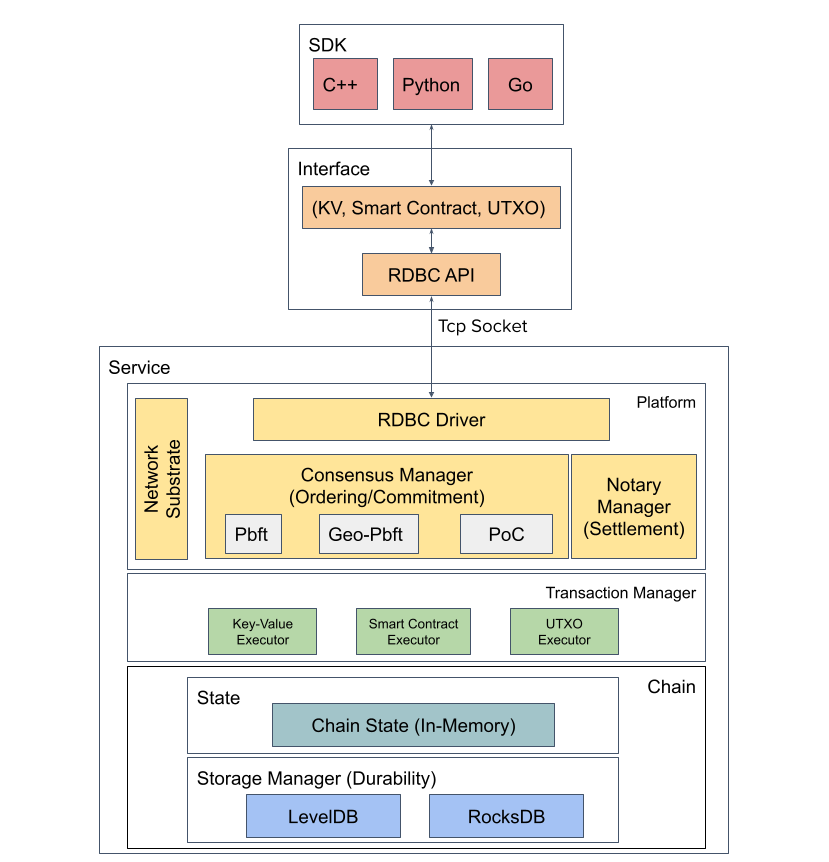
ResilientDB is a High Throughput Yielding Permissioned Blockchain Fabric founded by ExpoLab at UC Davis in 2018. ResilientDB advocates a system-centric design by adopting a multi-threaded architecture that encompasses deep pipelines. Further, ResilientDB separates the ordering of client transactions from their execution, which allows it to process messages out-of-order.
- ResilientDB orders client transactions through a highly optimized implementation of the PBFT [Castro and Liskov, 1998] protocol, which helps to achieve consensus among its replicas. ResilientDB also supports deploying other state-of-the-art consensus protocols [release are planned] such as GeoBFT [blog, released], PoE, RCC, RingBFT, PoC, SpotLess, HotStuff, and DAG.
- ResilientDB requires deploying at least 3f+1 replicas, where f (f > 0) is the maximum number of arbitrary (or malicious) replicas.
- ResilientDB supports primary-backup architecture, which designates one of the replicas as the primary (replica with identifier 0). The primary replica initiates consensus on a client transaction, while backups agree to follow a non-malicious primary.
- ResilientDB exposes a wide range of interfaces such as a Key-Value store, Smart Contracts, UTXO, and Python SDK. Following are some of the decentralized applications (DApps) built on top of ResilientDB: NFT Marketplace and Debitable.
- To persist blockchain, chain state, and metadata, ResilientDB provides durability through LevelDB and RocksDB.
- ResilientDB provides access to a seamless GUI display for deployment and maintenance, and supports Grafana for plotting monitoring data.
- [Historial Facts] The ResilientDB project was founded by Mohammad Sadoghi along with his students (Suyash Gupta as the lead Architect, Sajjad Rahnama, Jelle Hellings) at UC Davis in 2018 and was open-sourced in late 2019. On September 30, 2021, we released ResilientDB v-3.0. In 2022, ResilientDB was completely re-written and re-architected (Junchao Chen as the lead Architect along with the entire NexRes Team), paving the way for a new sustainable foundation, referred to as NexRes (Next Generation ResilientDB). Thus, on September 30, 2022, NexRes-v1.0.0 was born, marking a new beginning for ResilientDB.
The latest ResilientDB documentation, including a programming guide, is available on our blog repository. This README file provides basic setup instructions.
- Software Stack Architecture
- SDK Layer: Python SDK and Wallet - ResVault
- Interface Layer: Key-Value, Solidity Smart Contract, Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) Model, ResilientDB Database Connectivity (RDBC) API
- Platform Layer: Consensus Manager Architecture (ordering, recovery, network, chain management)
- Execution Layer: Transaction Manager Design (Runtime)
- Chain Layer: Chain State & Storage Manager Design (durability)
- Installing & Deploying ResilientDB
- Build Your First Application: KV Service, UTXO
- Dashboard: Monitoring, Deployment, Data Pipeline
- System Parameters & Configuration
- Continuous Integration & Testing
Ubuntu 20.*
Next, we show how to quickly build ResilientDB and deploy 4 replicas and 1 client proxy on your local machine. The proxy acts as an interface for all the clients. It batches client requests and forwards these batches to the replica designated as the leader. The 4 replicas participate in the PBFT consensus to order and execute these batches. Post execution, they return the response to the leader.
Install dependencies:
./INSTALL.sh
Run ResilientDB (Providing a Key-Value Service):
./service/tools/kv/server_tools/start_kv_service.sh
- This script starts 4 replicas and 1 client. Each replica instantiates a key-value store.
Build Interactive Tools:
bazel build service/tools/kv/api_tools/kv_service_tools
Run tools to set a value by a key (for example, set the value with key "test" and value "test_value"):
bazel-bin/service/tools/kv/api_tools/kv_service_tools service/tools/config/interface/service.config set test test_value
You will see the following result if successful:
client set ret = 0
Run tools to get value by a key (for example, get the value with key "test"):
bazel-bin/service/tools/kv/api_tools/kv_service_tools service/tools/config/interface/service.config get test
You will see the following result if successful:
client get value = test_value
Run tools to get all values that have been set:
bazel-bin/service/tools/kv/api_tools/kv_service_tools service/tools/config/interface/service.config getvalues
You will see the following result if successful:
client getvalues value = [test_value]
We also provide access to a deployment script that allows deployment on distinct machines.