Fully configurable Zwave to MQTT Gateway and Control Panel.
THIS PROJECT IS UNMAINTAINED. PLEASE CONSIDER MOVING TO Zwavejs
- Backend: NodeJS, Express, socket.io, Mqttjs, openzwave-shared, Webpack
- Frontend: Vue, socket.io, Vuetify
After a discussion with Openzwave maintainer all issues related to OZW 1.4 will be ignored and automatically closed as it isn't supported anymore, please use OZW 1.6+
- Zwave To MQTT
# Using volumes as persistence
docker run --rm -it -p 8091:8091 --device=/dev/ttyACM0 --mount source=zwave2mqtt,target=/usr/src/app/store robertslando/zwave2mqtt:latest
# Using local folder as persistence
mkdir store
docker run --rm -it -p 8091:8091 --device=/dev/ttyACM0 -v $(pwd)/store:/usr/src/app/store robertslando/zwave2mqtt:latest
# As a service
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/openzwave/zwave2mqtt/master/docker/docker-compose.yml
docker-compose upReplace
/dev/ttyACM0with your serial device
For more info about docker check here
kubectl apply -k https://raw.githubusercontent.com/OpenZWave/Zwave2Mqtt/master/kustomization.yamlYou will almost certainly need to instead use this as a base, and then layer on top patches or resource customizations to your needs or just copy all the resources from the kubernetes resources directory of this repo
-
Firstly you need to install the Open-Zwave library on your system.
cd ~ git clone https://github.com/OpenZWave/open-zwave.git cd open-zwave && make && sudo make install sudo ldconfig export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/lib64 sudo sed -i '$a LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/local/lib64' /etc/environment
For Raspberry check here
-
Test the library: go to openzwave directory
cd openzwave-*and run the commandMinOZW /dev/ttyACM0replace
/dev/ttyACM0with the USB port where your controller is connected -
Now you can use the packaged version (you don't need NodeJS/npm installed) or clone this repo and build the project:
-
For the packaged version:
cd ~ mkdir Zwave2Mqtt cd Zwave2Mqtt # download latest version curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/OpenZWave/Zwave2Mqtt/releases/latest \ | grep "browser_download_url.*zip" \ | cut -d : -f 2,3 \ | tr -d \" \ | wget -i - unzip zwave2mqtt-v*.zip ./zwave2mqtt
-
If you want to compile last code from github:
git clone https://github.com/OpenZWave/Zwave2Mqtt cd Zwave2Mqtt npm install npm run build npm start
-
-
Open the browser http://localhost:8091
If you need to setup ZWave To MQTT behind a reverse proxy that needs a subpath to work, take a look at the reverse proxy configuraiton docs.
Developers who wants to debug the application have to open 2 terminals.
In first terminal run npm run dev to start webpack-dev for front-end developing and hot reloading at http://localhost:8092
(THE PORT FOR DEVELOPING IS 8092)
In the second terminal run npm run dev:server to start the backend server with inspect and auto restart features (if you don't have nodemon installed: npm install -g nodemon)
To package the application run npm run pkg command and follow the steps
By default running npm run dev:server will proxy the reequests to a backend listening on localhost on port 8091.
If you want to run the development frontend against a different backend you have the following environment variables that you can use to redirect to a different backend:
- SERVER_HOST: [Default: 'localhost'] the hostname or IP of the backend server you want to use;
- SERVER_PORT: [Default: '8091'] the port of the backend server you want to use;
- SERVER_SSL: [Default: undefined] if set to a value it will use https/wss to connect to the backend;
- SERVER_URL: [Default: use the other variables] the full URL for the backend API, IE:
https://zwavetomqtt.home.net:8443/ - SERVER_WS_URL: [Default: use the other variables] the full URL for the backend Socket, IE:
wss://zwavetomqtt.home.net:8443/
Firstly you need to open the browser at the link http://localhost:8091 and edit the settings for Zwave, MQTT and the Gateway.
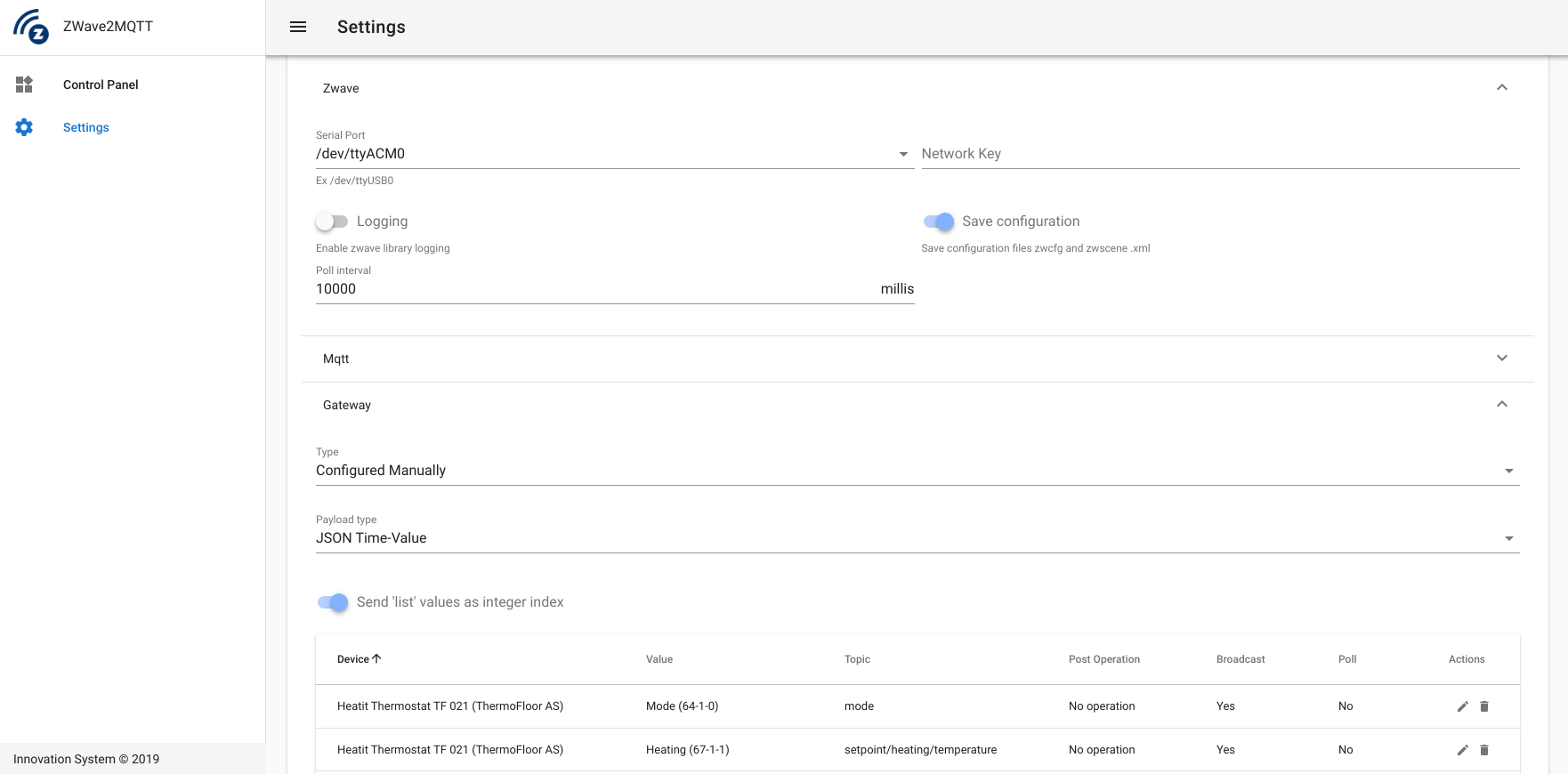
Zwave settings:
- Serial port: The serial port where your controller is connected
- Network key (Optional): Zwave network key if security is enabled. The correct format is
"0xCA,0xFE,0xBA,0xBE,.... "(16 bytes total) - Logging: Enable/Disable Openzwave Library logging
- Save configuration: Store zwave configuration in
zwcfg_<homeHex>.xmlandzwscene.xmlfiles this is needed for persistent node information like node name and location - Poll interval: Interval in milliseconds between polls (should not be less than 1s per device)
- Commands timeout: Seconds to wait before automatically stop inclusion/exclusion
- Configuration Path: The path to Openzwave devices config db
- Assume Awake: Assume Devices that support the Wakeup Class are awake when starting up OZW
- Auto Update Config File: Auto update Zwave devices database
- Hidden settings: advanced settings not visible to the user interface, you can edit these by setting in the settings.json
zwave.plugindefines a js script that will be included with thethiscontext of the zwave client, for example you could set this tohackand include ahack.jsin the root of the app withmodule.exports = zw => {zw.client.on("scan complete", () => console.log("scan complete")}zwave.optionsoverrides options passed to the zwave client seeIConstructorParametersin the open-zwave docs. For detail for examplezwave.options.options.EnforceSecureReception=trueto drop insecure messages from devices that should be secure.
Mqtt settings:
- Name: A unique name that identify the Gateway.
- Host: The url of the broker. Insert here the protocol if present, example:
tls://localhost. Mqtt supports these protocols:mqtt,mqtts,tcp,tls,wsandwss - Port: Broker port
- Reconnect period: Milliseconds between two reconnection tries
- Prefix: The prefix where all values are published
- QoS: Quality Of Service (check MQTT specs) of outgoing packets
- Retain: The retain flag of outgoing packets
- Clean: Sets the clean flag when connecting to the broker
- Store: Enable/Disable persistent storage of packets (QoS > 0). If disabled in memory storage will be used but all packets stored in memory are lost in case of shutdowns or unexpected errors.
- Allow self signed certs: When using encrypted protocols, set this to true to allow self signed certificates (WARNING this could expose you to man in the middle attacks)
- Ca Cert and Key: Certificate Authority, Client Key and Client Certificate files required for secured connections (if broker requires valid certificates, this fields can be leave empty otherwise)
- Auth: Enable this if broker requires auth. If so you need to enter also a valid username and password.
Gateway settings:
-
Gateway type: This setting specify the logic used to publish Zwave Nodes Values in MQTT topics. At the moment there are 3 possible configuration, two are automatic (all values are published in a specific topic) and one needs to manually configure which values you want to publish to MQTT and what topic to use. For every gateway type you can set custom topic values, if gateway is not in 'configure manually' mode you can omit the topic of the values (the topic will depends on the gateway type) and use the table to set values you want to
pollor if you want to scale them usingpost operation-
ValueId Topics: Automatically configured. The topic where zwave values are published will be:
<mqtt_prefix>/<?node_location>/<node_id>/<class_id>/<instance>/<index>mqtt_prefix: the prefix set in Mqtt Settingsnode_location: location of the Zwave Node (optional, if not present will not be added to the topic)node_id: the unique numerical id of the node in Zwave networkclass_id: the numerical class id of the valueinstance: the numerical value of value instanceindex: the numerical index of the value
-
Named Topics: Automatically configured. DEPRECATED After a discussion with Openzwave author lib we discourage users to use this configuration as we cannot ensure that value labels will be the same, they could change in future versions (and also they depends on localization added in OZW 1.6). You can find more info HERE
The topic where zwave values are published will be:
<mqtt_prefix>/<?node_location>/<node_name>/<class_name>/<?instance>/<value_label>mqtt_prefix: the prefix set in Mqtt Settingsnode_location: location of the Zwave Node (optional, if not present will not be added to the topic)node_name: name of the node, if not set will benodeID_<node_id>class_name: the node class name corresponding to given class id orunknownClass_<class_id>if the class name is not found?instance: Used just with multi-instance devices. The main instance (1) will not have this part in the topic but other instances will have:instance_<instance_index>value_label: the zwave value label (lower case and spaces are replaced with_)
-
Configured Manually: Needs configuration. The topic where zwave values are published will be:
<mqtt_prefix>/<?node_location>/<node_name>/<value_topic>mqtt_prefix: the prefix set in Mqtt Settingsnode_location: location of the Zwave Node (optional, if not present will not be added to the topic)node_name: name of the node, if not set will benodeID_<node_id>value_topic: the topic you want to use for that value (take from gateway values table).
-
-
Payload type: The content of the payload when an update is published:
-
JSON Time-Value: The payload will be a JSON object like:
{ "time": 1548683523859, "value": 10 } -
Entire Zwave value Object The payload will contain all info of a value from Zwave network:
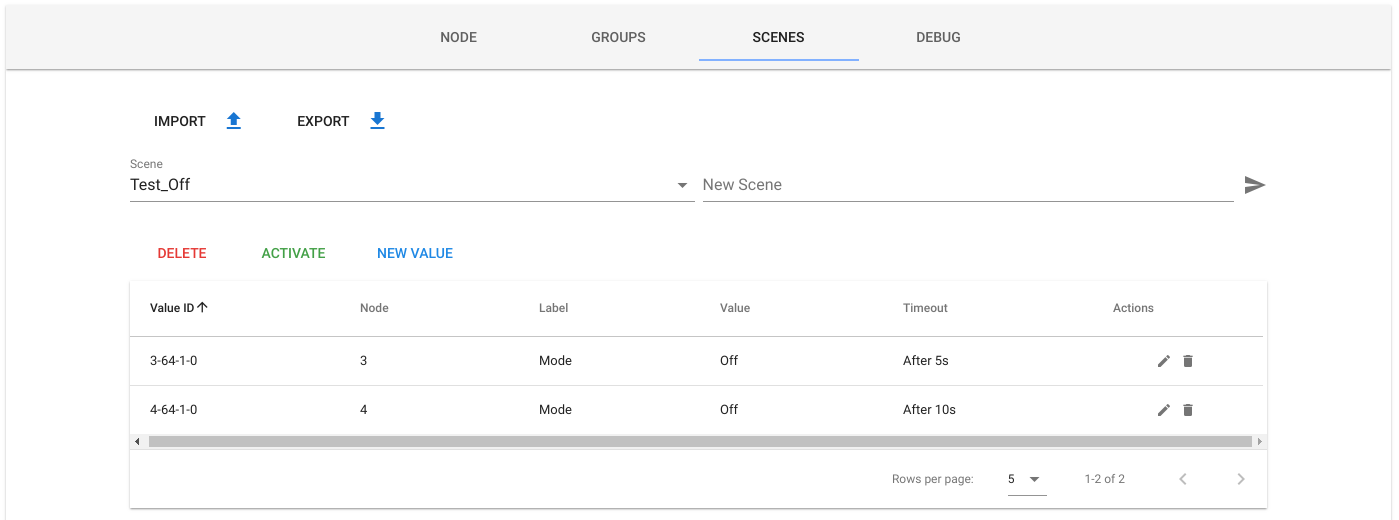
{ "value_id": "3-64-1-0", "node_id": 3, "class_id": 64, "type": "list", "genre": "user", "instance": 1, "index": 0, "label": "Mode", "units": "", "help": "", "read_only": false, "write_only": false, "min": 0, "max": 0, "is_polled": false, "values": ["Off", "Heat (Default)", "Cool", "Energy Heat"], "value": "Off" } -
Just value: The payload will contain only the row Numeric/String value
-
-
Ignore status updates: Enable this to prevent gateway to send an MQTT message when a node changes its status (dead/sleep == false, alive == true)
-
Ignore location: Enable this to remove nodes location from topics
-
Send Zwave Events: Enable this to send all Zwave client events to MQTT. More info here
-
Send 'list' as integer: Zwave 'list' values are sent as list index instead of string values
-
Use nodes name instead of numeric nodeIDs: When gateway type is
ValueIduse this flag to force to use node names instead of node ids in topic. -
⭐Hass discovery⭐: Enable this to automatically create entities on Hass using MQTT autodiscovery (more about this here)
-
Discovery Prefix: The prefix to use to send MQTT discovery messages to HASS
Once finished press SAVE and gateway will start Zwave Network Scan, than go to 'Control Panel' section and wait until the scan is completed to check discovered devices and manage them.
Settings, scenes and Zwave configuration are stored in JSON/xml files under project store folder that you can easily import/export for backup purposes.
- Node status (
trueif node is readyfalseotherwise) will be published in:
<mqtt_prefix>/<?node_location>/<node_name>/status
- Node events (value will be the event code) will be published in:
<mqtt_prefix>/<?node_location>/<node_name>/event
- Scene events will be published in:
OZW 1.4:
<mqtt_prefix>/<?node_location>/<node_name>/scene/event (value will be the scene event code)
OZW 1.6: In OZW 1.6 scenes are treated like a valueID (so the topic depends on gateway configuration). For example if the command class is 91 (central_scene) and gateway uses valueid topics
<mqtt_prefix>/<?node_location>/<node_name>/91/1/1 (value published in payload will depend on gateway payload type)
The Gateway values table can be used with all gateway types to customize specific values topic for each device type found in the network and do some operations with them. Each value has this properties:
- Device: The device type. Once scan is complete, the gateway creates an array with all devices types found in the network. A device has a
device_idthat is unique, it is composed by this node properties:<manufacturerid>-<productid>-<producttype>. - Value: The value you want to customize
- Device Class: If the value is a multilevel sensor, a binary sensor or a meter you can set a custom
device_classto use with home assistant discovery. Check sensor and binary sensor - Topic: The topic to use for this value. It is the topic added after topic prefix, node name and location. If gateway type is different than
Manualthis can be leave blank and the value topic will be the one based on the gateway configuration chosen - Post operation: If you want to convert your value (eg. '/10' '/100' '*10' '*100')
- Poll: Enable this to set the value
enablePollflag - Verify Changes: Used to verify changes of this values
- Parse Send: Enable this to allow users to specify a custom
function(value)to parse the value sent to MQTT. The function must be sync - Parse receive: Enable this to allow users to specify a custom
function(value)to parse the value received via MQTT. The function must be sync
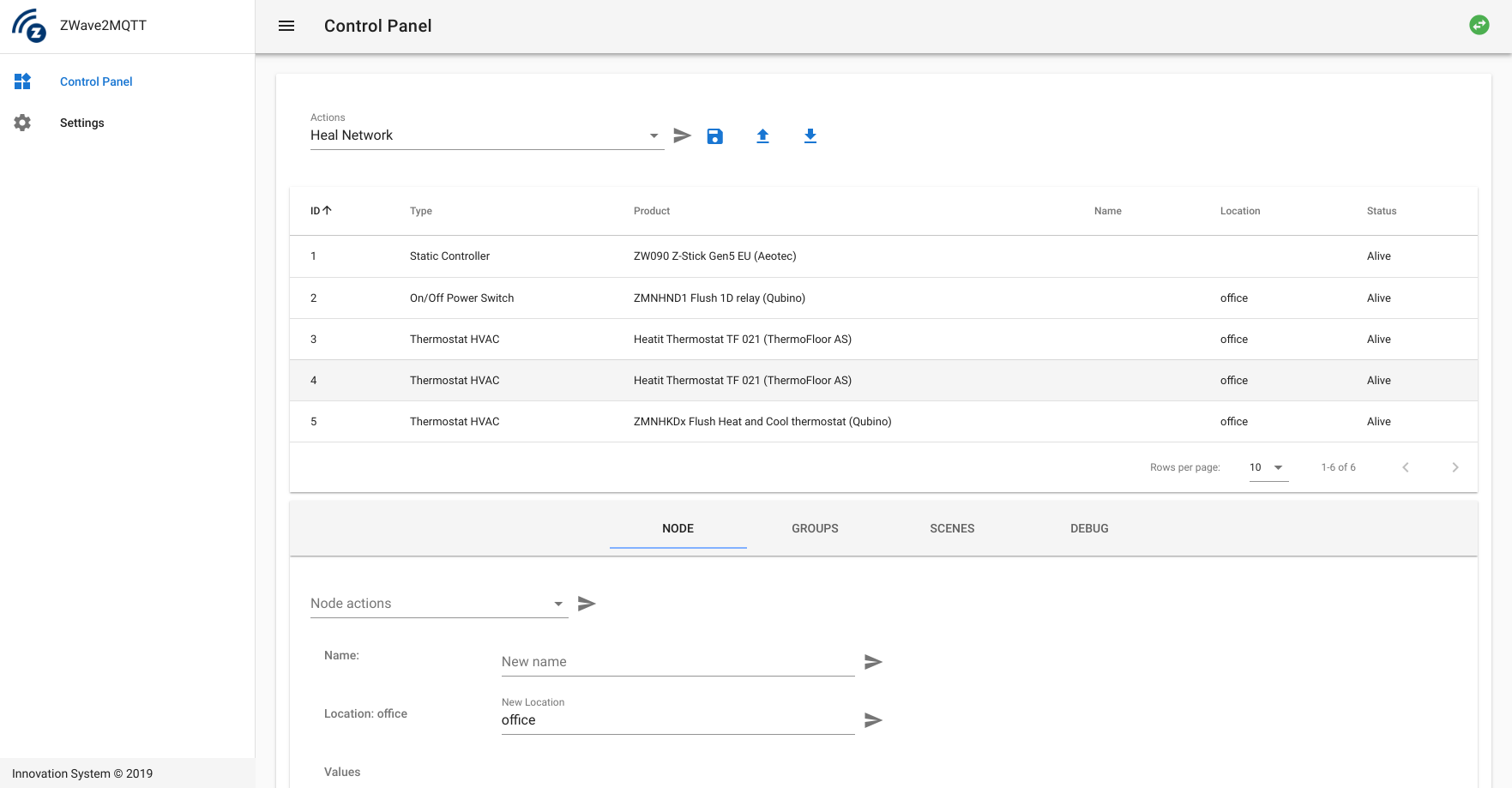
To add a node using the UI select the controller Action Add Node (inclusion), click send (:airplane:) button to enable the inclusion mode in your controller and enable the inclusion mode in your device to. Controller status will be waiting when inclusion has been successfully enabled on the controller and completed when the node has been successfully added. Wait few seconds and your node will be visible in the table once ready.
To add a node using the UI select the controller Action Remove Node (exclusion), click send (:airplane:) button to enable the exclusion mode in your controller and enable the exclusion mode in your device to. Controller status will be waiting when exclusion has been successfully enabled on the controller and completed when the node has been successfully removed. Wait few seconds and your node will be removed from the table.
To replace a failed node from the UI you have to use the command Replace Failed Node, if everything is ok the controller will start inclusion mode and status will be Waiting, now enable inclusion on your device to add it to the network by replacing the failed one.
If a node is missing or marked as dead. There is a way to cleanup the controller by executing Remove Failed Node. This will forcebly delete the node from the controller.
It can only succeed if:
- Node has ben first marked as failed using
Has node failed - Marked as Dead by the controller
Alive and Sleeping nodes cannot be deleted.
- Configurable Zwave to Mqtt Gateway
- Home Assistant integration (beta)
- Zwave Control Panel:
- Nodes management: check all nodes discovered in the z-wave network, send/receive nodes values updates directly from the UI and send action to the nodes and controller for diagnostics and network heal
- Custom Node naming and Location: Starting from v1.3.0 nodes
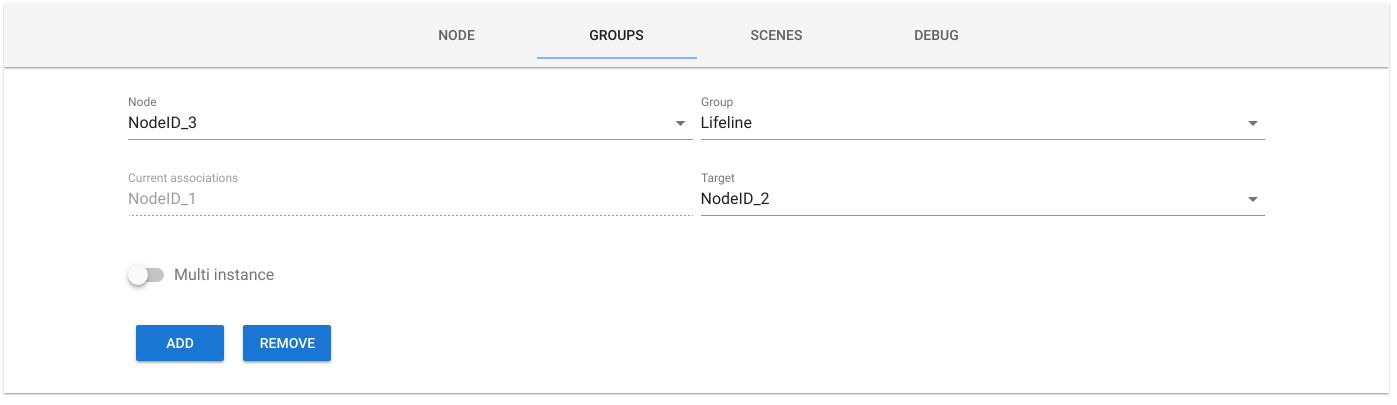
nameandlocationare stored in a JSON file namednodes.json. This because not all nodes have native support for naming and location features (#45). This change is back compatible with older versions of this package: on startup it will get all nodes names and location from thezwcfg_homeHEX.xmlfile (if present) and create the newnodes.jsonfile based on that. This file can be imported/exported from the UI control panel with the import/export buttons placed on the top of nodes table, on the right of controller actions select. - Groups associations: create associations between nodes (also supports multi-instance associations, need to use last version of openzwave-shared)
- Custom scenes management: (OpenZwave-Shared scenes management has actually some bugs and it's limited so I have made a custom scenes implementation that uses the same APIs but stores values in a JSON file that can be imported/exported and also allows to set a timeout to a value in a scene)
- Log debug in UI
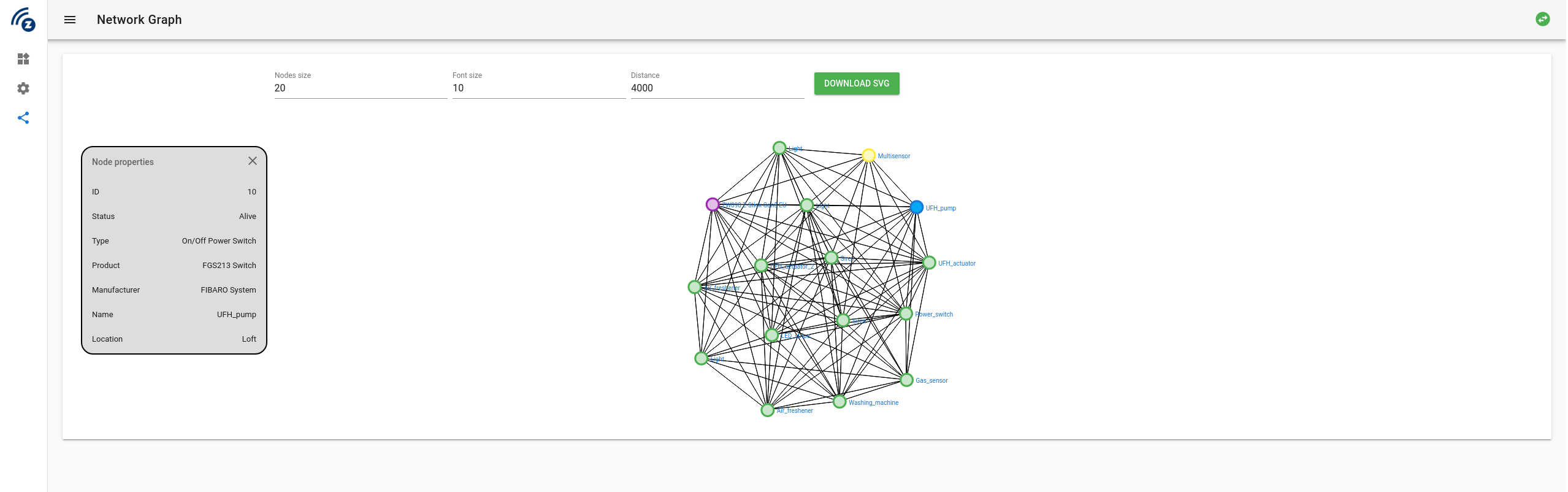
- Mesh graph showing devices neighbors
At least Home Assistant >= 0.84 is required!
The easiest way to integrate Zwave2Mqtt with Home Assistant is by using MQTT discovery. This allows Zwave2Mqtt to automatically add devices to Home Assistant. To enable this feature remember to set the flag Hass Discovery in Gateway settings configuration.
ATTENTION: Hass updates often break Zwave2Mqtt device discovery. For this reason Zwave2Mqtt will try to be always compatible with latest hass version. Check the changelog before update!
To achieve the best possible integration (including MQTT discovery):
- In your Zwave2Mqtt gateway settings enable
Homeassistant discoveryflag and enable the MQTT retain too. The retain flag for MQTT is suggested to be sure that, once discovered, each device get the last value published (otherwise you have to wait for a value change)
NB: Starting from version 4.0.0 the default Birth/Will topic is homeassistant/status in order to reflect defaults birth/will of Hass 0.113 th
- In your Home Assistant
configuration.yaml:
mqtt:
discovery: true
discovery_prefix: <your_discovery_prefix>
broker: [YOUR MQTT BROKER] # Remove if you want to use builtin-in MQTT broker
birth_message:
topic: 'hass/status' # or homeassistant/status if z2m version >= 4.0.0
payload: 'online'
will_message:
topic: 'hass/status' # or homeassistant/status if z2m version >= 4.0.0
payload: 'offline'Mind you that if you want to use the embedded broker of Home Assistant you have to follow this guide.
Zwave2Mqtt is expecting Home Assistant to send it's birth/will
messages to hass/status (or homeassistant/status if z2m version >= 4.0.0). Be sure to add this to your configuration.yaml if you want
Zwave2Mqtt to resend the cached values when Home Assistant restarts.
Zwave2Mqtt try to do its best to guess how to map devices from Zwave to HASS. At the moment it try to guess the device to generate based on zwave values command classes, index and units of the value. When the discovered device doesn't fit your needs you can you can set custom a device_class to values using Gateway value table.
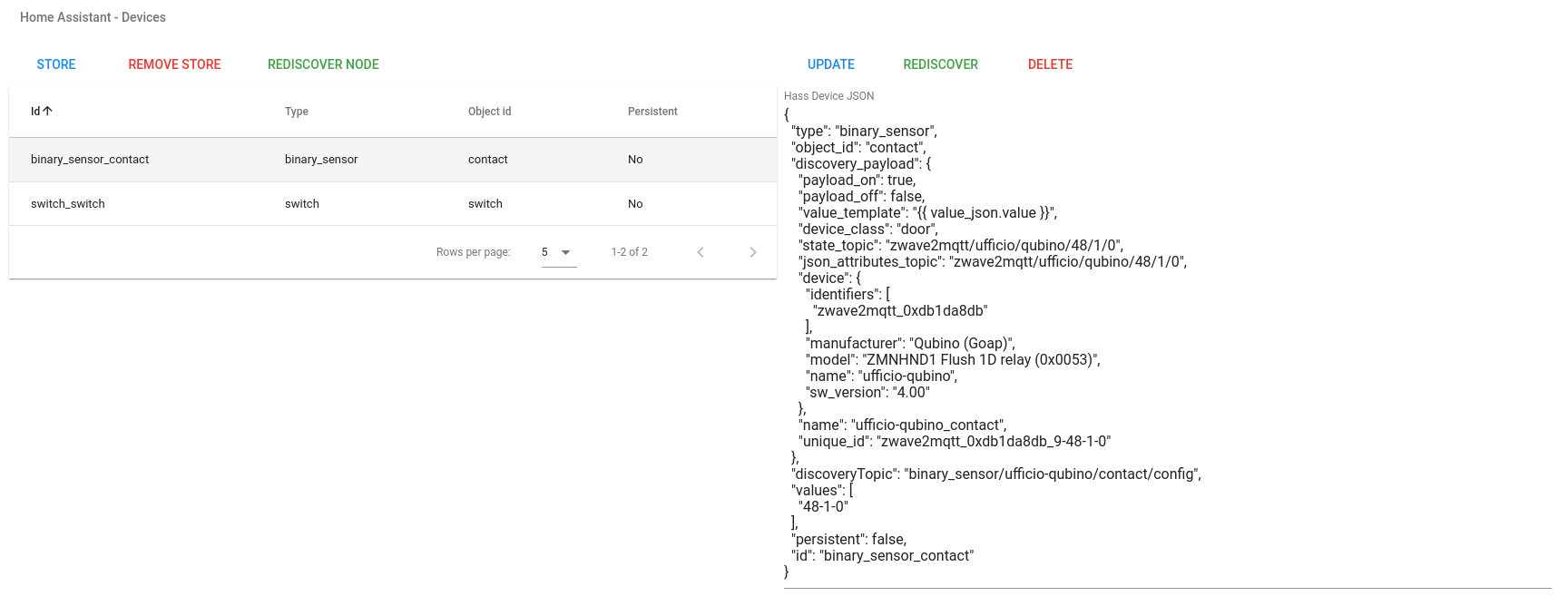
To see the components that have been discovered by Zwave2Mqtt go to Control Panel UI, select a Node from the Nodes table then select the Node tab from tabs menu at the bottom of Nodes table. Now at the Bottom of the page, after Node values section you can find a new section called Home Assistant - Devices. Here you will see a table with all devices created for the selected node.
ATTENTION
Once edited the devices will loose all their customizations after a restart. To prevent this you can store the node hassDevices by pressing STORE button at the top of hass devices table. By pressing it the hassDevices will be stored in nodes.json file that can be imported/exported easily from control panel UI at the top of nodes table.
If you update node name/location you have to also rediscover values of this node as they may have wrong topics. To do this press on REDISCOVER NODE green button on top of Home Assistant - Devices table (check previous picture)
If you select a device it's configuration will be displayed as a JSON object on the right. With the selected device you can edit it and send some actions:
Update: Update in-memory hass device configurationRediscover: Re-discover this device using thediscoveryTopicanddiscovery_payloadof the configurationDelete: Delete the device from Hass entities of selected node
If no device is selected you can manually insert a device JSON configuration. If the configuration is valid you can press the button Add to add it to devices. If the process complete successfully the device will be added to the Hass Devices table and you can now select it from the table and press on Rediscover to discover your custom device
At the moment auto discovery just creates components like sensor, cover binary_sensor and switch. For more complex components like climate and fan you need to provide a configuration. Components configurations are stored in hass/devices.js file. Here are contained all components that Zwave2MQTT needs to create for each Zwave device type. The key is the Zwave device unique id (<manufacturerid>-<productid>-<producttype>) the value is an array with all HASS components to create for that Zwave Device.
UPDATE: Starting from version 2.0.7 you can specify your custom devices configuration inside store/customDevices(.js|.json) file. This allows users that use Docker to create their custom hass devices configuration without the need to build a new container. If using .json format Zwave2Mqtt will watch for file changes and automatically load new components on runtime without need to restart the application.
ONCE YOU SUCCESSFULLY INTEGRATE NEW COMPONENTS PLEASE SEND A PR!
Starting from version 2.2.0 device id is shown on node tab of control panel before the inputs for update the node name and locations.
Before version 2.2.0 you can get the device id in this ways:
First (and easier) option is to add a random value in gateway values table for the desired device, the device id will be visible in first column of the table (Devices) between square brackets [<deviceID>] Device Name
Second option would be to retrieve it from here. Each device has Manufacturerid, product id and a product type in HEX format and needs to be converted in decimal:
<Manufacturer id="019b" name="ThermoFloor AS">
<Product config="thermofloor/heatit021.xml" id="0001" name="Heatit Thermostat TF 021" type="0001"/>
<Product config="thermofloor/heatit056.xml" id="0202" name="Heatit Thermostat TF 056" type="0003"/>
<Product config="thermofloor/heatit-zdim.xml" id="2200" name="Heatit ZDim" type="0003"/>
</Manufacturer>In this example, if we have choose Heatit Thermostat TF 056:
- Manufacturer Id:
19b-->411 - Product Id:
202-->514 - Product type:
3-->3
So in decimal format will become: 411-514-3. This is the device id of Heatit Thermostat TF 056
{
"411-1-1":[
{ // Heatit Thermostat TF 021 (ThermoFloor AS)
"type": "climate",
"object_id": "thermostat",
"values": ["64-1-0", "49-1-1", "67-1-1", "67-1-2"],
"mode_map": {"off": "Off", "heat": "Heat (Default)", "cool": "Cool"},
"setpoint_topic": { "Heat (Default)": "67-1-1", "Cool": "67-1-2" },
"default_setpoint": "67-1-1",
"discovery_payload": {
"min_temp": 15,
"max_temp": 30,
"modes": ["off", "heat", "cool"],
"mode_state_topic": "64-1-0",
"mode_command_topic": true,
"current_temperature_topic": "49-1-1",
"current_temperature_template": "{{ value_json.value }}",
"temperature_state_template": "{{ value_json.value }}",
"temperature_command_topic": true
}
}
]
}- type: The hass MQTT component type
- object_id: The unique id of this object (must be unique for the device)
- values: Array of values used by this component
- mode_map: Key-Value object where keys are MQTT Climate modes and values are the matching thermostat modes values
- setpoint_topic: Key-Value object where keys are the modes of the Zwave thermostat and values are the matching setpoint
value_id(use this if your thermostat has more than one setpoint) - default_setpoint: The default thermostat setpoint.
- discovery_payload: The payload sent to hass to discover this device. Check here for a list with all supported options
- min_temp/max_temp: Min/Max temperature of the thermostat
- modes: Array of Hass Climate supported modes. Allowed values are
[“auto”, “off”, “cool”, “heat”, “dry”, “fan_only”] - mode_state_topic:
value_idof mode value - current_temperature_topic:
value_idof current temperature value - current_temperature_template/temperature_state_template: Template used to fetch the value from the MQTT payload
- temperature_command_topic/mode_command_topic: If true this values are subscribed to this topics to send commands from Hass to change this values
Thermostats are most complex components to create, in this device example the setpoint topic changes based on the mode selected. Zwave2Mqtt handles the mode changes by updating the device discovery payload to match the correct setpoint based on the mode selected.
{ // GE 1724 Dimmer
"type": "fan",
"object_id": "dimmer",
"values": ["38-1-0"],
"discovery_payload": {
"command_topic": "38-1-0",
"speed_command_topic": "38-1-0",
"speed_state_topic": "38-1-0",
"state_topic": "38-1-0",
"speeds": ["off", "low", "medium", "high"],
"payload_low_speed": 24,
"payload_medium_speed": 50,
"payload_high_speed": 99,
"payload_off": 0,
"payload_on": 99,
"state_value_template": "{% if (value_json.value | int) == 0 %} 0 {% else %} 99 {% endif %}",
"speed_value_template": "{% if (value_json.value | int) == 25 %} 24 {% elif (value_json.value | int) == 51 %} 50 {% elif (value_json.value | int) == 99 %} 99 {% else %} 0 {% endif %}"
}
}- type: The hass MQTT component type
- object_id: The unique id of this object (must be unique for the device)
- values: Array of values used by this component
- discovery_payload: The payload sent to hass to discover this device. Check here for a list with all supported options
- command_topic: The topic to send commands
- state_topic: The topic to receive state updates
- speed_command_topic: The topic used to send speed commands
- state_value_template: The template used to set the value ON/OFF based on the payload received
- speed_value_template: The template to use to set the speed
["off", "low", "medium", "high"]based on the payload received
The main template is like the thermostat template. The things to add are:
{ // GoControl GC-TBZ48 (Linear Nortek Security Control LLC)
"type": "climate",
"object_id": "thermostat",
"values": [
"49-1-1",
"64-1-0",
"66-1-0", // <-- add fan values
"67-1-1",
"67-1-2",
"68-1-0" // <-- add fan values
],
"fan_mode_map": { // <-- add fan modes map
"on": "On",
"auto": "Auto"
},
"mode_map": {
"off": "Off",
"heat": "Heat",
"cool": "Cool",
"auto": "Auto"
},
"setpoint_topic": {
"Heat": "67-1-1",
"Cool": "67-1-2"
},
"default_setpoint": "67-1-1",
"discovery_payload": {
"min_temp": 60,
"max_temp": 85,
"modes": [
"off",
"heat",
"cool",
"auto"
],
"fan_modes": [ // <-- add fan supported modes
"on",
"auto"
],
"action_topic": "66-1-0",
"mode_state_topic": "64-1-0",
"mode_command_topic": true,
"current_temperature_topic": "49-1-1",
"current_temperature_template": "{{ value_json.value }}",
"temperature_state_template": "{{ value_json.value }}",
"temperature_low_command_topic": true,
"temperature_low_state_template": "{{ value_json.value }}",
"temperature_high_command_topic": true,
"temperature_high_state_template": "{{ value_json.value }}",
"fan_mode_command_topic": true,
"fan_mode_state_topic": "68-1-0" // <-- add fan state topic
}
}You have full access to all Openzwave-Shared APIs (and more) by simply using MQTT.
If Send Zwave Events flag of Gateway settings section is enabled all Zwave events are published to MQTT. Here you can find a list with all available events
Topic
<mqtt_prefix>/_EVENTS_/ZWAVE_GATEWAY-<mqtt_name>/<event name>
Payload
{
"data": [ "1.4.3319" ] // an array containing all args in order
}Topic
zwave2mqtt/_EVENTS/ZWAVE_GATEWAY-z2m/node_ready
Payload
{
"data": [
1,
{
"manufacturer": "AEON Labs",
"manufacturerid": "0x0086",
"product": "ZW090 Z-Stick Gen5 EU",
"producttype": "0x0001",
"productid": "0x005a",
"type": "Static PC Controller",
"name": "",
"loc": ""
}
]
}To call a Zwave API you just need to publish a JSON object like:
{
"args": [2, 1]
}Where args is an array with the args used to call the api, the topic is:
<mqtt_prefix>/_CLIENTS/ZWAVE_GATEWAY-<mqtt_name>/api/<api_name>/set
The result will be published on the same topic without /set
Example: If I publish the previous json object to the topic
zwave/_CLIENTS/ZWAVE_GATEWAY-office/api/getAssociations/set
I will get this response (in the same topic without the suffix /set):
{
"success": true,
"message": "Success zwave api call",
"result": [1]
}result will contain the value returned from the API. In this example I will get an array with all node IDs that are associated to the group 1 (lifeline) of node 2.
There are some custom apis that can be called that are not part of Zwave Client:
- All Zwave Clients scenes management methods if preceeded by a
_will use the internal scenes management instead of OZW scenes:_createScene_removeScene_setScenes_getScenes_sceneGetValues_addSceneValue_removeSceneValue_activateScene
_setNodeNameand_setNodeLocationwill use internal nodes store to save nodes names/locations in a json filerefreshNeighborns: Returns an Array, the Array index is the nodeId, array value is an Array with all node neighbornsgetNodes: Returns an array with all nodes in the network (and their info/valueids)getInfo: Returns an object with:homeid: homeIdname: homeId Hexversion: OpenZwave versionuptime: Seconds from when the app process is started. It's the result ofprocess.uptime()lastUpdate: Timestamp of latest event received from OZWstatus: Client status. Could be: 'driverReady', 'connected', 'scanDone', 'driverFailed', 'closed'cntStatus: Controller status received from ozw notifications controller command. If inclusion/exclusion is running it wold beWaiting
To write a value using MQTT you just need to send the value to set in the same topic where the value updates are published by adding the suffix /set to the topic (READONLY VALUES CANNOT BE WRITE).
Example with gateway configured with named topics:
If I publish the value 25.5 (also a payload with a JSON object with the value in value property is accepted) to the topic
zwave/office/nodeID_4/thermostat_setpoint/heating/set
I will set the Heating setpoint of the node with id 4 located in the office to 25.5. To check if the value has been successfully write just check when the value changes on the topic:
zwave/office/nodeID_4/thermostat_setpoint/heating
You can send broadcast values to all values with a specific suffix in the network.
Broadcast API is accessible from:
<mqtt_prefix>/_CLIENTS/ZWAVE_GATEWAY-<mqtt_name>/broadcast/<value_topic_suffix>/set
value_topic_suffix: the suffix of the topic of the value I want to control using broadcast.
It works like the set value API without the node name and location properties.
If the API is correctly called the same payload of the request will be published
to the topic without /set suffix.
Example of broadcast command (gateway configured as named topics):
zwave/_CLIENTS/ZWAVE_GATEWAY-test/broadcast/thermostat_setpoint/heating/set
Payload: 25.5
All nodes with command class thermostat_setpoint and value heating will be set to 25.5 and I will get the same value on the topic:
zwave/_CLIENTS/ZWAVE_GATEWAY-test/broadcast/thermostat_setpoint/heating
/health: Returns 200 if both mqtt and zwave client are connected, 500 otherwise
/health/mqtt: Returns 200 if mqtt client is connected, 500 otherwise
/health/zwave: Returns 200 if zwave client is connected, 500 otherwise
Remember to add the header: Accept: text/plain to your request.
Example: curl localhost:8091/health/zwave -H "Accept: text/plain"
Note: Each one of the following environment variables corresponds to their respective options in the UI settings and options saved in the UI take presence over these environment variables.
OZW_NETWORK_KEYOZW_SAVE_CONFIGOZW_POLL_INTERVALOZW_AUTO_UPDATE_CONFIGOZW_CONFIG_PATHOZW_ASSUME_AWAKE
A: Why when I add a value to Gateway values table I don't see all my devices?
B: When adding values to the gateway values table it shows JUST ONE DEVICE FOR EACH TYPE. This is to make it easier and faster to setup your network as if you have a network with lot devices (light, light dimmers for example) you just need to add the values you want to bridge to mqtt (for a light it will always be just the switch to turn it on/off for exmple without all configuration values) and it will bridge those values for all the devices of that type (without configure the values one by one).
A: My device is X and has been discovered as Y, why?
B: Hass Discovery is not easy, zwave have many different devices with different values. To try to understand how to discover a specific value I have used this file that shows what kind of value is expeted based on value class and index. Unfortunally not all devices respect this specifications so for those cases I have created Hass Devices table where you can manually fix the discovery payload and than save it to make it persistent. I have also created a file /hass/devices.js where I place all devices specific values configuration, your contribution is needed there, so submit a PR with your files specification to help it grow.
Thanks to this people for help with issues tracking and contributions:
- Better logging
- Dockerize application
- Package application with PKG
- HASS integration, check zigbee2mqtt
- Add unit test
- JSON validator for settings and scenes
- Better nodes status management using 'testNode'
- Network graph to show neighbours using vue-d3-network
Support me on Patreon ❤️