
oc patch OperatorHub cluster --type json -p '[{"op": "add", "path": "/spec/disableAllDefaultSources", "value": true}]'# download and extract the opm utility
cd ~/ocp && wget https://mirror.openshift.com/pub/openshift-v4/x86_64/clients/ocp/4.10.0/opm-linux-4.10.0.tar.gz
tar -zxf opm-linux-4.10.0.tar.gz
mv opm /usr/local/bin/
# check if opm is installed
opm versionAuthenticate with registry.redhat.io
podman login registry.redhat.io --authfile /root/mirroring/pull-secret.jsonAuthenticate with the target registry
podman login local-registry.caas.eazytraining.lab:5000 --authfile /root/mirroring/pull-secret.jsonPrune the source index of all but the specified packages
opm index prune \
-f registry.redhat.io/redhat/redhat-operator-index:v4.10 \
-p cluster-logging,openshift-gitops-operator,elasticsearch-operator\
,devspaces,devworkspace-operator,serverless-operator,servicemeshoperator\
,openshift-pipelines-operator-rh,vertical-pod-autoscaler,redhat-oadp-operator\
,kiali-ossm,jaeger-product,cincinnati-operator \
-t local-registry.caas.eazytraining.lab:5000/olm/redhat-operator-index:v4.10Push the new index image to the target registry
podman push local-registry.caas.eazytraining.lab:5000/olm/redhat-operator-index:v4.10Add the catalog source to the cluster
oc apply -f ~/okd-upi-install/manifests/catalogSource.yamlTroubleshooting
- DHCP troubleshooting
cat /var/log/messages | grep dhcp
journalctl -u dhcpd- Apache troubleshooting
cat /var/log/httpd/access_log | grep -iE '*.ign'- You can collect logs from all cluster hosts by running the following command from the 'ocp-svc' host:
openshift-install gather bootstrap --dir ocp-install --bootstrap=192.168.110.110 --master=192.168.110.111 --master=192.168.110.112 --master=192.168.110.113Reference
i. https://docs.okd.io/4.10/installing/installing_bare_metal/installing-bare-metal.html
ii. https://docs.okd.io/4.10/installing/installing-troubleshooting.html