You’re a fintech engineer who’s working at one of the five largest banks in the world. You were recently promoted to act as the lead developer on their decentralized finance team. Your task is to build a blockchain-based ledger system, complete with a user-friendly web interface. This ledger should allow partner banks to conduct financial transactions (that is, to transfer money between senders and receivers) and to verify the integrity of the data in the ledger.
You’ll make the following updates to the provided Python file for this assignment, which already contains the basic PyChain ledger structure that you created throughout the module:
-
Create a new data class named
Record. This class will serve as the blueprint for the financial transaction records that the blocks of the ledger will store. -
Modify the existing
Blockdata class to storeRecorddata. -
Add Relevant User Inputs to the Streamlit interface.
-
Test the PyChain Ledger by Storing Records.
Download the following files to help you get started:
Open the pychain.py file included in the Homework's Starter_code folder. You’ll use this file to complete the steps for this assignment. Notice that the PyChain ledger that you built throughout this unit already includes the functionality to create blocks, perform the proof of work consensus protocol, and validate blocks in the chain.
The steps for this assignment are divided into the following sections:
-
Create a Record Data Class
-
Modify the Existing Block Data Class to Store Record Data
-
Add Relevant User Inputs to the Streamlit Interface
-
Test the PyChain Ledger by Storing Records
Define a new Python data class named Record. Give this new class a formalized data structure that consists of the sender, receiver, and amount attributes. To do so, complete the following steps:
-
Define a new class named
Record. -
Add the
@dataclassdecorator immediately before theRecordclass definition. -
Add an attribute named
senderof typestr. -
Add an attribute named
receiverof typestr. -
Add an attribute named
amountof typefloat.
Note that you’ll use this new Record class as the data type of your record attribute in the next section.
Rename the data attribute in your Block class to record, and then set it to use an instance of the new Record class that you created in the previous section. To do so, complete the following steps:
-
In the
Blockclass, rename thedataattribute torecord. -
Set the data type of the
recordattribute toRecord.
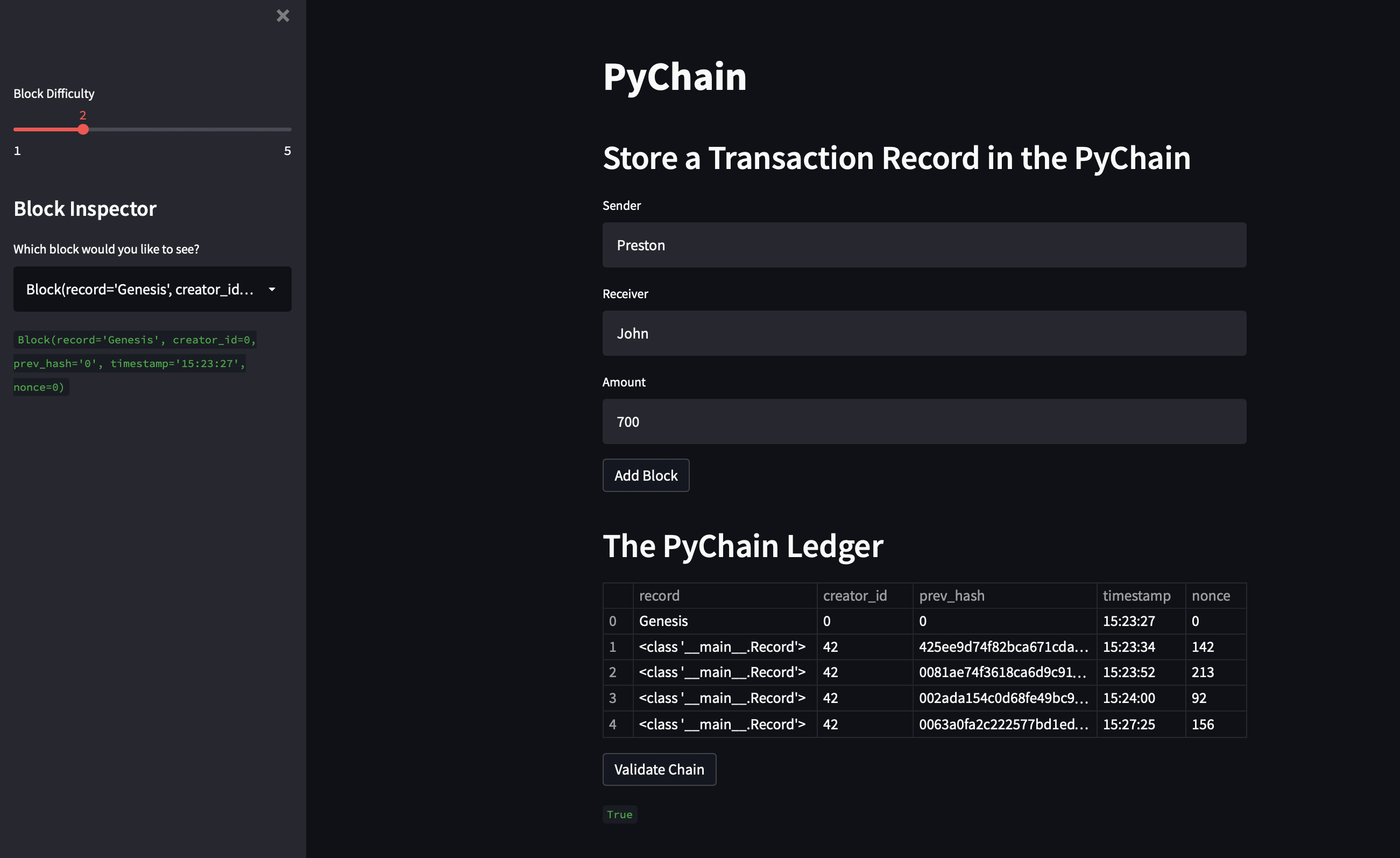
Code additional input areas for the user interface of your Streamlit application. Create these input areas to capture the sender, receiver, and amount for each transaction that you’ll store in the Block record. To do so, complete the following steps:
-
Delete the
input_datavariable from the Streamlit interface. -
Add an input area where you can get a value for
senderfrom the user. -
Add an input area where you can get a value for
receiverfrom the user. -
Add an input area where you can get a value for
amountfrom the user. -
As part of the “Add Block” button functionality, update
new_blockso thatBlockconsists of an attribute namedrecord, which is set equal to aRecordthat contains thesender,receiver, andamountvalues. The updatedBlockshould also include the attributes forcreator_idandprev_hash.
Test your complete PyChain ledger and user interface by running your Streamlit application and storing some mined blocks in your PyChain ledger. Then test the blockchain validation process by using your PyChain ledger. To do so, complete the following steps:
-
In the terminal, navigate to the project folder where you've coded this assignment.
-
In the terminal, run the Streamlit application by using
streamlit run pychain.py. -
Enter values for the sender, receiver, and amount, and then click the Add Block button. Do this several times to store several blocks in the ledger.
-
Verify the block contents and hashes in the Streamlit dropdown menu. Take a screenshot of the Streamlit application page, which should detail a blockchain that consists of multiple blocks. Include the screenshot in the
README.mdfile for your GitHub repository. -
Test the blockchain validation process by using the web interface. Take a screenshot of the Streamlit application page, which should indicate the validity of the blockchain. Include the screenshot in the
README.mdfile for your homework repository.