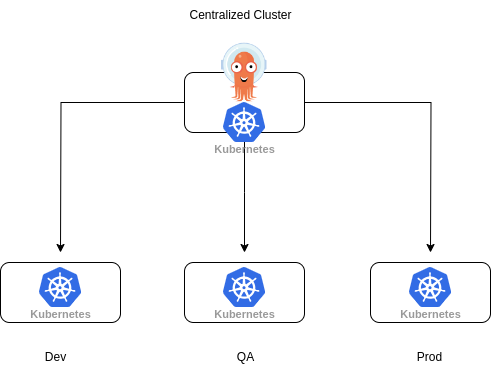
A hub and spoke setup of ArgoCD means having one or more ArgoCD instances running in a centralized location, e.g. a management or service cluster and use this instance for deployment in other clusters.
In a setup that only allows for unidirectional traffic, we can configure the ArgoCD instance to allow for deploying directly to the remote clusters. In order to do this we need to give it access to the other clusters. This is done by adding a secret with the required data and label for ArgoCD to pick it up. The documentation outlines the process for this.
ArgoCD comes with its own RBAC which should be configured appropiately based on the needs of the organization and the teams. On top of this we also need to configure the RBAC for the application controller, as this is the component that will be doing the actual deployment of resources. For this we will want to restrict the permissions to only include the required resources.
The RBAC for ArgoCD should map to the requirements of the team and organization. Commonly the focus will be about mapping teams and the ArgoCD Projects they can use for their deployments.
For OpenShift GitOps, this RBAC is defined in the custom resource representing an ArgoCD instance. For example:
spec:
rbac:
defaultPolicy: 'role:default'
policy: |
p, role:default, applications, *, default/*, allow
g, OCP-admins, role:adminNote: All authenticated users will have the default role applied to them unless given another role specifically
A good practice is to restrict the default role to only meet the requirements.
Here is an example of how to only allow certain resources to be managed by the application controller. This needs to exist on all the remote clusters and bound to a service account ArgoCD can use.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: limited-argo-role
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- "pods"
verbs:
- "*"
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- "configmaps"
verbs:
- "*"
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- "persistentvolumeclaims"
verbs:
- "*"
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- "services"
verbs:
- "*"
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- "serviceaccounts"
verbs:
- "*"
- apiGroups:
- "route.openshift.io"
resources:
- "routes"
verbs:
- "*"
- apiGroups:
- "route.openshift.io"
resources:
- "routes/custom-host"
verbs:
- "*"
- apiGroups:
- "apps"
resources:
- "deployments"
verbs:
- "*"
- apiGroups:
- "bitnami.com"
resources:
- "sealedsecrets"
verbs:
- "*"
- apiGroups:
- "argoproj.io"
resources:
- "applications"
verbs:
- "*"
- apiGroups:
- "batch"
resources:
- "jobs"
verbs:
- "*"
- apiGroups:
- "batch"
resources:
- "cronjobs"
verbs:
- "*"The actual requirements will depend on the organization and teams working with it.
The AppProject is a resource that we deploy our Applications to. Which AppProject that we can use will depend on the configured RBAC inside of ArgoCD and the configuration of the AppProject will determine what we can deploy and where.
spec:
destinations: # 1
- namespace: '*'
server: '*'
sourceRepos: # 2
- '*'
clusterResourceWhitelist: # 3
- group: '*'
kind: '*'
roles: # 4
- name: admins- Where can the ArgoCD Applications be deployed?
- List of Git repositories that this project will monitor for application configurations.
- What resources can be deployed in this Project
- Who are allowed to deploy
Currently the two most widely deployment methods are ApplicationSets and the AppofApp pattern.
The AppofApps pattern has been around longer and is more well known. In short, it is a way of deploying and managing multiple applications within a cluster. The pattern relies on having a meta-application or "App of Apps" that defines and manages the deployment of other applications.
---
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: appofapp
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
destination:
namespace: openshift-gitops
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: team-1
source:
path: 'applications/team-one/'
repoURL: git@github.com/deployments.git
targetRevision: main
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: false
selfHeal: trueIf and when using this for application deployments, it is necessary to ensure that Applications are not deployed in the same namespace as a ArgoCD instance, as it can be used to make changes to ArgoCD itself.
ApplicationSets allows you to define and manage multiple applications using a templated approach. It enables you to scale your application deployments by dynamically generating configurations based on templates and a set of parameters.
It also allows for deployment to multiple clusters directly.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ApplicationSet
metadata:
name: guestbook
spec:
generators:
- list:
elements:
- cluster: engineering-dev
url: https://1.2.3.4
- cluster: engineering-prod
url: https://2.4.6.8
- cluster: finance-preprod
url: https://9.8.7.6
template:
metadata:
name: '{{cluster}}-guestbook'
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd.git
targetRevision: HEAD
path: applicationset/examples/list-generator/guestbook/{{cluster}}
destination:
server: '{{url}}'
namespace: guestbook
When having a single ArgoCD controlling multiple clusters it is possible to do sharding This will generate a controller pod per shard. If the application controller faced memory pressure due to large number of clusters, it is optimal to utilize sharding.
I would recommend looking into this blog post ArgoCD Multi-Tenancy Strategy for a deeper dive into how to work with ArgoCD.