A sample Postgres, PostgREST, PGAdmin, Nginx and Swagger development environment.
Replace the shell or SQL scripts in the the initdb folder to populate the database with your own data, if you wish or use the sample data already provided.
docker-compose up -d --detachdocker-compose down --remove-orphans To remove the created Docker volumes that data is persisted to use the following command:
docker-compose down --remove-orphans --volumesTo remove the created Docker images and volumes that data is persisted to use the following command:
docker-compose down --remove-orphans --volumes --rmi allSome issues have been reported with running this example on Windows. There two culprits.
-
Make sure that the scripts in the folder intidb are in *nix format with only LF and not the default Windows CRFL. You can remedy this by using dos2unix command line program or most editors will allow for the translation.
-
Next issue is the pathing issues with how Windows resolves them. Recommended work around is to use Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) to run the docker-compose command and to change the
./initdbentry in thedbcontainer specification for volumes in thedocker-compose.ymlfile to the fully pathed WSL folder name. See example below:
volumes:
# anything in initdb directory is created in the database
# see "How to extend this image" section at https://hub.docker.com/r/_/postgres/
- "/mnt/c/Users/MyUserName/MyDirectory/postgrest-docker-compose/initdb:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d"
#- "./initdb:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d"
- local_pgdata:/var/lib/postgresql/dataTry the above two solutions together if you get a cannot load initd log message in the db container or invalid format error in the db container log messages.
Test out the web application that is driven by the PostgREST API calls This is served from the Nginx server Postgres-demo (using port 80) in the docker-compose file to serve up a simple web application that uses the rest calls.
Now test the REST Get statements:
- Get the cities in the database
- Get the countries in the database
- Get the languages in the database
- Get cities named Springfield from the database
- Get cities in the USA city view with 'ie' in the name from the database
- Get cities with a population greater than or equal to 3,000,000
- Get cities tha end in "Island"
- Get cities where the district like Island and the population is less than 1000; selecting only the city name
NOTE: All calls to port 3333 are routed through the Nginx reverse proxy. You can find the description of the reverse proxy in the nginx section of the docker-compose and Dockerfile scripts in the repository.
Show the REST API endpoints for Get, Post, Delete and Patch
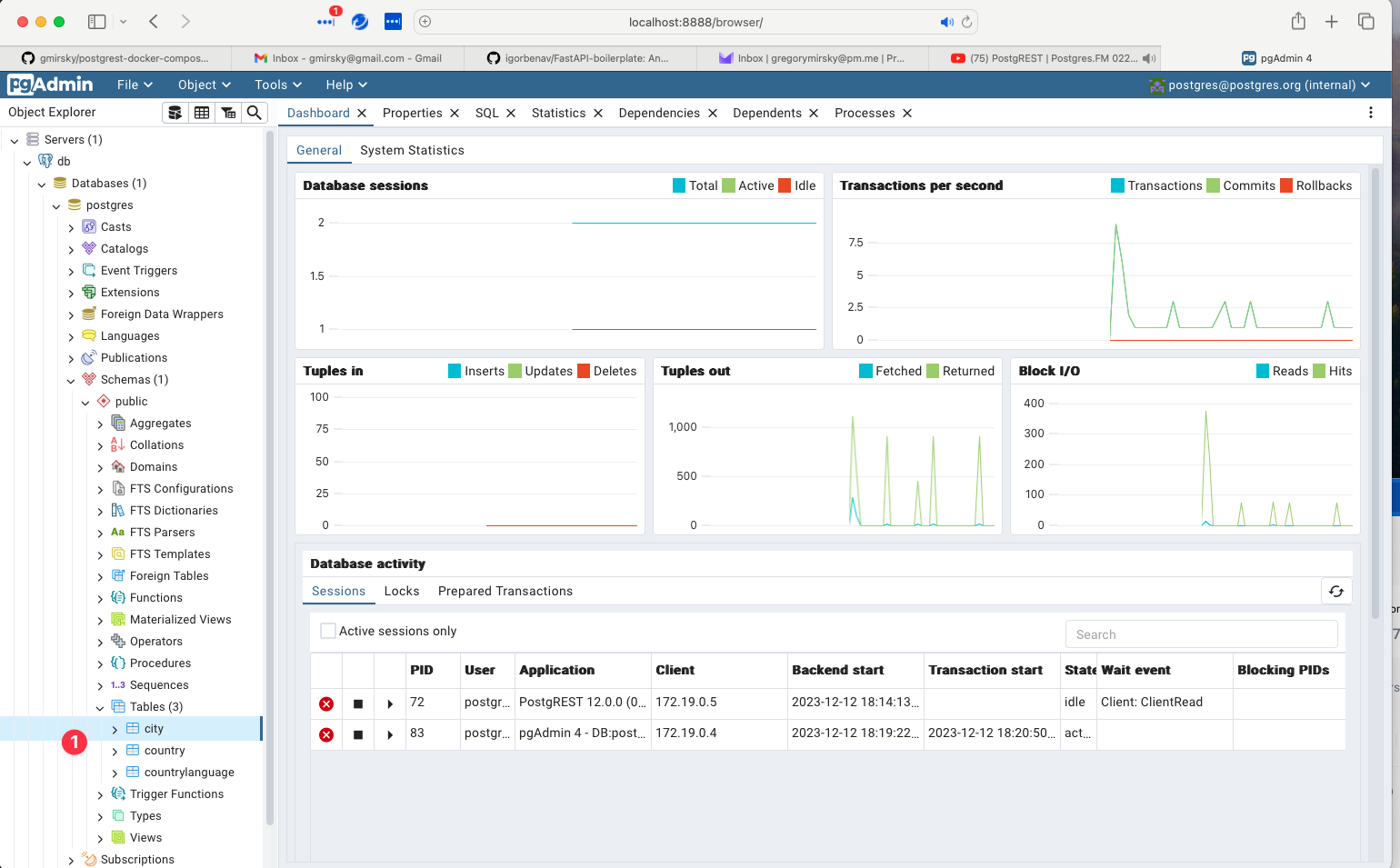
Navigate to the PgAdmin URL to open up PGAdmin (you might need to give it a minute or two to be ready).
Use the values PGADMIN_USER and PGADMIN_PASSWORD in the .env file to log into PgAdmin.
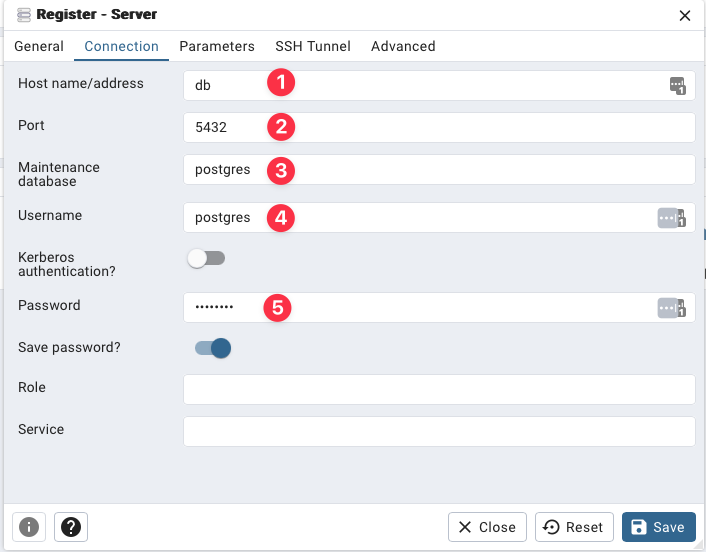
Under the section Quick Links click on Add New Server to open up the database connection dialog.
- The value should be
db, the same name as the database service in the docker-compose script. - Leave as port
5432(unless you changed the database port in the docker-compose script). - Use the value in
POSTGRES_DBin the .env file. - Use the value in
POSTGRES_USERin the .env file. - Use the value in
POSTGRES_PASSWORDin the .env
Once successully logged into the database, you should be able to navigate the tree on the left down to tables.
- You should see the tables
CITY,COUNTRYandCOUNTRYLANGUAGEhas been created from the code in theinitdbfolder of this repository.
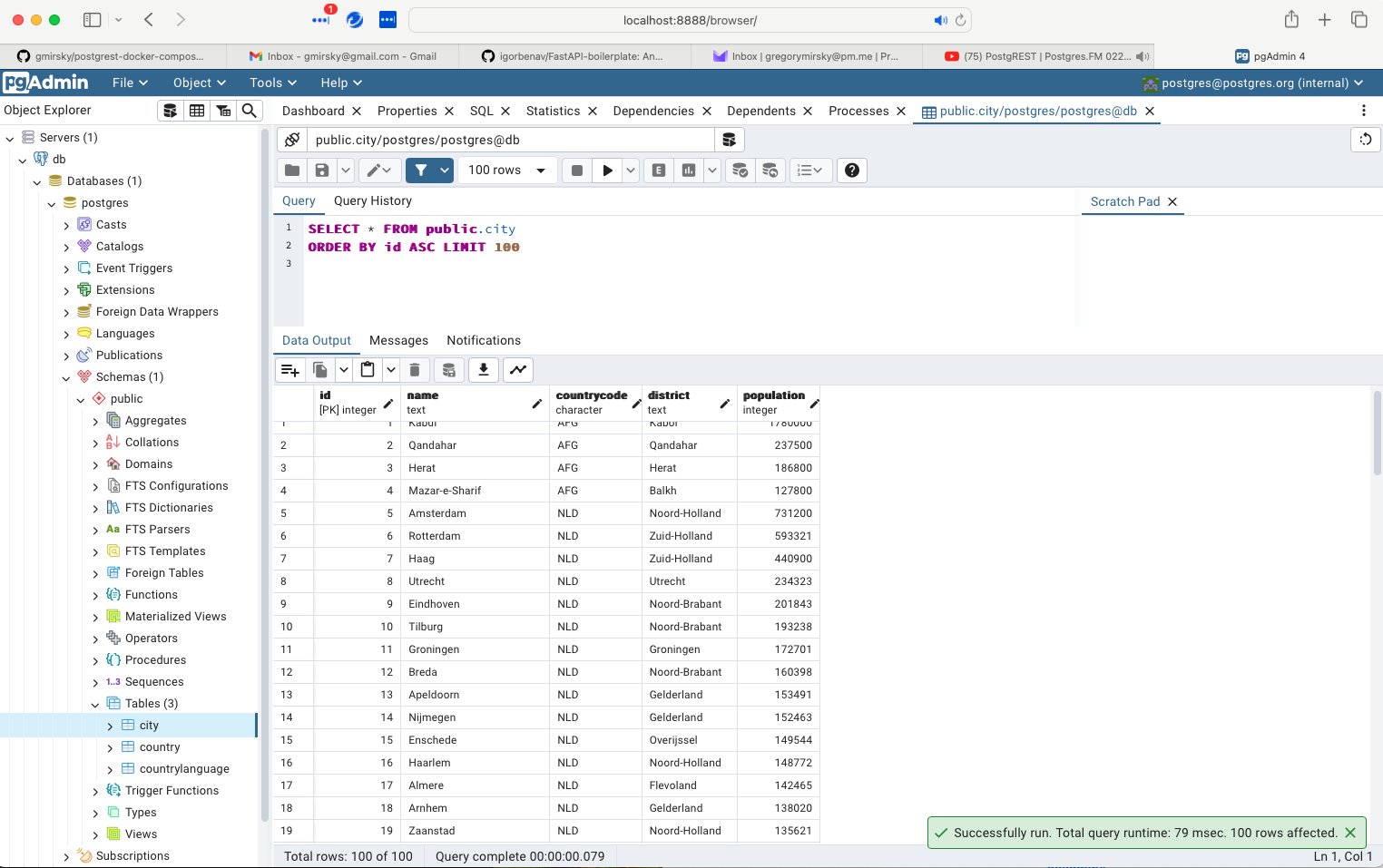
Right click on one of the tables and select View/Edit Data > First 100 Rows you should get a result like this:
PostgREST Documentation Swagger Documentation Postgresql Documentation Nginx Documentation PGAdmin Documetation PostgREST-py