Stemmpages helps you to create your own Github Pages Blog with your Steemit posts.
Steempages has the following benefits:
- You can create your own blog site using your Steemit posts.
- You don't need any paid Server hosting services, IT'S FREE!
- You can use Disqus, Google Analytics, and more just like Github Pages.
Check out DEMO blog!
Steempages uses the build feature of Travis CI to synchronize your Steemit posts to Github Pages repo.
First, you need Github Pages repo for blog.
You can make your own Github Pages repo by following
Jekyll Now Guide.
Fork this repository by clicking the Fork button in the top right corner.
You don't need to make any changes yet.
Steempages need your Personal Access Token to update your Github Pages repo.
Click Here to create a Personal Access Token.
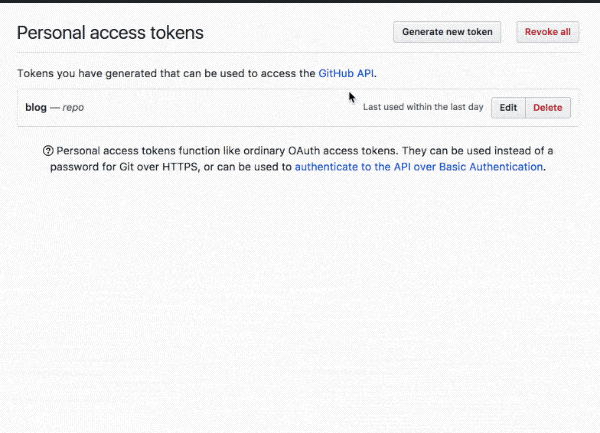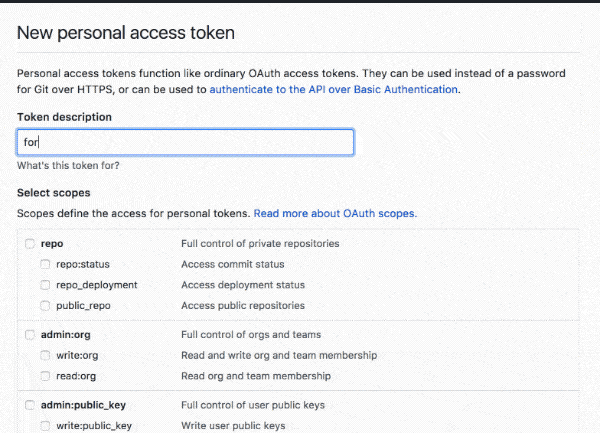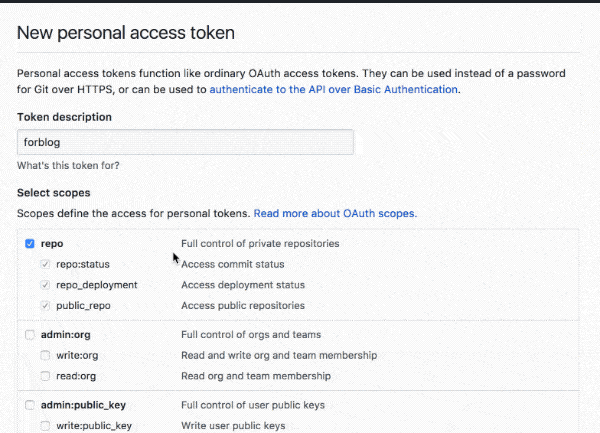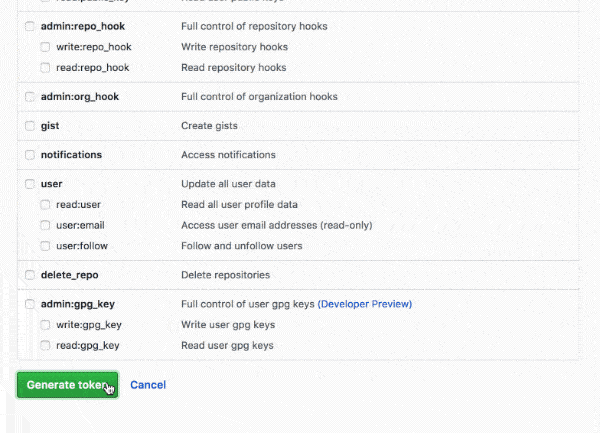
Check the repo permission as shown below.
No other permissions are required.
Once the token is generated, copy the token and keep it in a temporary safe place. it's required in the next step.
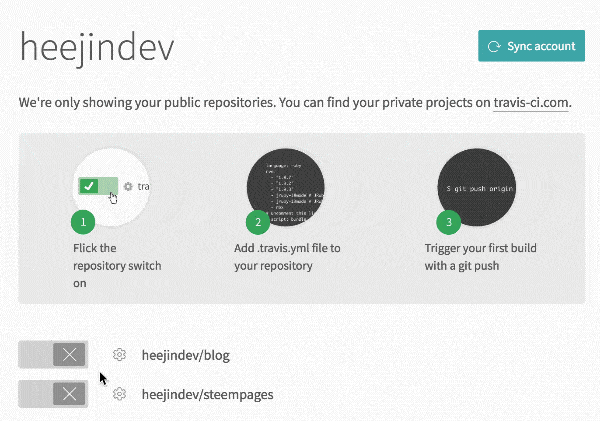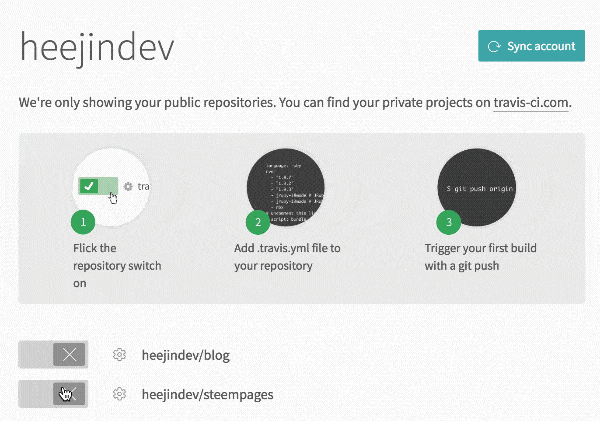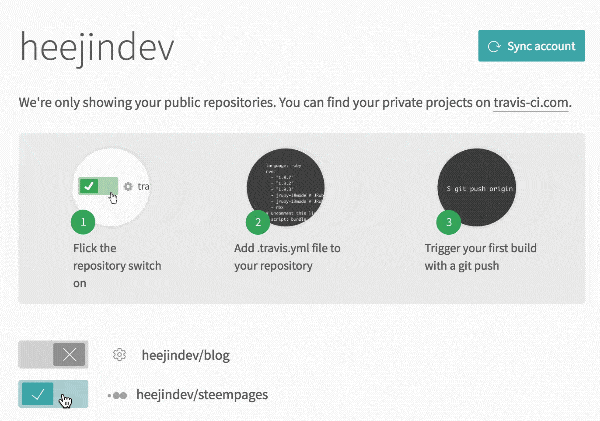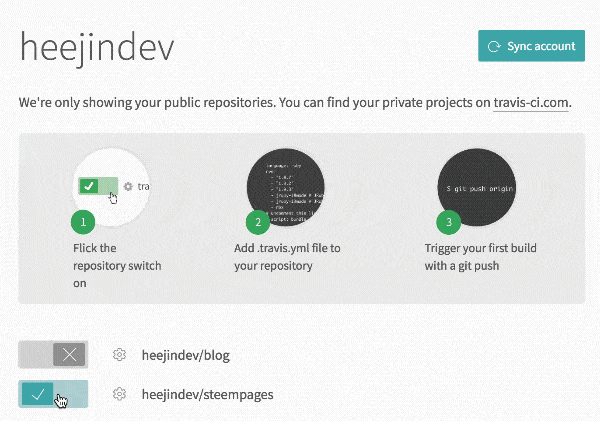
Travis CI is required for automatic synchronization. You can use Travis CI with your Github account.
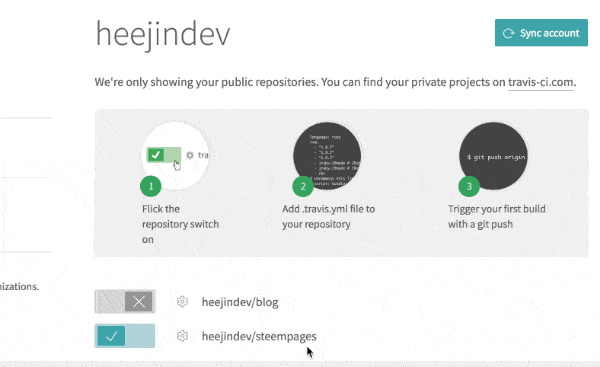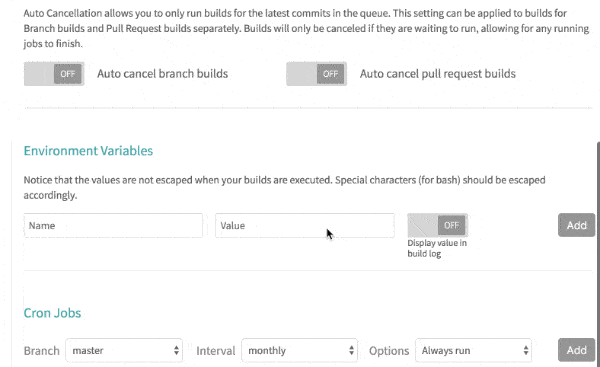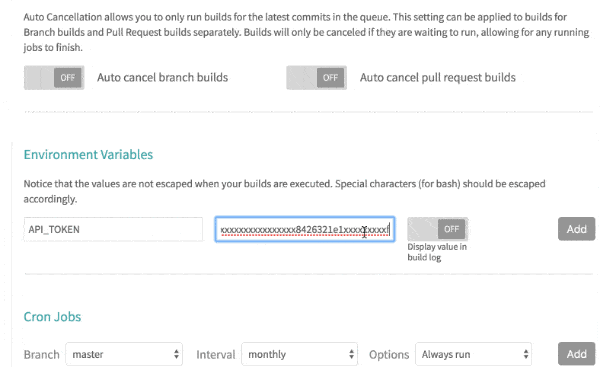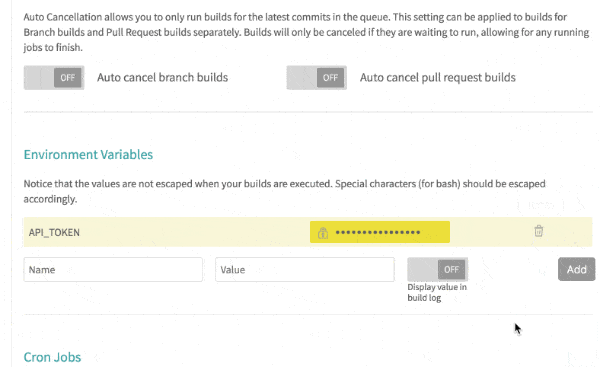
You will see steempages on your Accounts page.
Turn on the option to use Travis CI in your steempages repo and open the Settings for the repo.
In Environment Variables of Settings, Enter name as API_TOKEN, value as the Personal Access Token generated in Step 3, and press Add button to add environment variable.
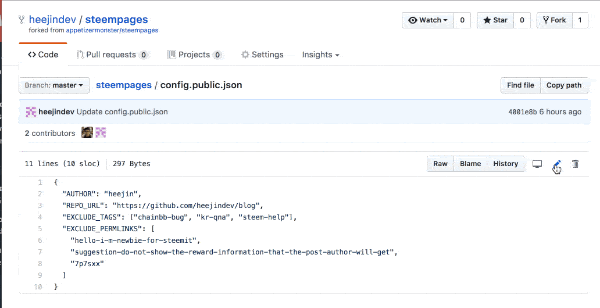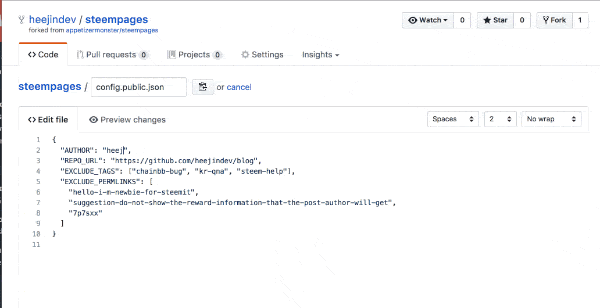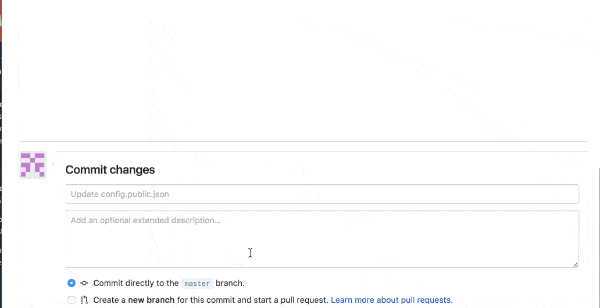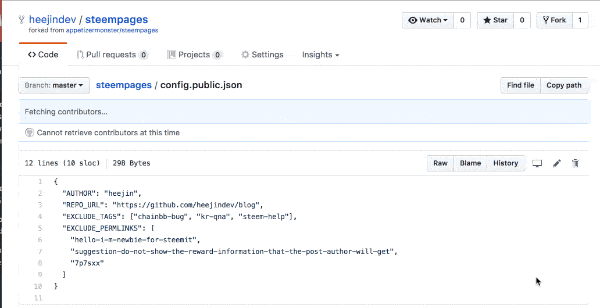
Open the steempages repository forked in Step 2. You have to edit config.public.json file.
Open the config file as shown in the figure below.
Put your Steemit ID for AUTHOR, and the URL of your Github Pages repository in REPO_URL (for example: https://github.com/appetizermonster/blog)
You can customize the rest settings.
Finally, when you save and commit the file, Steemit posts will be uploaded to your Github Pages repo.
You can check the build status in the Travis CI.
After the build, you can see the Steemit posts on your blog!
Steemit and Github Pages have different ways of markdown rendering.
So there may be some rendering issuses.
If you have issues, please report the issue.
Any pull requests are welcome!