tweegraph is a collection of functions, a class and some scripts that use tweepy to provide an interface for crawling twitter relationships. Aimed for small research tasks that involve either the studying of topological traits of a network (sub-graphs of twitter) and that can involve up to some hundreds of thousands of ids (i.e crawling ~100000 ids with 5 api keys can be done in under an hour) or / and user data (collecting 2gb of timeline data takes me usually 5-6 hours).
Can be used from small research groups that cannot afford the money and / or time for setting up large clusters for distributed crawling on aws or azure and want to easily set up a crawling procedure. The crawler takes advantage of multiple api tokens, if provided, but also works with one. Adding more than one obviously speeds up the crawling significantly.
For running the crawling of user ids you need tweepy and pandas. For crawling timelines you also need MongoDB with pymongo. If you want to use the plot_graph.py script to visually plot the collected graph you additionally need networkx. If you want all the above just pip install -r requirements, then install MongoDb and you will be up to date with everything that the project uses.
The graph searching algorithm is a fixed BFS. Fixed means that you have to provide a specific breadth up to which the neighbors of a node will be discovered. This helps with discovering larger parts of the network faster and the crawling not being stuck in nodes with extremely high in-out degree (e.g. The crawler would spend more than 9 days to collect all the followers of Kanye West and it would end up creating an single asterisk instead of a highly interconnected network whose properties can be studied).
The crawler needs an initial seed that must be a list of ids (one or more). Choose a good set on initial nodes (ids) for faster start up and more meaningfull crawling. Usually nodes with high in-out degree are a better choice. But of course that depends on the type of research you are using the crawler for.
The crawler is fault taulerant. You can initiate a crawling and leave it run for a day or more (note that I have never left it run for more than a single day).
The graph traversing mechanism is implemented in /tweegraph/traverser.py by the TwitterGraphTraverser class which provides an interface for using the mechanism. All connection are stored into links.csv in the form (follwer, node). That also means that the crawler treats the network as a directed graph. The collect_graph.py script showcases how the crawler can be used for collecting user relations and collect_timelines.py uses the links.csv as a seed for starting multiple crawling of timeline data of the unique nodes in the file.
Here is a simple example for how to initiate a crawling process
# collect_graph.py
import json
from time import sleep
from tweegraph.traverser import TwitterGraphTraverser
if __name__ == "__main__":
with open('credentials.json') as credentials_file:
credentials = json.load(credentials_file)
starting_ids = [21447363, # katy perry
27260086, # justin bieber
813286, # barack obama
25365536, # kim kardashian
23375688, # selena gomez
50393960, # bill gates
31927467, # pitbull
2292454922] # tsipras_eu
# create TwitterGraphTraverser instance.
traverser = TwitterGraphTraverser(breadth=None,
graph_size=2500,
starting_ids=starting_ids,
directions=['following'],
credentials=credentials)
# start exploring graph
traverser.start()
# export collected relations to file every 5 sec
while True:
if traverser.get_size() > 0:
traverser.export_data()
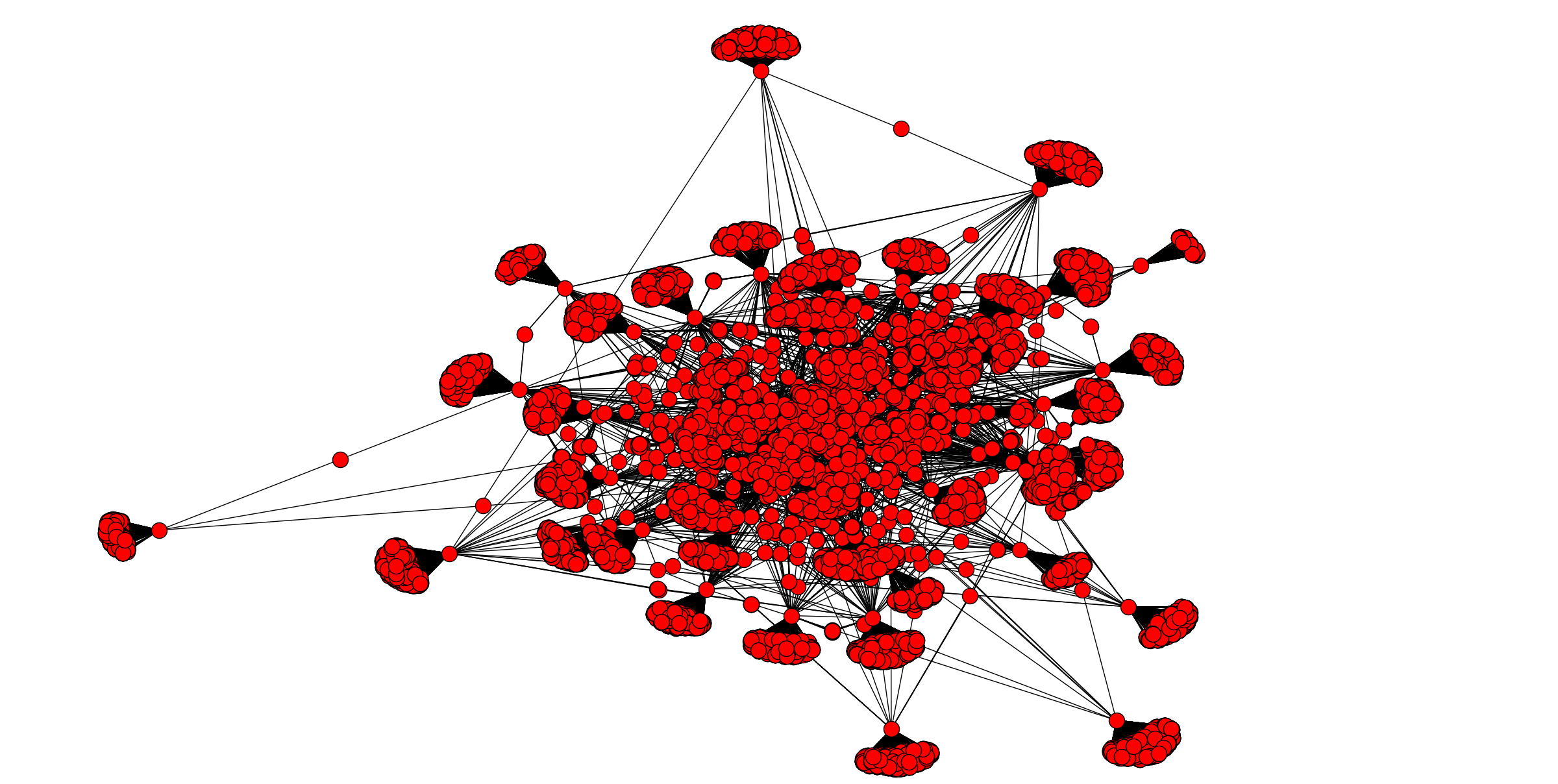
sleep(5)Here is a snapshot of a network with 23104 edges collected in about 5-10min
For the collect_timelines.py script I have used MongoDB to store the results. But handling the results can be easily modified from anyone to fit his/her needs.
I haven't yet added a LICENSE to the project but have in mind that the code comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY. I have been using the crawler as a tool for my diploma dissertation and I would be more than happy if it could be usefull to other people or reasearch groups. Feel free to contact me or open an issue for feedback, possible extensions or problems.
####author Gryllos Prokopios (gryllosprokopis@gmail.com)