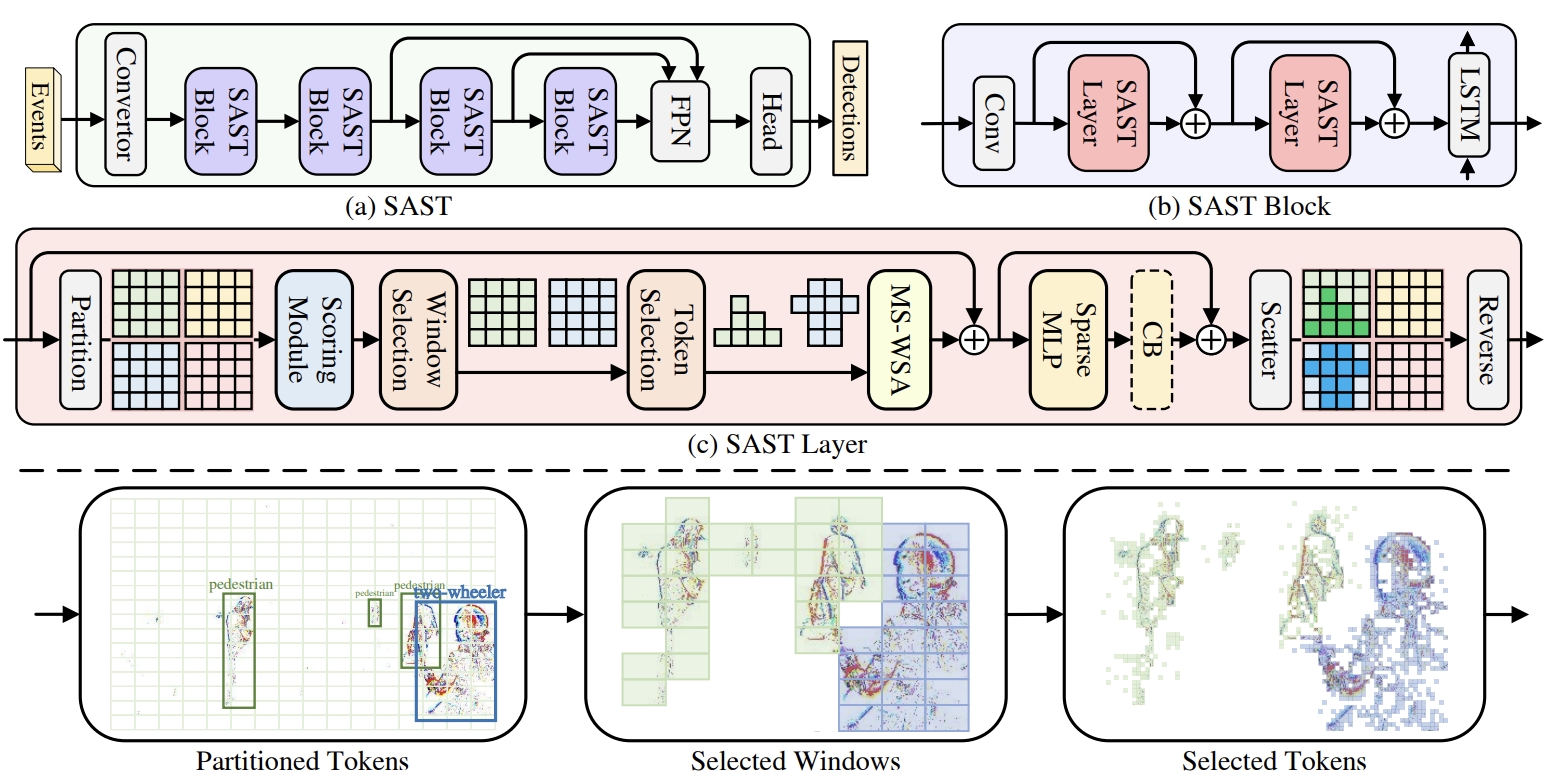
Probably the first sparse transformer to implement window-token co-sparsification. Feel free to use its principle to sparse whatever you want.
@InProceedings{peng2024sast,
author = {Yansong Peng and Hebei Li and Yueyi Zhang and Xiaoyan Sun and Feng Wu},
title = {Scene Adaptive Sparse Transformer for Event-based Object Detection},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
year = {2024},
}Conda Installation (same as RVT)
conda create -y -n rvt python=3.9 pip
conda activate sast
conda config --set channel_priority flexible
CUDA_VERSION=11.8
conda install -y h5py=3.8.0 blosc-hdf5-plugin=1.0.0
hydra-core=1.3.2 einops=0.6.0 torchdata=0.6.0 tqdm numba
pytorch=2.0.0 torchvision=0.15.0 pytorch-cuda=$CUDA_VERSION
-c pytorch -c nvidia -c conda-forge
python -m pip install pytorch-lightning==1.8.6 wandb==0.14.0
pandas==1.5.3 plotly==5.13.1 opencv-python==4.6.0.66 tabulate==0.9.0
pycocotools==2.0.6 bbox-visualizer==0.1.0 StrEnum=0.4.10
python -m pip install 'git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git'Detectron2 is not strictly required but speeds up the evaluation.
Required Data (same as RVT)
To evaluate or train SAST you will need to download the required preprocessed datasets:
| 1 Mpx | Gen1 | |
|---|---|---|
| pre-processed dataset | download | download |
| crc32 | c5ec7c38 | 5acab6f3 |
You may also pre-process the dataset yourself by following the instructions.
| 1 Mpx | Gen1 | |
|---|---|---|
| pre-trained checkpoint | download | download |
- Set
DATA_DIRas the path to either the 1 Mpx or Gen1 dataset directory - The training code uses W&B for logging during the training.
Hence, we assume that you have a W&B account.
- The training script below will create a new project called
SAST. Adapt the project name and group name if necessary.
- The training script below will create a new project called
BATCH_SIZE_PER_GPU=4
GPU_NUMBER=$(nvidia-smi --list-gpus | wc -l)
GPUS=$(seq -s "," 0 $((GPU_NUMBER - 1)))
lr=$(python -c "import math; print(2e-4*math.sqrt(${BATCH_SIZE_PER_GPU}*${GPU_NUMBER}/8))")
DATA_DIR=??? python train.py model=rnndet dataset=gen4 dataset.path=${DATA_DIR} wandb.project_name=SAST
wandb.group_name=1mpx hardware.num_workers.train=2 batch_size.train=${BATCH_SIZE_PER_GPU}
hardware.num_workers.eval=2 batch_size.eval=${BATCH_SIZE_PER_GPU}
hardware.gpus=[${GPUS}] +experiment/gen4="base.yaml"
training.learning_rate=${lr} validation.val_check_interval=10000python train.py model=rnndet dataset=gen1 dataset.path=${DATA_DIR} wandb.project_name=SAST
wandb.group_name=gen1 hardware.num_workers.train=2 batch_size.train=${BATCH_SIZE_PER_GPU}
hardware.num_workers.eval=2 batch_size.eval=${BATCH_SIZE_PER_GPU}
hardware.gpus=[${GPUS}] +experiment/gen1="base.yaml"
training.learning_rate=${lr} validation.val_check_interval=10000- Set
DATA_DIRas the path to either the 1 Mpx or Gen1 dataset directory - Set
CKPT_PATHto the path of the correct checkpoint matching the choice of the model and dataset. - Set
USE_TEST=1to evaluate on the test set, orUSE_TEST=0to evaluate on the validation set
- Set
GPU_IDto the PCI BUS ID of the GPU that you want to use. e.g.GPU_ID=0. Only a single GPU is supported for evaluation
DATA_DIR=??? CKPT_PATH=??? USE_TEST=??? GPU_ID=??? python validation.py dataset=gen4 dataset.path=${DATA_DIR} checkpoint=${CKPT_PATH}
use_test_set=${USE_TEST} hardware.gpus=${GPU_ID} batch_size.eval=4 +experiment/gen4="base.yaml"python validation.py dataset=gen1 dataset.path=${DATA_DIR} checkpoint=${CKPT_PATH}
use_test_set=${USE_TEST} hardware.gpus=${GPU_ID} batch_size.eval=4 +experiment/gen1="base.yaml"This project has used code from the following projects: