Max-Mahalanobis Training (MMT) is a novel training method, which can learn more robust models without hurting clean accuracy and with little extra computational cost. Technical details are specified in:
Max-Mahalanobis Linear Discriminant Analysis Networks (ICML 2018)
Tianyu Pang, Chao Du and Jun Zhu
Rethinking Softmax Cross-Entropy Loss for Adversarial Robustness (ICLR 2020)
Tianyu Pang, Kun Xu, Yinpeng Dong, Chao Du, Ning Chen and Jun Zhu
This project is tested under the following environment settings:
- OS: Ubuntu 16.04.3
- GPU: Geforce 1080 Ti or Tesla P100
- Cuda: 9.0, Cudnn: v7.03
- Python: 2.7.12
- cleverhans: 2.1.0
- Keras: 2.2.4
- tensorflow-gpu: 1.9.0
We also thank the authors of keras-resnet for providing their code. Our codes are widely adapted from their repositories. For convenience, we provide the requirement.txt file to install the virtualenv that is sufficient run the codes.
In the following, we first provide the codes for training. After that, the evaluation codes, such as attacking, are provided.
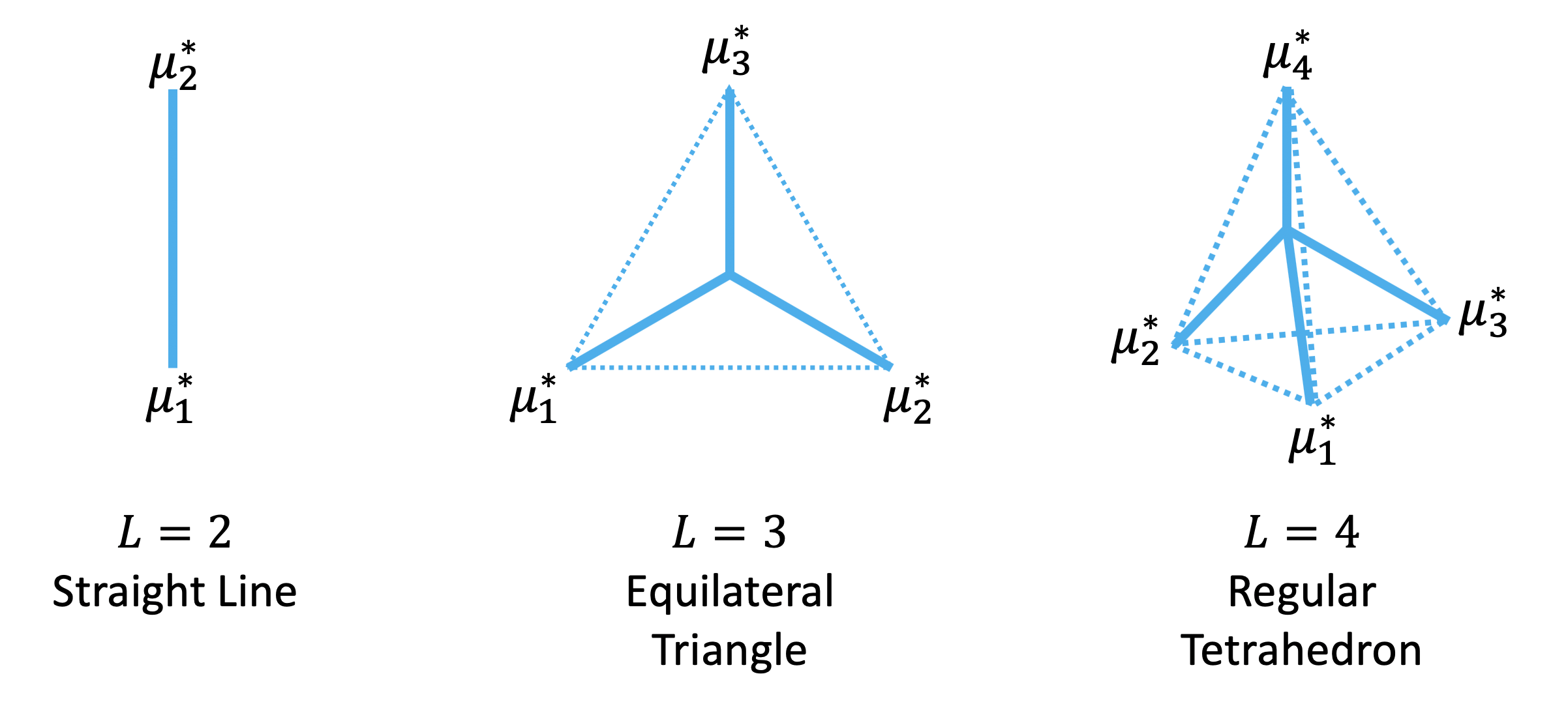
This plot shows the MM centers under different number of classes L.
Let dataset be mnist, cifar10 or cifar100, the command for training models with the SCE loss is
python train.py --batch_size=50 --dataset=[dataset] --optimizer='mom' --lr=0.01 --version=2 --use_MMLDA=False --use_BN=True --use_dense=True --use_leaky=FalseHere the initial learning rate is 0.01, the optimizer is mom and we use the Resnet-v2 architecture proposed by He et al. (2016). The training epoch on MNIST is set as 40, on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 is set as 200.
Similarly, let dataset be mnist, cifar10 or cifar100, the command for training models with the MMC loss is
python train.py --batch_size=50 --mean_var=10 --dataset=[dataset] -optimizer='mom' --lr=0.01 --version=2 --use_MMLDA=True --use_ball=True --use_BN=True --use_random=False --use_dense=True --use_leaky=FalseHere the basic training setting, e.g., learning rate and optimizer are the same as them for the SCE loss. The meanvar parameter is the use_ball is False, the command run the training with the MMLDA loss.
For the adversarial training, we apply the most widely studied PGD-based method proposed by Madry et al. (2017).
python advtrain.py --batch_size=50 --dataset=[dataset] --optimizer='mom' --lr=0.01 --version=2 --adv_ratio=1.0 --use_MMLDA=False --use_ball=False --use_target=False --attack_method='MadryEtAl' --use_BN=True --use_random=FalseHere the adv_ratio is set as 1, which means we only use adversarial examples in the training phase as suggested in previous work. The bool flag use_target indicates whether uses targeted attack or untargeted attack when crafting adversarial examples for training.
The adversarial training command is similar for the MMC loss
python advtrain.py --batch_size=50 --mean_var=10 --dataset=[dataset] --optimizer='mom' --lr=0.01 --version=2 --adv_ratio=1.0 --use_MMLDA=True --use_ball=True --use_target=True --attack_method='MadryEtAl' --use_BN=True --use_random=FalseThe pretrained models are provided below for Resnet110 (n=18):
MMC + adv-training (CIFAR-100).
In this setting, the attacking methods are usually iterative-based. For examples, the command of applying targeted PGD-10 to evade the models trained by the MMC loss is
python advtest_iterative.py --batch_size=50 --attack_method='MadryEtAl' --attack_method_for_advtrain=None --dataset=[dataset] --target=True --num_iter=10 --use_ball=True --use_MMLDA=True --use_advtrain=False --epoch=[epoch] --use_BN=True --normalize_output_for_ball=False --use_random=False --use_target=FalseHere attack_method could be 'MadryEtAl' (PGD), 'FastGradientMethod' (FGSM), 'MomentumIterativeMethod' (MIM) and 'BasicIterativeMethod' (BIM). The target indicates whether use targeted or untargeted attack; num_iter is the iteration steps of the performed attacks; epoch is the epoch of the checkpoint to load; normalize_output_for_ball is a bool flag to decide whether apply a softmax function to return predictions in the inference phase.
Note that our evaluation is based on cleverhans: 2.1.0. To perform adaptive attack, please manually modify the function model_loss of the file utils_tf.pyby substituting the softmax cross-entropy loss with other adaptive objectives, e.g., out=-tf.reduce_sum(logits * y, axis=-1).
When attacking the adversarially trained models, we should set the use_advtrain as True, and the attack_method_for_advtrain to be 'MadryEtAl' since we use the PGD-based adversarial training methods. The use_target is set the same as in the training codes. For examples, the command of applying untargeted PGD to evade the models adversarially trained by the MMC loss is
python advtest_iterative.py --mean_var=10 --batch_size=50 --attack_method='MadryEtAl' --attack_method_for_advtrain='MadryEtAl' --dataset=[dataset] --target=False --num_iter=10 --use_ball=True --use_MMLDA=True --use_advtrain=True --epoch=[epoch] --use_BN=True --normalize_output_for_ball=False --use_random=False --adv_ratio=1.0 --use_target=FalseNote that here we set normalize_output_for_ball be False to perform an adaptive attacks.
In this setting, the attacking methods are usually optimization-based. In the C&W method, there is a binary search mechanism for the constant parameter to find sucessful adversarial examples with minimal distortion. The command below gives an example of applying targeted C&W attack on the models trained by the MMC loss.
python advtest_others.py --mean_var=10 --batch_size=50 --attack_method='CarliniWagnerL2' --attack_method_for_advtrain=None --dataset=[dataset] --target=True --use_ball=True --use_MMLDA=True --use_advtrain=False --adv_ratio=1.0 --use_target=False --epoch=[epoch] --use_BN=True --normalize_output_for_ball=False --use_random=False --use_dense=True --use_leaky=False --CW_confidence=0.The specific parameter settings of the C&W attack can be found in the code. The attack_method could also be 'ElasticNetMethod' to perform EAD attack.
For the black-box transfer-based setting, we apply the MIM and PGD attacks. An example command using the untargeted PGD-10 attack is shown below
python advtest_iterative_blackbox.py --batch_size=50 --optimizer='Adam' --attack_method='MadryEtAl' --dataset=[dataset] --target=False --num_iter=10 --use_random=False --use_dense=True --use_leaky=False --epoch=[epoch] --use_BN=True --model_1='AT-MMC-100' --model_2='SCE'Here model_1 is the substitute model used to craft adversarial examples, model_2 is the original model used to classify these adversarial examples. These two parameters could be SCE, MMC-10, MMC-100, AT-SCE, AT-MMC-10, AT-MMC-100. The epoch here is the training epoch of checkpoint for both the model_1 and model_2.
For the black-box gradient-free setting, we apply the SPSA attack. This attacks is based on numerical approximations of the model gradients, and can evade the defenses that based on gradient masking. An example command is given below for untargeted SPSA-10 attack on the models trained by the MMC loss.
python advtest_others.py --mean_var=10 --batch_size=50 --attack_method='SPSA' --attack_method_for_advtrain=None --dataset=[dataset] --target=False --use_ball=True --use_MMLDA=True --use_advtrain=False --adv_ratio=1.0 --use_target=False --epoch=[epoch] --use_BN=True -normalize_output_for_ball=False --use_random=False --use_dense=True --use_leaky=False --SPSA_epsilon=8More details of the parameter settings can be found in the code.
To further test the robustness of our method, we investigate the general-purpose attacks. We add the Gaussian random noise and random rotation transformation on the input images to perform the attacks. An example command is
python advtest_simple_transform.py --mean_var=10 --batch_size=50 --attack_method='Rotation' --attack_method_for_advtrain='MadryEtAl' --dataset=[dataset] --use_ball=True --use_MMLDA=True --use_advtrain=True --epoch=[epoch] --adv_ratio=1.0 --use_target=False --normalize_output_for_ball=FalseThe attack_method could be 'Rotation' for rotation transformation or 'Gaussian' for Gaussian noise. Detailed parameter settings are provided in the code.