##Arduino Library - Simple Thread and Time Counter
This library was created as a simple tool to develop applications which require counting long periods of time, and at the same time, as an alternative for splitting the arduino loop() into timeblocks that are used as Threads.
Also included in the library is an LED indicator class to allow simple messaging using a blinking LED, which is an implementation of a Thread built in the library.
The library has the basic building blocks to create real time applications, without requiring RTC hardware, as long as the accuracy of the arduino clock is sufficient for the task.
Library timming is derived from millis() and it does not use any hardware resources other than the pin for the LED indicator.
##Compatibility
This version has been tested only with AVR ang Galileo. While the timing classes are compatible with any architecture that supports millis() the indicatorLED has only being optimized for AVR (Port manipulation) and uses digitalWrite for all other processors, including Galileo (OUTPUT_FAST). Optimization for other processors is possible, but not in the present roadmap.
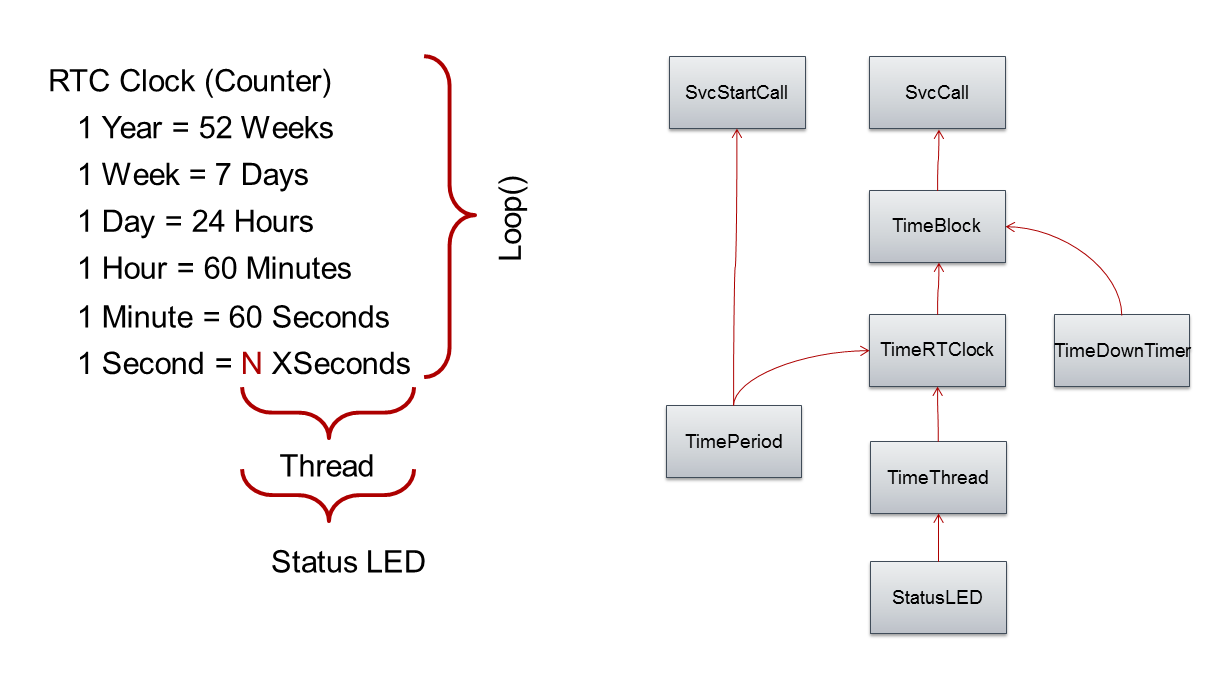
####Dividing Time Time is divided in fractions, here called xsecs. The default time base is 20 xsecs = 1 second. The library keeps time in xsecs, secs, mins, hrs, days, weeks.
It is possible to change the number of fractions corresponding to one second, which we call the time base. The time base for the library is applicable to all TimeBlocks.
####Actions The diagram shows the relationship between the classes part of the library. At the completion of each time segment Thread or Block, a function is called to servicing that object. SvcCall Class provides the infrastructure for fulfilling services on time events (TimeThread, TimeDownTimer, TimePeriod, and StatusLED). Additionally, TimePeriod is also serviced at the start of the period by SvcStartCall.
####indicatorLED When working with Arduino, is always helpful to have a simple status LED. As part of the implementation of Threads, the library also includes a StatusLED Class. The service of StatusLED is explicit, providing flexibility to where in loop()_ is performed.
The indicator works by shifting a value, providing a countable number of flashes.
| LED Codes Status | LED Codes Status |
|---|---|
| Code 0x00 OFF | Code 0x10 On |
| Code 0x01 On 1 | Code 0x09 Off 1 |
| Code 0x02 On 2 | Code 0x0A Off 2 |
| Code 0x03 On 3 | Code 0x0B Off 3 |
| Code 0x04 On 4 | Code 0x0C Off 4 |
| Code 0x05 On 5 | Code 0x0D Off 5 |
| Code 0x06 On 6 | Code 0x0E Off 6 |
| Code 0x07 On 7 | Code 0x0F Off 7 |
| Code 0x08 Flash | End of Table |
The speed of LED flashing is given by the duration by the timebase (number of fractions per second). To make the flashing of the LED humanly countable when using fast threads, there is also an LED speed parameter to divide the thread count and slow it down.
The declaration of the LED indicator also includes the state where the LED is ON. For example:
// StatusLED indicatorLED (Pin_LED, HIGH, LED_Speed, threadStart)
StatusLED indicatorLED (13, HIGH, 2, 0);