This is the code for the following paper:
Bugra Tekin, Sudipta N. Sinha and Pascal Fua, "Real-Time Seamless Single Shot 6D Object Pose Prediction", CVPR 2018.
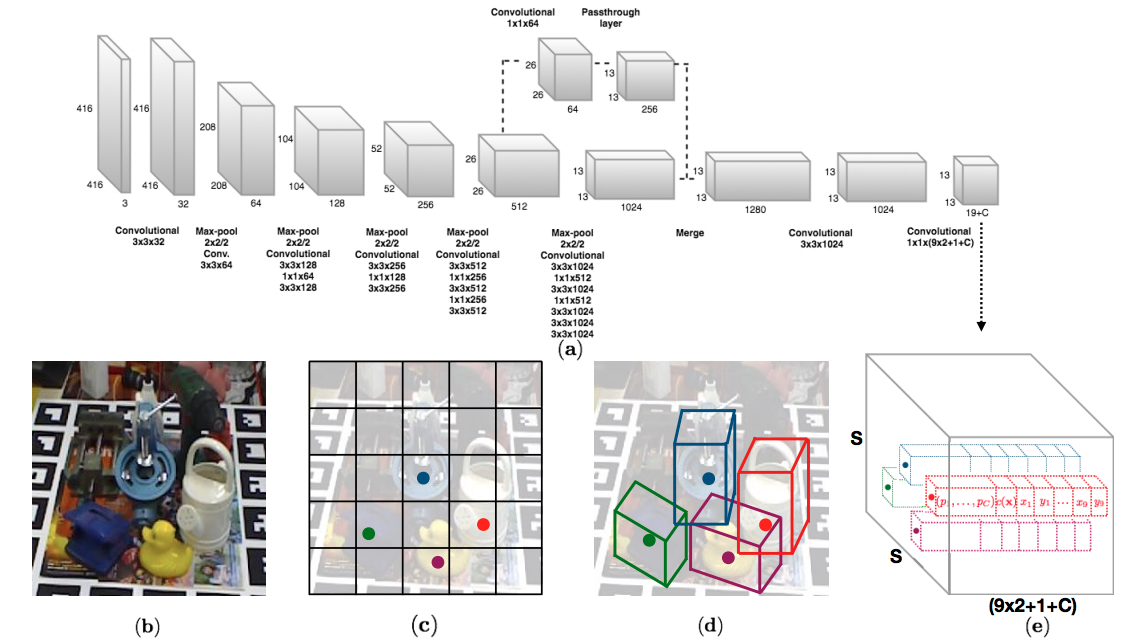
We propose a single-shot approach for simultaneously detecting an object in an RGB image and predicting its 6D pose without requiring multiple stages or having to examine multiple hypotheses. The key component of our method is a new CNN architecture inspired by the YOLO network design that directly predicts the 2D image locations of the projected vertices of the object's 3D bounding box. The object's 6D pose is then estimated using a PnP algorithm. Paper, arXiv
If you use this code, please cite the following
@inproceedings{tekin18,
TITLE = {{Real-Time Seamless Single Shot 6D Object Pose Prediction}},
AUTHOR = {Tekin, Bugra and Sinha, Sudipta N. and Fua, Pascal},
BOOKTITLE = {CVPR},
YEAR = {2018}
}
SingleShotPose is released under the MIT License (refer to the LICENSE file for details).
The code is tested on Linux with CUDA v8 and cudNN v5.1. The implementation is based on PyTorch 0.3.1 and tested on Python2.7. The code requires the following dependencies that could be installed with conda or pip: numpy, scipy, PIL, opencv-python
Inside the main code directory, run the following to download and extract (1) the preprocessed LINEMOD dataset, (2) trained models for the LINEMOD dataset, (3) the trained model for the OCCLUSION dataset, (4) background images from the VOC2012 dataset respectively.
wget -O LINEMOD.tar --no-check-certificate "https://onedrive.live.com/download?cid=05750EBEE1537631&resid=5750EBEE1537631%21135&authkey=AJRHFmZbcjXxTmI"
wget -O backup.tar --no-check-certificate "https://onedrive.live.com/download?cid=0C78B7DE6C569D7B&resid=C78B7DE6C569D7B%21191&authkey=AP183o4PlczZR78"
wget -O multi_obj_pose_estimation/backup_multi.tar --no-check-certificate "https://onedrive.live.com/download?cid=05750EBEE1537631&resid=5750EBEE1537631%21136&authkey=AFQv01OSbvhGnoM"
wget https://pjreddie.com/media/files/VOCtrainval_11-May-2012.tar
wget https://pjreddie.com/media/files/darknet19_448.conv.23 -P cfg/
tar xf LINEMOD.tar
tar xf backup.tar
tar xf multi_obj_pose_estimation/backup_multi.tar -C multi_obj_pose_estimation/
tar xf VOCtrainval_11-May-2012.tar
Alternatively, you can directly go to the links above and manually download and extract the files at the corresponding directories. The whole download process might take a long while (~60 minutes).
To train the model run,
python train.py datafile cfgfile initweightfile
e.g.
python train.py cfg/ape.data cfg/yolo-pose.cfg backup/ape/init.weights
[datafile] contains information about the training/test splits and 3D object models
[cfgfile] contains information about the network structure
[initweightfile] contains initialization weights. The weights "backup/[OBJECT_NAME]/init.weights" are pretrained on LINEMOD for faster convergence. We found it effective to pretrain the model without confidence estimation first and fine-tune the network later on with confidence estimation as well. "init.weights" contain the weights of these pretrained networks. However, you can also still train the network from a more crude initialization (with weights trained on ImageNet). This usually results in a slower and sometimes slightly worse convergence. You can find in cfg/ folder the file <<darknet19_448.conv.23>> that includes the network weights pretrained on ImageNet. Alternatively, you can pretrain your own weights by setting the regularization parameter for the confidence loss to 0 as explained in "Pretraining the model" section.
At the start of the training you will see an output like this:
layer filters size input output
0 conv 32 3 x 3 / 1 416 x 416 x 3 -> 416 x 416 x 32
1 max 2 x 2 / 2 416 x 416 x 32 -> 208 x 208 x 32
2 conv 64 3 x 3 / 1 208 x 208 x 32 -> 208 x 208 x 64
3 max 2 x 2 / 2 208 x 208 x 64 -> 104 x 104 x 64
...
30 conv 20 1 x 1 / 1 13 x 13 x1024 -> 13 x 13 x 20
31 detection
This defines the network structure. During training, the best network model is saved into the "model.weights" file. To train networks for other objects, just change the object name while calling the train function, e.g., "python train.py cfg/duck.data cfg/yolo-pose.cfg backup/duck/init.weights"
To test the model run
python valid.py datafile cfgfile weightfile
e.g.,
python valid.py cfg/ape.data cfg/yolo-pose.cfg backup/ape/model_backup.weights
[weightfile] contains our trained models.
Models are already pretrained but if you would like to pretrain the network from scratch and get the initialization weights yourself, you can run the following:
python train.py cfg/ape.data cfg/yolo-pose-pre.cfg cfg/darknet19_448.conv.23 cp backup/ape/model.weights backup/ape/init.weights
During pretraining the regularization parameter for the confidence term is set to "0" in the config file "cfg/yolo-pose-pre.cfg". "darknet19_448.conv.23" includes the weights of YOLOv2 trained on ImageNet.
Inside multi_obj_pose_estimation/ folder
Testing:
python valid_multi.py cfgfile weightfile
e.g.,
python valid_multi.py cfg/yolo-pose-multi.cfg backup_multi/model_backup.weights
Training:
python train_multi.py datafile cfgfile weightfile
e.g.,
python train_multi.py cfg/occlusion.data cfg/yolo-pose-multi.cfg backup_multi/init.weights
Our label files consist of 21 values. We predict 9 points corresponding to the centroid and corners of the 3D object model. Additionally we predict the class in each cell. That makes 9x2+1 = 19 points. In multi-object training, during training, we assign whichever anchor box has the most similar size to the current object as the responsible one to predict the 2D coordinates for that object. To encode the size of the objects, we have additional 2 numbers for the range in x dimension and y dimension. Therefore, we have 9x2+1+2 = 21 numbers.
Respectively, 21 numbers correspond to the following: 1st number: class label, 2nd number: x0 (x-coordinate of the centroid), 3rd number: y0 (y-coordinate of the centroid), 4th number: x1 (x-coordinate of the first corner), 5th number: y1 (y-coordinate of the first corner), ..., 18th number: x8 (x-coordinate of the eighth corner), 19th number: y8 (y-coordinate of the eighth corner), 20th number: x range, 21st number: y range.
The coordinates are normalized by the image width and height: x / image_width and y / image_height. This is useful to have similar output ranges for the coordinate regression and object classification tasks.
To train on your own dataset, simply create the same folder structure with the provided LINEMOD dataset and adjust the paths in cfg/[OBJECT].data, [DATASET]/[OBJECT]/train.txt and [DATASET]/[OBJECT]/test.txt files. The folder for each object should contain the following:
(1) a folder containing image files,
(2) a folder containing label files (labels should be created using the same output representation explained above),
(3) a text file containing the training images (train.txt),
(4) a text file contraining the test images (test.txt),
(5) a .ply file containing the 3D object model
(6) optionally, a folder containing segmentation masks (if you want to change the background of your training images to be more robust to diverse backgrounds),
The code is written by Bugra Tekin and is built on the YOLOv2 implementation of the github user @marvis
For any questions or bug reports, please contact Bugra Tekin