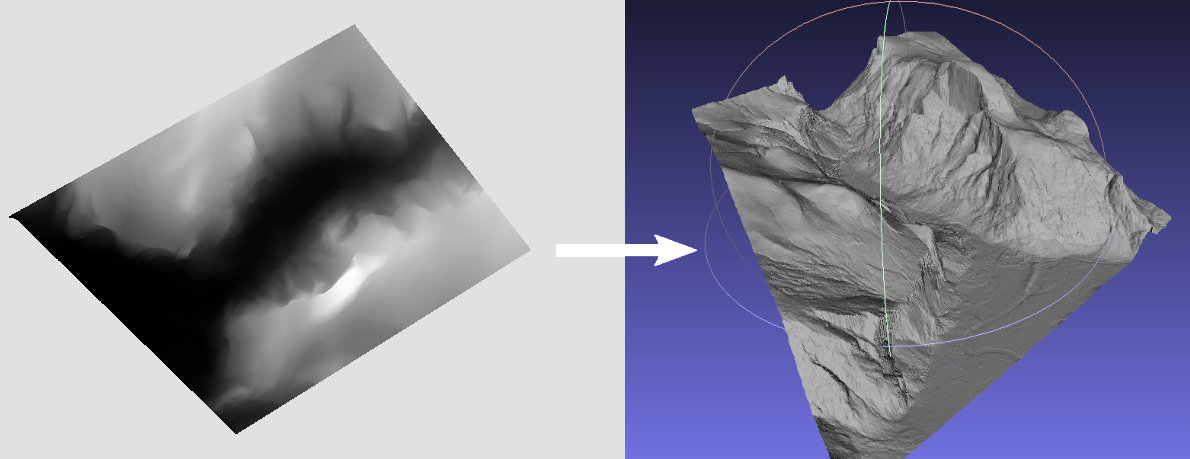
Fast generation of 2.5D meshes from elevation models.
docker run -it --rm -v /path-your-data:/data kladess/dem2mesh dem2mesh -rtc -verbose -inputFile /data/dem.tif -outputFile /data/mesh.plyGDAL and OpenMP are the only dependencies. To install it run:
sudo apt-get install -y libgdal-dev libomp-dev
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make./dem2mesh -rtc -verbose -inputFile dem.tif -outputFile mesh.plygdalwarp to reproject the raster DEM. https://www.gdal.org/gdalwarp.html
| Flag | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| -inputFile | Path to DEM raster datasource (GDAL compatible) | ✔ |
| -outputFile | Path to PLY mesh output | ✔ |
| -maxVertexCount | Target number of vertices for the output mesh. This number is not always guaranteed to be reached. Defaults to 100000 |
|
| -maxTileLength | Max length of a tile. Smaller values take longer to process but reduce memory usage by splitting the meshing process into tiles. Defaults to 1000. |
|
| -aggressiveness | Value between 1 and 10 that specifies how "aggressive" the mesh simplification process should be at each iteration. Higher values simplify the mesh more aggressively but can decrease the fidelity of the mesh. Defaults to 5. |
|
| -bandNum | Raster band # to use. Defaults to 1. |
|
| -maxConcurrency | Maximum number of threads to use. Defaults to all CPUs available. | |
| -edgeSwapThreshold | Dot product threshold (between 0-1) to perform edge collapses. Performing edge collapses can violate the 2.5D constraints, but leads to better triangles for vertical structures. Defaults to disabled. |
|
| -rtc | Use Relative To Center (RTC) X/Y coordinates in the output PLY mesh. This can be useful since most 3D visualization software use floating coordinate precision to represent vertices and using absolute coordinates might lead to jittering artifacts. | |
| -verbose | Print verbose output. |
How does it compare to https://github.com/heremaps/tin-terrain ?
The main difference is the meshing approach and output type. Tin-terrain uses a greedy approach, dem2mesh uses a gridding + simplification approach. Tin-terrain can output to quantized-mesh format (useful for displaying in Cesium), dem2mesh does not.
The meshing approach changes the way triangles are placed in the mesh. Greedy approaches tend to generate areas with large triangles in flat parts of the mesh, which is something we wanted to avoid in dem2mesh. The gridding approach generates more evenly sized and distributed triangles. Good sized triangles are important in OpenDroneMap for generating good orthophotos during the texturing step.
- Fast Quadric Mesh Simplification code modified from https://github.com/sp4cerat/Fast-Quadric-Mesh-Simplification
- Command line parser library modified from https://github.com/mkazhdan/PoissonRecon