Machine Learning and Real World data
https://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/teaching/2122/MLRD/
- Sentiment Classification (NLP)
- Hidden States Prediction (Hidden Markov Model)
Dependency
NLTK-Natural Language Toolkit IDE: PyCharm
Sentiment Lexicon Database
Given a list of tokens from a tokenized review and a lexicon containing both sentiment and magnitude of a word, determine whether the sentiment of each review in the test set is positive or negative based on whether there are more positive or negative words.
Classification: label Lexicons into postive and negative.
Evaluation: Based on reviews on IMDb.
Improve the classifier using thresholds for decision bounds.
Your accuracy: 0.6355555555555555
Your improved accuracy: 0.6888888888888889
Naive Bayes Classifier
Parameter estimation
How to deal with a word in a review was not present in the training dataset?\
Ignore its contribution or using add-one (Laplace) Smoothing
Your accuracy using simple classifier: 0.63
Your accuracy using unsmoothed probabilities: 0.49
Your accuracy using smoothed probabilities: 0.795
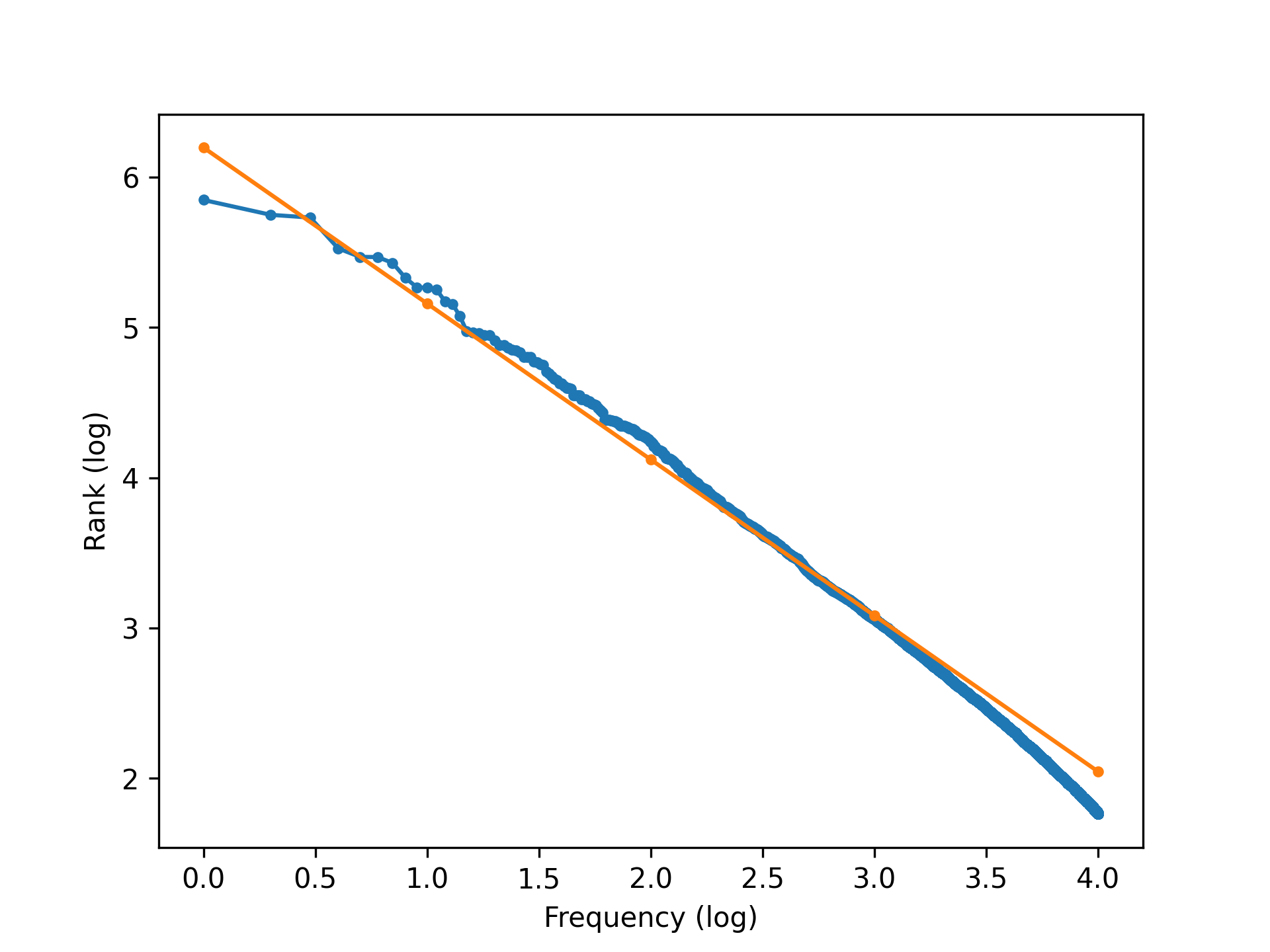
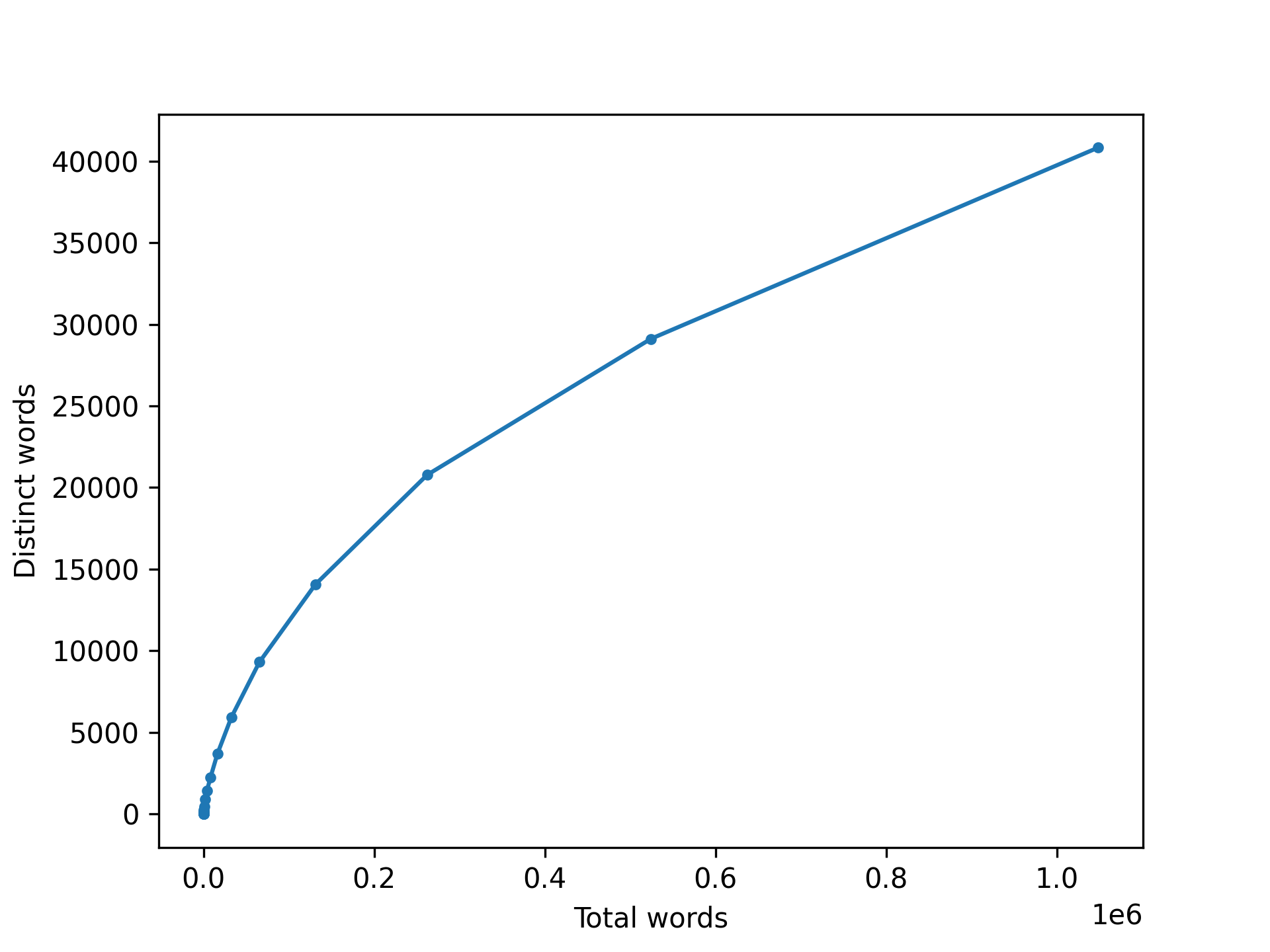
Zipf’s Law and Heaps’ Law
Zipf’s law says that there is a reverse exponential relationship between the frequency of a word (fw) in a large natural language text, and its relative frequency rank (rw; the ranking of its frequency in comparison with other words’ frequencies)
 Heaps’ law relates the number of distinct words in a text to the overall number of words in the text.
Heaps’ law relates the number of distinct words in a text to the overall number of words in the text.
Statistical Significance Testing
Modify the simple classifier to include the information about the magnitude of a sentiment.
A word with a strong intensity should be weighted four times as high for the evaluator.
Implement the two-sided sign test algorithm to determine if one classifier is significantly better or worse than another. The sign for a result should be determined by which classifier is more correct and the ceiling of the least common sign total should be used to calculate the probability.
The p-value of the two-sided sign test for classifier_a "classifier simple" and classifier_b "classifier magnitude": 0.6722499772048186
The p-value of the two-sided sign test for classifier_a "classifier magnitude" and classifier_b "naive bayes classifier": 0.07683763213126037
Cross-Validation and Evaluation Sets
Training and Evaluation Sets
- Random: Assign the datapoints to folds randomly.
- Stratified random: Assign the datapoints to folds randomly but make sure that there is the same number of positive and negative reviews in each fold.
Random cross validation accuracies: [0.8, 0.8111111111111111, 0.8444444444444444, 0.7888888888888889, 0.8222222222222222, 0.8277777777777777, 0.8222222222222222, 0.8055555555555556, 0.8333333333333334, 0.7888888888888889]
Random cross validation mean accuracy: 0.8144444444444444
Random cross validation variance: 0.00031604938271604933
Stratified cross validation accuracies: [0.8055555555555556, 0.8388888888888889, 0.8555555555555555, 0.8666666666666667, 0.8222222222222222, 0.7611111111111111, 0.8388888888888889, 0.7944444444444444, 0.8388888888888889, 0.7944444444444444]
Stratified cross validation mean accuracy: 0.8216666666666667
Stratified cross validation variance: 0.0009472222222222234
Smoothed Naive Bayes accuracy on held-out data: 0.84
Confusion matrix:
ACTUAL
| pos | neg |
-----+-----+-----+
pos | 92 | 24 |
PRED -----+-----+-----+
neg | 8 | 76 |
-----+-----+-----+
Smoothed Naive Bayes accuracy on 2016 data: 0.8333333333333334
Confusion matrix:
ACTUAL
| pos | neg |
-----+-----+-----+
pos | 8 | 0 |
PRED -----+-----+-----+
neg | 4 | 12 |
-----+-----+-----+
Simple Sentiment Classifier performance accuracy on held-out data: 0.615
Simple Sentiment Classifier performance accuracy on 2016 data: 0.7916666666666666
P-value of significance test between NB and Simple Classifier on 2016 data: 1.0
Nuanced Classifier
Agreement table; Calculate Fleiss’ kappa
Your accuracy on the nuanced dataset: 0.5926851851851852
Agreement table for this year.
REVIEW
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+
pos | 63 | 6 | 2 | 102 |
SENT -----+-----+-----+-----+-----+
neg | 42 | 99 | 103 | 3 |
-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+
The cohen kappa score for the review predictions is 0.6454024550722497.
The cohen kappa score for the review predictions of review 1 and 2 is 0.3275457197751368.
The cohen kappa score for the review predictions of review 3 and 4 is 0.906218599977671.
Agreement table for the years 2019 to 2022.
REVIEW
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+
pos | 309 | 30 | 8 | 454 |
SENT -----+-----+-----+-----+-----+
neg | 163 | 442 | 464 | 18 |
-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+
The cohen kappa score for the review predictions from 2019 to 2022 is 0.6523603977342954.
Hidden Markov Models (HMM)
Two matrices for the HMM: transition matrix (A) and emission matrix (B).
Viterbi Algorithm: DP
Evaluation: precision, recall and F-measure
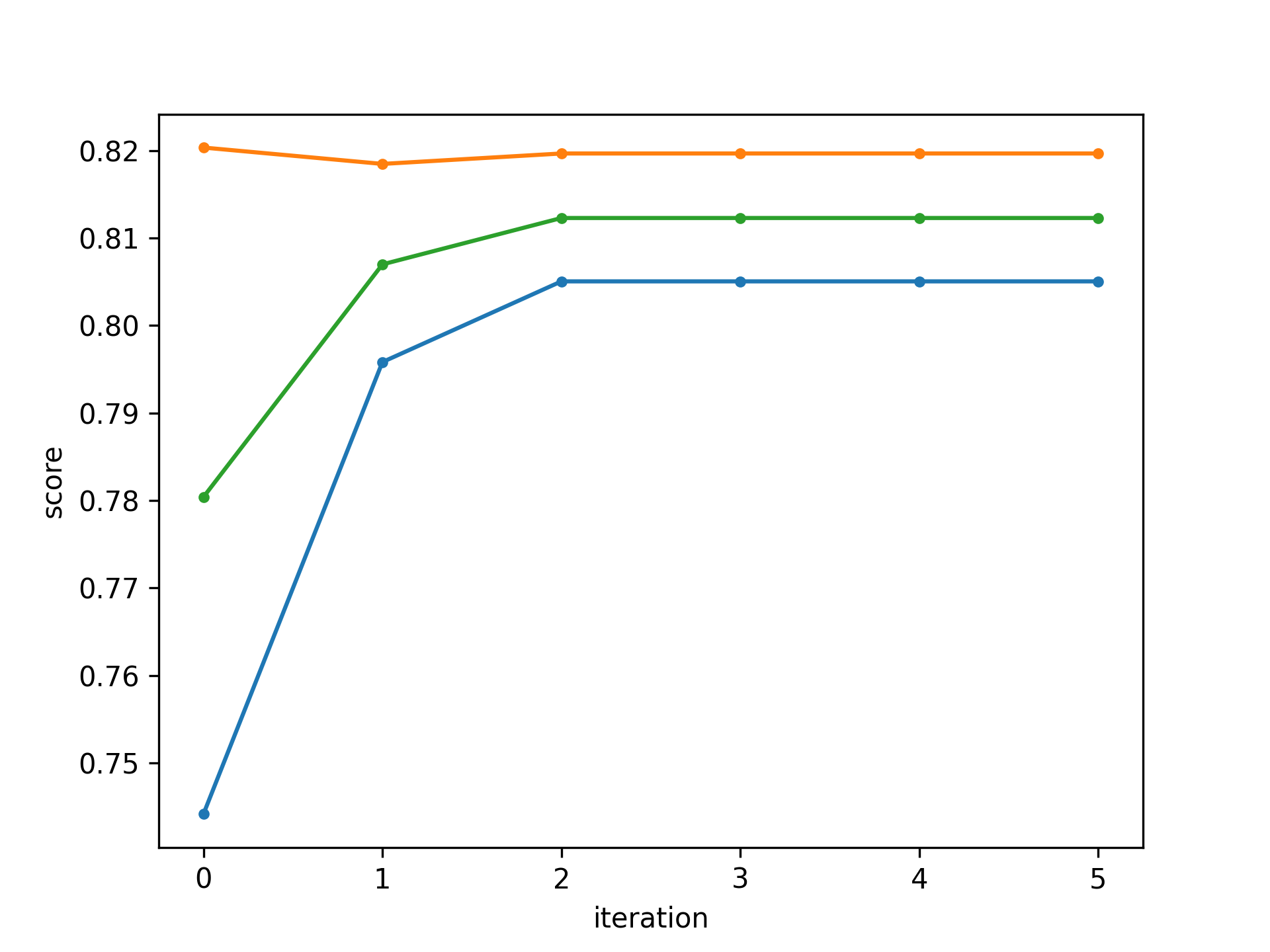
Semi-Supervised Learning with Self-Training
0. Train an HMM model with the available labelled training data as done in the first part of the task.
- Use the trained model to predict the hidden sequences of all available unlabelled data.
- Merge the labelled data with the new pseudo-labelled data.
- Train a new HMM model on the merged data.
- Repeat Step 1 (for the now pseudo-labelled data) to 3 for a total of t iterations.
Social Networks
Undirected and unweighted graph, Node, Link.
e.g, Facebook-style networks, Twitter-style networks
Visualize the network with Gephi
Find the degree of each node.
Determine the diameter of the network using a breadth-first all-pairs shortest path (APSP) algorithm.
Calculate betweenness centrality using Brandes algorithm: networkx.centrality
Clustering
Girvan-Newman algorithm on facebook_circle.edges