Table of contents
- What is Frogbot?
- Pull requests scanning
- Pull requests opening
- Installing and using Frogbot
- Contributions
🤖 What is Frogbot?
Frogbot is a Git bot that does the following:
- Scans pull requests for security vulnerabilities.
- Opens pull requests with fixes for security vulnerabilities.
Pull requests scanning
General
Frogbot uses JFrog Xray to scan your pull requests. It adds the scan results as a comment on the pull request. If no new vulnerabilities are found, Frogbot will also add a comment, confirming this. For pull requests scanning, please note that GitHub, GitLab and Bitbucket Server are supported. Projects that use one of the following tools to download their dependencies are currently supported.
- Npm
- Maven
- Gradle
- Go
- Pip
- Pipenv
- Nuget
- Dotnet
🕵️♀️ How does pull requests scanning work?
GitHub
For security reasons, Frogbot is not triggered automatically. After you create a new pull request, the maintainer of the git repository can trigger Frogbot to scan the pull request from the pull request UI. The scan output will include only new vulnerabilities added by the pull request. Vulnerabilities that aren't new, and existed in the code prior to the pull request creation, will not be included in the report.
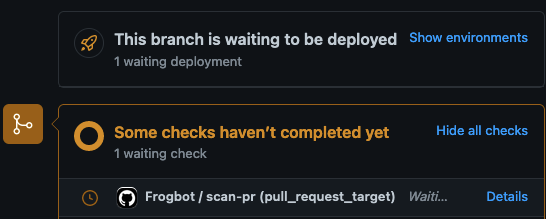
- A developer opens a pull request.
- The Frogbot workflow automatically gets triggered and a GitHub environment named frogbot is pending for the maintainer's approval:
- A Maintainer reviews the pull request and approves the scan:

- Frogbot can be triggered again following new commits, by repeating steps 2 and 3.
GitLab
For security reasons, Frogbot is not triggered automatically. After you create a new pull request, the maintainer of the git repository can trigger Frogbot to scan the pull request from the pull request UI. The scan output will include only new vulnerabilities added by the pull request. Vulnerabilities that aren't new, and existed in the code prior to the pull request creation, will not be included in the report.
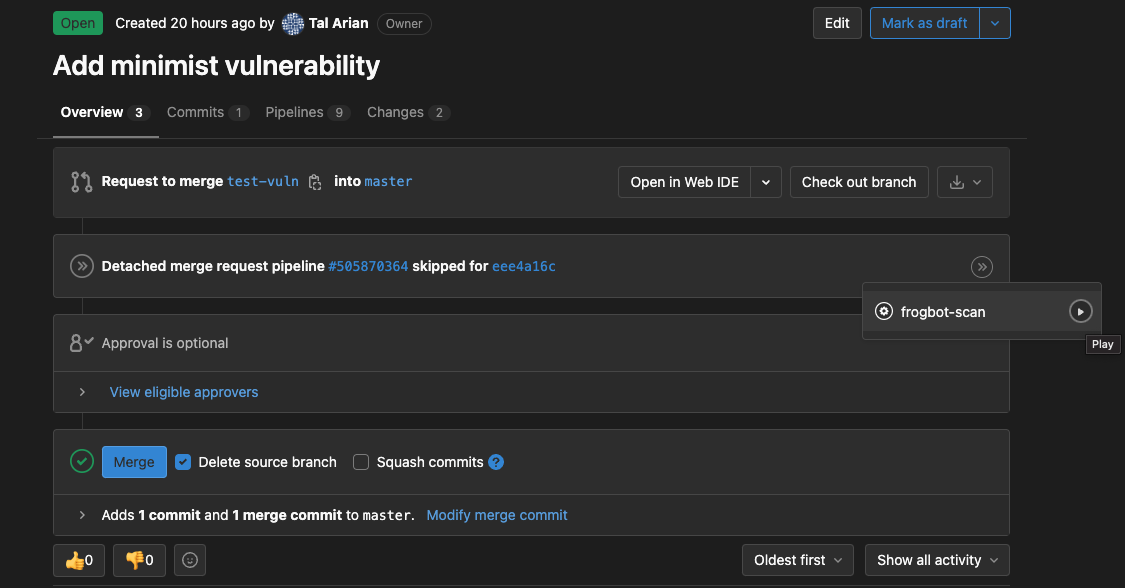
- A developer opens a merge request.
- A maintainer of the repository triggers the manual frogbot-scan job.
- Frogbot is triggered by the job, scans the merge request, and adds a comment with the scan results.
- Frogbot can be triggered again following new commits, by triggering the frogbot-scan job again.
[
 ]
]
Bitbucket Server
After you create a new pull request, Frogbot will automatically scan it. The scan output will include only new vulnerabilities added by the pull request. Vulnerabilities that aren't new, and existed in the code prior to the pull request creation, will not be included in the report.
- A developer opens a pull request.
- Frogbot is triggered and scans the pull request, and adds a comment with the scan results.
- Frogbot can be triggered again following new commits, by adding a comment with the
rescantext.
Pull request comments
👍 No issues
If no new vulnerabilities are found, Frogbot automatically adds the following comment to the pull request:
👎 Issues were found
If new vulnerabilities are found, Frogbot adds them as a comment on the pull request. For example:
Pull requests opening
Frogbot scans your Git repository and automatically opens pull requests for upgrading vulnerable dependencies to a version with a fix. Frogbot uses JFrog Xray for the scanning. The scanning is triggered following commits that are pushed to the repository. For pull requests opening, please note that GitHub and GitLab are currently supported and Bitbucket will be supported soon. Projects that use one of the following tools to download their dependencies are currently supported.
- npm
- Maven
- Go
🖥️ Installing and using Frogbot
General
- Frogbot requires a JFrog environment to scan pull requests. Don't have a JFrog environment? No problem - Set Up a FREE JFrog Environment in the Cloud. You'll later save the connection details (URL, username, and password) as secrets in Git.
- Setting up Frogbot on GitHub repositories
- Setting up Frogbot on GitLab repositories
- Setting up Frogbot on Bitbucket Server repositories
Set up a FREE JFrog Environment in the cloud
Need a FREE JFrog environment in the cloud, so Frogbot can scan your pull requests?
Just run one of the following commands in your terminal, to set up an environment in less than a minute. The commands will do the following:
- Install JFrog CLI on your machine.
- Create a FREE JFrog environment in the cloud for you.
After the setup is complete, you'll receive an email with your JFrog environment connection details, which you can then store as secrets in Git.
On macOS and Linux using cUrl
curl -fL https://getcli.jfrog.io?setup | sh
On Windows using PowerShell
powershell "Start-Process -Wait -Verb RunAs powershell '-NoProfile iwr https://releases.jfrog.io/artifactory/jfrog-cli/v2-jf/[RELEASE]/jfrog-cli-windows-amd64/jf.exe -OutFile $env:SYSTEMROOT\system32\jf.exe'" ; jf setup
Setting up Frogbot on GitHub repositories
Frogbot is installed on GitHub repositories using GitHub Actions. Here's how you install it:
-
Make sure you have the connection details of your JFrog environment.
-
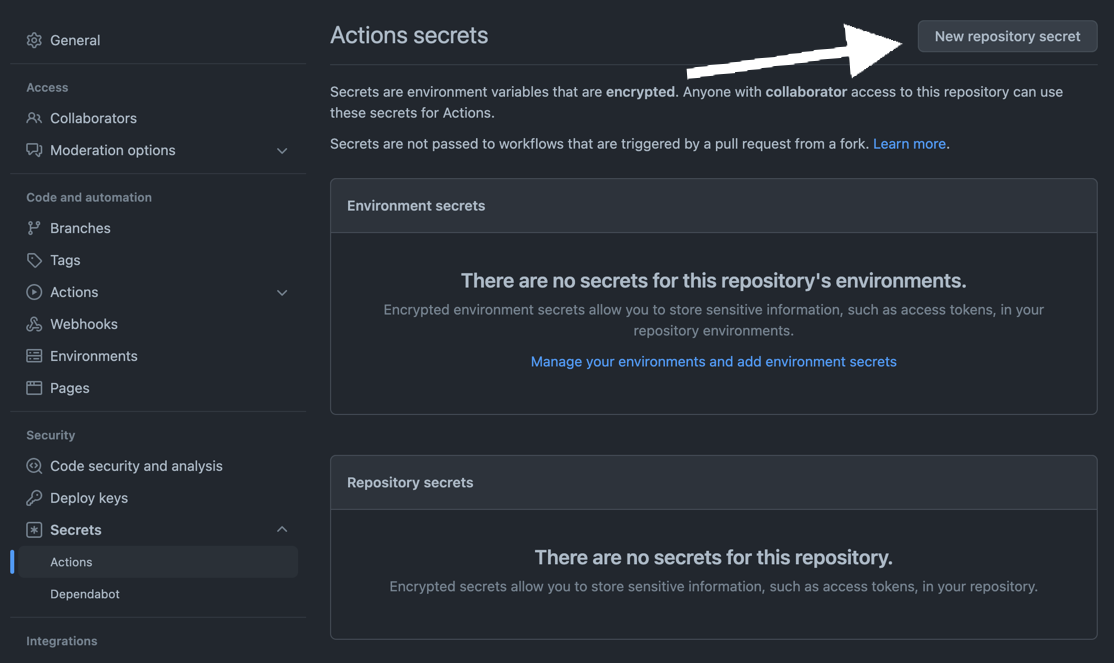
At your GitHub repository settings, save the JFrog connection details as repository secrets with the following names - JF_URL, JF_USER, and JF_PASSWORD (You can also use JF_XRAY_URL and JF_ARTIFACTORY_URL instead of JF_URL, and JF_ACCESS_TOKEN instead of JF_USER and JF_PASSWORD)
-
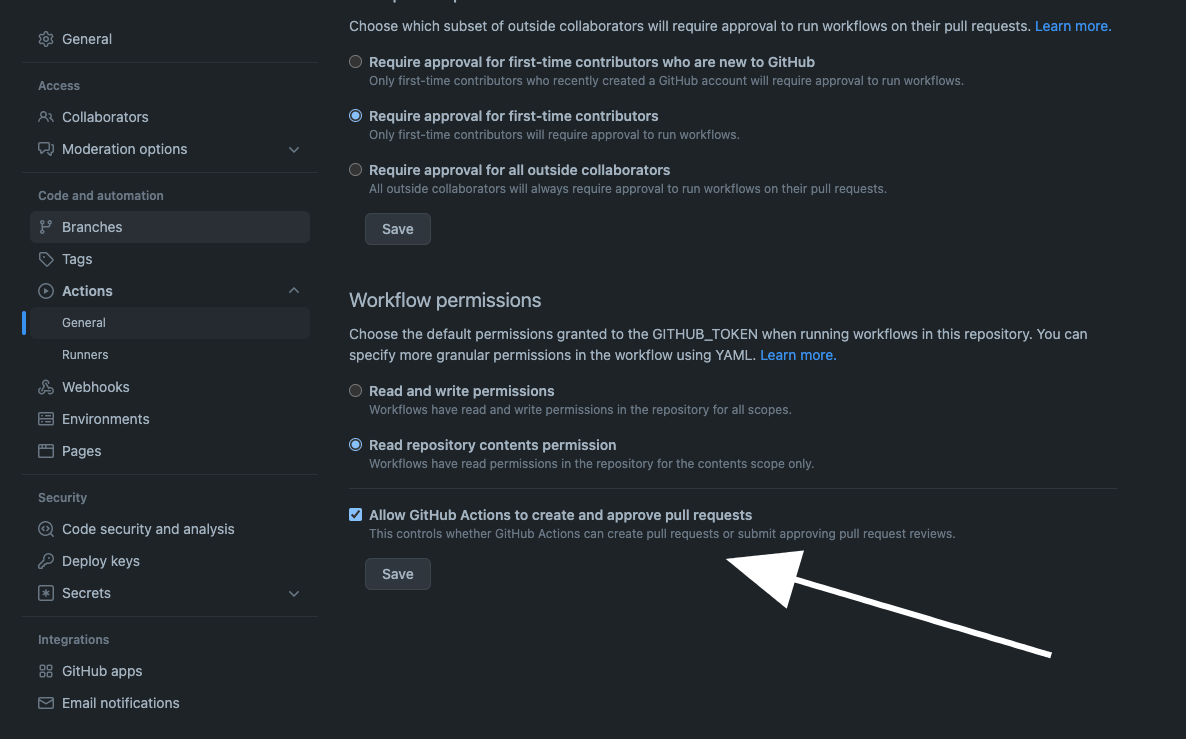
Make sure GitHub Actions has permissions to create pull requests.
-
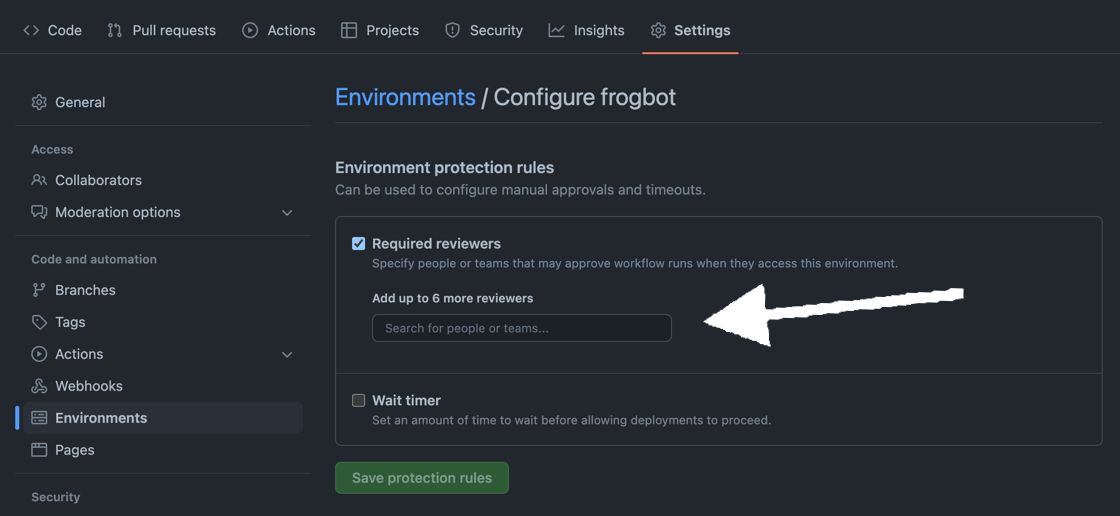
Create a new "frogbot" GitHub environment and add people or public teams as reviewers. The chosen reviewers are authorized to trigger Frogbot scan on pull requests.
-
Use these GitHub Actions templates to add Frogbot workflows to your project.
-
Push the workflow files to the
.github/workflowsdirectory in the root of your GitHub repository.
Setting up Frogbot on GitLab repositories
Frogbot is installed on GitLab repositories using GitLab CI. Here's how you install it:
- Make sure you have the connection details of your JFrog environment.
- Save the JFrog connection details as secrets in GitLab with the following names: JF_URL, JF_USER and JF_PASSWORD (You can also use JF_XRAY_URL and JF_ARTIFACTORY_URL instead of JF_URL and JF_ACCESS_TOKEN instead of JF_USER and JF_PASSWORD).
- Add a job named
frogbot-scanto your.gitlab-ci.ymlfile in your GitLab repository using the below structure.
Important Guidelines
- For npm, pip, pipenv, nuget or dotnet: Make sure to set the command in a way that it downloads your project dependencies as the value of the JF_INSTALL_DEPS_CMD variable. For example,
npm iornuget restore - Make sure that either JF_USER and JF_PASSWORD or JF_ACCESS_TOKEN are set, but not both.
frogbot-scan:
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == 'merge_request_event'
when: manual
variables:
FROGBOT_CMD: "scan-pull-request"
# Creating fix pull requests will be triggered by any push to the default branch.
# You can change it to any other branch you want, for example:
# if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == "dev"
- if: $CI_COMMIT_BRANCH == $CI_DEFAULT_BRANCH
variables:
FROGBOT_CMD: "create-fix-pull-requests"
when: manual
variables:
# [Mandatory only for projects which use npm, pip, pipenv, nuget and dotnet to download their dependencies]
# The command that installs the project dependencies (e.g "npm i", "nuget restore" or "dotnet restore")
JF_INSTALL_DEPS_CMD: ""
# [Mandatory]
# JFrog platform URL
JF_URL: $JF_URL
# [Mandatory if JF_ACCESS_TOKEN is not provided]
# JFrog user and password with 'read' permissions for Xray
JF_USER: $JF_USER
JF_PASSWORD: $JF_PASSWORD
# [Mandatory]
# GitLab accesses token with the following permissions scopes: api, read_api, read_user, read_repository
JF_GIT_TOKEN: $USER_TOKEN
# Predefined GitLab variables. There's no need to set them.
JF_GIT_PROVIDER: gitlab
JF_GIT_OWNER: $CI_PROJECT_NAMESPACE
JF_GIT_REPO: $CI_PROJECT_NAME
JF_GIT_BASE_BRANCH: $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_TARGET_BRANCH_NAME
JF_GIT_PULL_REQUEST_ID: $CI_MERGE_REQUEST_IID
# Uncomment the below options if you'd like to use them.
# [Optional, default: https://gitlab.com]
# API endpoint to GitLab
# JF_GIT_API_ENDPOINT: https://gitlab.example.com
# [Mandatory if JF_USER and JF_PASSWORD are not provided]
# JFrog access token with 'read' permissions for Xray
# JF_ACCESS_TOKEN: $JF_ACCESS_TOKEN
# [Optional, default: "."]
# Relative path to the project in the git repository
# JF_WORKING_DIR: path/to/project/dir
# [Optional]
# Xray Watches. Learn more about them here: https://www.jfrog.com/confluence/display/JFROG/Configuring+Xray+Watches
# JF_WATCHES: <watch-1>,<watch-2>...<watch-n>
# [Optional]
# JFrog project. Learn more about it here: https://www.jfrog.com/confluence/display/JFROG/Projects
# JF_PROJECT: <project-key>
script:
# For Linux / MacOS runner:
- curl -fLg "https://releases.jfrog.io/artifactory/frogbot/v2/[RELEASE]/getFrogbot.sh" | sh
- ./frogbot ${FROGBOT_CMD}
# For Windows runner:
# iwr https://releases.jfrog.io/artifactory/frogbot/v2/[RELEASE]/frogbot-windows-amd64/frogbot.exe -OutFile .\frogbot.exe
# .\frogbot.exe ${FROGBOT_CMD}Setting up Frogbot on Bitbucket Server repositories
Frogbot is installed on Bitbucket Server repositories using Jenkins. Here's how you install it:
- Make sure you have the connection details of your JFrog environment.
- Save the JFrog connection details as Credentials in Jenkins with the following Credential IDs: JF_URL, JF_USER and JF_PASSWORD (You can also use JF_XRAY_URL and JF_ARTIFACTORY_URL instead of JF_URL and JF_ACCESS_TOKEN instead of JF_USER and JF_PASSWORD).
- Save your Bitbucket access token as a Credential in Jenkins with the BITBUCKET_TOKEN Credential ID.
- Create a Pipeline job in Jenkins with the below Jenkinsfile content.
- In the Jenkinsfile, set the values of all the mandatory variables.
- In the Jenkinsfile, modify the code inside the
Download FrogbotandScan Pull Requestsaccording to the Jenkins agent operating system.
Important Guidelines
- For npm, pip, pipenv, nuget or dotnet: Make sure to set inside the Jenkinsfile the command in a way that it downloads your project dependencies as the value of the JF_INSTALL_DEPS_CMD variable. For example,
npm iornuget restore - Make sure that either JF_USER and JF_PASSWORD or JF_ACCESS_TOKEN are set in the Jenkinsfile, but not both.
- Make sure that all necessary build tool that are used to build the scanned project are installed on the Jenkins agent.
// Run the job every 5 minutes
CRON_SETTINGS = '''*/5 * * * *'''
pipeline {
agent any
triggers {
cron(CRON_SETTINGS)
}
environment {
// [Mandatory only for projects which use npm, pip, pipenv, nuget and dotnet to download their dependencies]
// The command that installs the project dependencies (e.g "npm i", "nuget restore" or "dotnet restore")
JF_INSTALL_DEPS_CMD= ""
// [Mandatory]
// JFrog platform URL
JF_URL= credentials("JF_URL")
// [Mandatory if JF_ACCESS_TOKEN is not provided]
// JFrog user and password with 'read' permissions for Xray
JF_USER= credentials("JF_USER")
JF_PASSWORD= credentials("JF_PASSWORD")
// [Mandatory]
// Bitbucket accesses token with the following permissions
JF_GIT_TOKEN= credentials("BITBUCKET_TOKEN")
JF_GIT_PROVIDER= "bitbucket"
// [Mandatory]
// Bitbucket project namespace
JF_GIT_OWNER= ""
// [Mandatory]
// Bitbucket repository name
JF_GIT_REPO= ""
// [Mandatory]
// API endpoint to Bitbucket server
JF_GIT_API_ENDPOINT= ""
// Uncomment the below options if you'd like to use them.
// [Mandatory if JF_USER and JF_PASSWORD are not provided]
// JFrog access token with 'read' permissions for Xray
// JF_ACCESS_TOKEN= credentials("JF_ACCESS_TOKEN")
// [Optional, default: "."]
// Relative path to the project in the git repository
// JF_WORKING_DIR= path/to/project/dir
// [Optional]
// Xray Watches. Learn more about them here: https://www.jfrog.com/confluence/display/JFROG/Configuring+Xray+Watches
// JF_WATCHES= <watch-1>,<watch-2>...<watch-n>
// [Optional]
// JFrog project. Learn more about it here: https://www.jfrog.com/confluence/display/JFROG/Projects
// JF_PROJECT= <project-key>
}
stages {
stage ('Download Frogbot') {
steps {
// For Linux / MacOS runner:
sh """ curl -fLg "https://releases.jfrog.io/artifactory/frogbot/v2/[RELEASE]/getFrogbot.sh" | sh"""
// For Windows runner:
// powershell """iwr https://releases.jfrog.io/artifactory/frogbot/v2/[RELEASE]/frogbot-windows-amd64/frogbot.exe -OutFile .\frogbot.exe"""
}
}
stage ('Scan Pull Requests') {
steps {
sh "./frogbot scan-pull-requests"
// For Windows runner:
// powershell """.\frogbot.exe scan-pull-requests"""
}
}
}
}💻 Contributions
We welcome pull requests from the community. To help us improve this project, please read our Contribution guide.