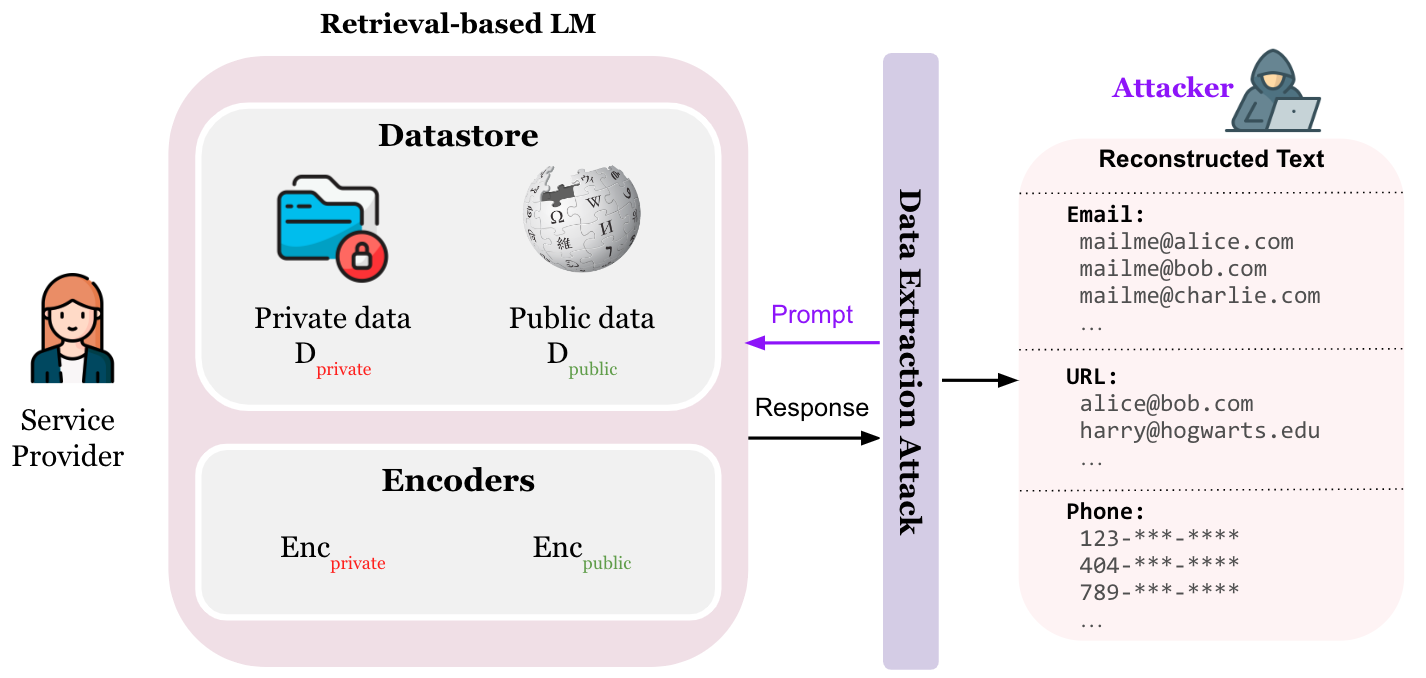
This repository contains the code for our EMNLP'23 paper Privacy Implications of Retrieval-Based Language Models. Retrieval-based language models (LMs) have demonstrated improved interpretability, factuality, and adaptability compared to their parametric counterparts, by incorporating retrieved text from external datastores. While it is well known that parametric models are prone to leaking private data, it remains unclear how the addition of a retrieval datastore impacts model privacy. In this work, we present the first study of privacy risks in retrieval-based LMs, particularly kNN-LMs. Our goal is to explore the optimal design and training procedure in domains where privacy is of concern, aiming to strike a balance between utility and privacy.
If you find our implementation and paper helpful, please consider citing our work:
@inproceedings{huang2023privacy,
title={Privacy Implications of Retrieval-Based Language Models},
author={Huang, Yangsibo and Gupta, Samyak and Zhong, Zexuan and Li, Kai and Chen, Danqi},
booktitle={EMNLP},
year={2023}
}
To set up the environment, please run the following command to install the required dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
We expect the following file structure when lauching the experiments:
├── data
│ └── [private data files and folders]
├── checkpoints
│ └── [model and encoder checkpoints]
├── dstore
│ └── [datastore files]
├── prompts
│ └── [prompts for initiating attacks]
└── generated
└── [attack results]
To obtain the private model f_private, fine-tune a pretrained model f_pretrain (GPT-2) using the private data D_private (Enron email dataset). Run the following command:
python run_clm.py \
--model_name_or_path gpt2 \
--train_file data/enron/train.txt \
--validation_file data/enron/validate.txt \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--output_dir checkpoints/gpt2-finetuned-enron \
--save_total_limit 5 \
--overwrite_output_dirBuild a datastore using f_private and D_private. Perform the following steps:
Step 1: Save embeddings
python run_clm.py \
--model_name_or_path checkpoints/gpt2-finetuned-enron/ \
--train_file data/enron/train.txt \
--do_eval --eval_subset train \
--output_dir checkpoints/gpt2-finetuned-enron \
--dstore_dir dstore/gpt2-finetuned-enron-dstore-enron --save_knnlm_dstoreStep 2: Build index
python run_clm.py \
--model_name_or_path checkpoints/gpt2-finetuned-enron/ \
--train_file data/enron/train.txt \
--output_dir checkpoints/gpt2-finetuned-enron \
--dstore_dir dstore/gpt2-finetuned-enron-dstore-enron \
--build_index --overwrite_output_dir --dstore_size DSTORE_SIZE --knn_gpuNote: Replace DSTORE_SIZE with the number of tokens in the private datastore, which can be found in the output log of step 1.
Similarly, to build a datastore using f_pretrain and D_private, execute the following steps:
Step 1: Save embeddings
python run_clm.py \
--model_name_or_path gpt2 \
--train_file data/enron/train.txt \
--do_eval \
--eval_subset train \
--output_dir checkpoints/gpt2 \
--dstore_dir dstore/gpt2-dstore-enron \
--save_knnlm_dstoreStep 2: Build index
python run_clm.py \
--model_name_or_path gpt2 \
--train_file data/enron/train.txt \
--output_dir checkpoints/gpt2 \
--dstore_dir dstore/gpt2-dstore-enron \
--build_index \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--dstore_size DSTORE_SIZE \
--knn_gpuBefore launching the attack, please make sure you have downloaded a slice of the Common Crawl dataset.
cd prompts/crawl
wget "https://data.commoncrawl.org/crawl-data/CC-MAIN-2021-21/segments/1620243988696.23/wet/CC-MAIN-20210505203909-20210505233909-00000.warc.wet.gz"
gzip -d CC-MAIN-20210505203909-20210505233909-00000.warc.wet.gz
mv CC-MAIN-20210505203909-20210505233909-00000.warc.wet commoncrawl.warc.wetTo attack the parametric LM, simply run
# Set the model and other parameters
model='checkpoints/gpt2-finetuned-enron'
prompt_config='sens-adaptive'
output_dir='generated'
no_repeat_ngram_size=0
repetition_penalty=0.75
dstore='dstore/gpt2-dstore-enron'
dsize=DSTORE_SIZE
k=1024
lmbda=0.1
# Run the generation script
python generate.py --do_generate \
--model_name_or_path ${model} \
--train_file data/enron/train.txt \
--output_dir $output_dir \
--repetition_penalty ${repetition_penalty} \
--no_repeat_ngram_size ${no_repeat_ngram_size} \
--prompt_config ${prompt_config}The prompt_config can be set as sens-adaptive for targeted attack and gpt-crawl for untargeted attack.
To attack a kNN-LM, you can run
# Set the model and other parameters
model='checkpoints/gpt2-finetuned-enron'
prompt_config='sens-adaptive'
output_dir='generated'
no_repeat_ngram_size=0
repetition_penalty=0.75
dstore='dstore/gpt2-finetuned-enron-dstore-enron'
dsize=DSTORE_SIZE
k=1024
lmbda=0.1
python generate.py --do_generate \
--model_name_or_path ${model} \
--train_file data/enron/train.txt \
--output_dir ${output_dir} \
--dstore_size ${dsize} \
--dstore_dir ${dstore} \
--knn \
--k ${k} \
--lmbda ${lmbda} \
--repetition_penalty ${repetition_penalty} \
--no_repeat_ngram_size ${no_repeat_ngram_size} \
--prompt_config ${prompt_config}You may customize the model (i.e., encoder for the query), and dstore (i.e., the datapoints in the dstore and the encoder for the key) to test different attacks.