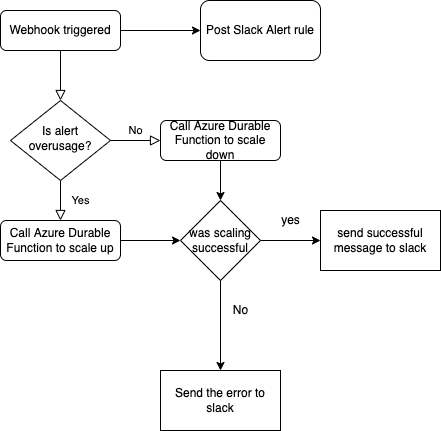
This repository implements Autoscaling of Azure Elastic SQL pool using the structure defined here
The implementation contains three sections
- Alert Rules
- Azure Logic App
- Azure Durable Functions
This solution contains two alert rules which have been set for SQL Elastic Pool
- High Usage trigger
condition: Whenever the maximum dtu percentage is greater than 50%
Alert rule name: DTU percentage is high
action group name: ScaleElasticSQLLogicAppTrigger - Low Usage Trigger
condition: Whenever the maximum dtu percentage is less than or equal to 35% (and) Whenever the maximum edtu limit is greater than 100
Alert rule name: DTU percentage is too low
action group name: ScaleElasticSQLLogicAppTrigger
The action group is set to Azure logic app webhook.
The Azure Logic App is triggered by webhook(the action group) and if the alert rule name contains high the scaling is set to up and if the alert rule name contains low the scaling variable is set to down and it posts the scaling variable to the slack. Furthermore, it calls Azure durable function Orchestrator with variable scaling. After completion of the function, it will post its output to the slack channel.
"workflows_sql_elastic_scale_logic_app_name": <the logic app name>
"connections_slack_1_externalid": <the slack connection id>
"durable_function_orchestrator_uri": <the http link of durable function orchestrator>
"subscription_id": <subscription id of logic app name>
"slack_channel_id": <the id of slack channel>
"alert_rule_name_high": <the alert rule name for high usage trigger>
"alert_rule_name_low": <the alert rule name for low usage trigger>
As in the Azure documents you can use a script to scale and change attributes of SQL Elastic pool. To automate this process you can use Azure Functions to run scripts whenever you need. As mentioned here the scale request and changing SQL Elastic Pool attributes may take more than two minutes and the Webhook call of Azure functions/Webhooks in Azure Logic Apps timeouts after two minutes. So, we need to call the scale request asynchronously using Azure Durable Functions.
The Azure Durable Function has three parts: Starter, Orchestrator, and the Activity Function. For more information check out the documentation.
I used Powershell environment for my Activity Function SQLPoolScale
in this function. First we log in to the Az through Az-connect you can create a service principal and grant contributor to the SQL Pool and SQL server. The next step we get the real-time dtu of the SQL pool, and based on the defined SCALE_MARGIN, the dtu range (MIN_DTU_RANGE, MAX_DTU_RANGE), and the passing parameter scaling(up or down), we choose the right standardEditionDtu. Just remember that the eDTU of SQL POOl has limited values (50,100,200,300,400,800,1200,1600,2000,2500,3000) so you should choose the RANGE values wisely. Furthermore, both the dtu value of Elastic Pool and the DatabaseDtuMax of all the DBs in the elastic Pool will be set to the standardEditionDtu.
After calling Set-AzSqlElasticPool cmd, the output retrieved from the cmd will be print out to the slack channel. if the scaling operation was successful the scale is Ready will print and if the scaling failed the scale is Unknown print.
"AzureWebJobsStorage": "<Azure storage Connection String>",
"FUNCTIONS_WORKER_RUNTIME": "powershell",
"FUNCTIONS_WORKER_RUNTIME_VERSION": "~7",
"SQL_ELASTIC_SCALE_SP_ID": "<service principal id of elastic access>",
"SQL_ELASTIC_SCALE_SP_PASS": "<service principal password of elastic access>",
"TENANT_ID":"<tenant id of elastic sql pool>",
"SQL_POOL_SUBSCRIPTION_ID":"<subscription id of elastic sql pool>",
"SQL_POOL_RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME":"<resource group of elastic sql pool>",
"SQL_POOL_LOCATION":"<location of elastic sql pool>",
"SQL_POOL_NAME":"<elastic sql pool name>",
"SQL_SERVER_NAME":"<server name of elastic sql pool>",
"SCALE_MARGIN":"#margin of the real dtu",
"MAX_DTU_RANGE":"#max range of dtu",
"MIN_DTU_RANGE":"#min range of dtu"