Zheng Wang1, Xinyu Yan1, Yahong Han1*, Meijun Sun1
1 College of Intelligence and Computing, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China
* Corresponding author: Yanhong Han
{xinyuyan, wzheng,yahong,sunmeijun}@tju.edu.cn
(王征:天津大学机器学习与数据挖掘实验室)
Video salient object detection has been attracting more and more research interests recently. However, the definition of salient objects in videos has been controversial all the time, which has become a critical bottleneck in video salient object detection. Specifically, the sequential information contained in videos results in a fact that objects have a relative saliency ranking between each other rather than specific saliency. This implies that simply distinguishing objects into salient or not-salient as usual could not represent the information about saliency comprehensively. To address this issue, 1) in this paper we propose a completely new definition for the salient objects in videos---ranking salient objects, which considers relative saliency ranking assisted with eye fixation points. 2) Based on this definition,a ranking video salient object dataset(RVSOD) is built. 3) Leveraging our RVSOD, a novel neural network called Synthesized Video Saliency Network (SVSNet) is constructed to detect both traditional salient objects and human eye movements in videos. Finally, a ranking saliency module (RSM) takes the results of SVSNet as input to generate the ranking saliency maps. We hope our approach will serve as a baseline and lead to a conceptually new research in the field of video saliency.
Ranking Video Salient Object Detection, Zheng Wang, Xinyu Yan, Yahong Han, Meijun Sun. ACM Multimedia 2019 Nice,[ project page | bib | official version | code | pdf ][poster | Results | RVSOD Dataset (Baidu | Google)]
'videos': original videos(videoname.avi)
'img': original frames to be annotated(videoname_framenum.jpg)
'eye fixation data/mat': eye fixation annotations stored in mat files
'eye fixation data/img': eye fixation annotations in '.jpg' format
'manually annotated masks':manually annotated masks of salient object segmentation in '.png' format
'ranking saliency masks/img': masks of salient objects with gray values of 0 to 1 in '.png' format
'readme.txt': introduction to the dataset
===============================================================================
Training set: 185 videos,5336 labeled frames.
Validation set: 70 videos,2013 labeled frames.
Testing set: 109 videos,3176 labeled frames.
===============================================================================
The datasets currently used for video saliency object detection are all these for video object segmentation.As a result, three problems have arisen.
1.Insufficient quantity:The size of these datasets is not large enough, and there is a high degree of correlation between frames, which cannot meet the requirement for training a depth model.
2.Inappropriate Ground-truth:On the one hand,the existing datasets only are dedicated to video segmentation,but not for detection of salient objects.Truly salient information cannot be learned from these datasets by the network.On the other hand, the motion attribute of objects detected from these videos cannot be considered as correct indicator for determining whether these objects are salient or not.In other word,moving objects in the video are not necessarily salient ones,vice verse.
3. Incomplete saliency information:Up to now,the study of object saliency detection of video only distinguishes the objects from salient or unsalient.In the scene with multiple objects,the salient values of the objects are all set to 1.But in reality,these objects have different degrees of saliency due to the temporal continuity of frames and frames in the video,as well as the size,color,and type of the objects.For example,new characters often get more attention;in scenes where both humans and things are present,people are often more saliency.These objective laws have not been reflected in previous salient object research and datasets.
Therefore, in these contexts, it is very necessary to propose a large-scale video saliency object dataset that is specifically targeted at saliency object detection and that can reflect different degrees of saliency between objects.
===============================================================================
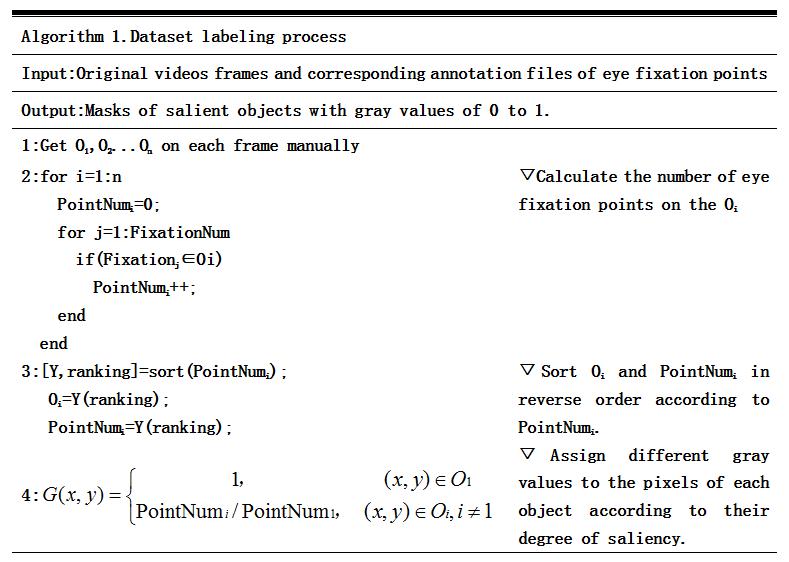
 -------------------------------------------Figure 1.Dataset labeling process-------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------Figure 1.Dataset labeling process-------------------------------------------
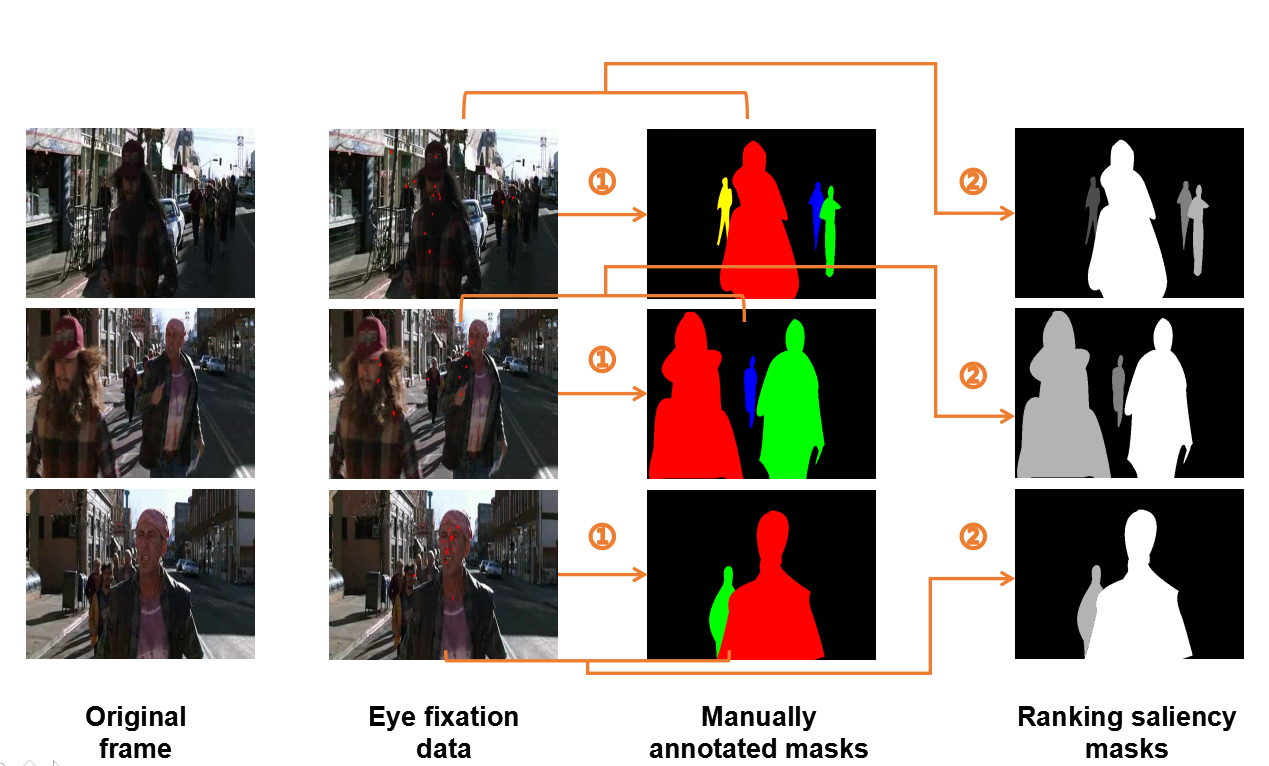
We have established a ranking saliency object dataset,called RVSOD (Ranking Video Salient Object Dataset) which marks the objects with the eye fixation points on the basis of the currently existing eye fixation datasets.The number of eye fixation points is used to determine the degree of saliency of each object, and different gray values are assigned to these objects according to associated degree of saliency. More eye fixation points placed on the object means higher degree of saliency.And the gray values of the pixels are closer to 1. The dataset contains 364 carefully selected video sequences. We labeled one frame in every five frames,and marked a total of 10K frames. We removed video sequences that appear similar in the UCF and HOLLYWOOD2 datasets and these are not suitable for salient object detection (such as video sequences with close-ups of people or video sequences without subject objects).Our RVSOD contains video sequences with different number of object,object types, motion information,and scene complexity. To our best knowledge,this is the first large-scale dataset in the context of video saliency object detection.RVSOD introduces a new definition, ranking video saliency object detection, and provides a benchmark dataset for the field. In addition, the establishment of our dataset help address the problem of training data lacking for learning-based video saliency object detection as well.
===============================================================================
1. Manually mark the salient objects according to the position of the eye fixation points.
Manually mark the objects O1, O2, ... On in each frame of the image with eye fixation points.(such as the ones shown in Fig. 1(①))
2. Assign different gray values to the salient objects according to the number of eye fixation points.
According to the eye fixation points annotation files, the number of eye fixation points on each marked object in each frame image is calculated. The object with the highest number of eye fixation points is considered to be the most salient object, and the gray values of its pixels are set to 1.And the gray values of the pixels of the remaining objects are set according to the ratio of the number of eye fixation points to the number of eye fixation points of the most salient object.In this way,in each video frame,the gray values of the salient objects are distributed between 0 and 1.More eye fixation points placed on the object means higher degree of saliency.And the gray values of the pixels are closer to 1.Conversely,these gray values are near to 0.(such as the ones shown in Fig. 1(②))
----------------------------------------------------Figure 2.Algorithm---------------------------------------------------
 The overall architecture of SVSNet.Our model is built on a two-branch FCN architecture with ResNet-50 as a pretrained model. At a high level, we feed an input video sequence {It}t=1T with T frames into ResNet-50 continuously to capture multi-level spatial information about every frame's saliency regions. Note that we only keep the first four blocks of the ResNet-50. Then, these features from the ResNet-50 are fed into the two branches--- fixation predicting branch and salient object detection branch, respectively.Finally,the outputs of the two branches are sent into the ranking saliency module(RSM) to generate the ranking saliency map.
The overall architecture of SVSNet.Our model is built on a two-branch FCN architecture with ResNet-50 as a pretrained model. At a high level, we feed an input video sequence {It}t=1T with T frames into ResNet-50 continuously to capture multi-level spatial information about every frame's saliency regions. Note that we only keep the first four blocks of the ResNet-50. Then, these features from the ResNet-50 are fed into the two branches--- fixation predicting branch and salient object detection branch, respectively.Finally,the outputs of the two branches are sent into the ranking saliency module(RSM) to generate the ranking saliency map.
 -------------------------------Qualitative comparisons of diffenrent SOD methods on RVSOD.--------------------------------
-------------------------------Qualitative comparisons of diffenrent SOD methods on RVSOD.--------------------------------
 -----------------------------------------Evaluation for ranking saliency detection.-----------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------Evaluation for ranking saliency detection.-----------------------------------------