Apache Spark is written in Scala programming language. To support Python with Spark, Apache Spark community released a tool, PySpark. Using PySpark, you can work with RDDs in Python programming language also. It is because of a library called Py4j that they are able to achieve this.
- Pyspark is the combo of python spark
- Scalable
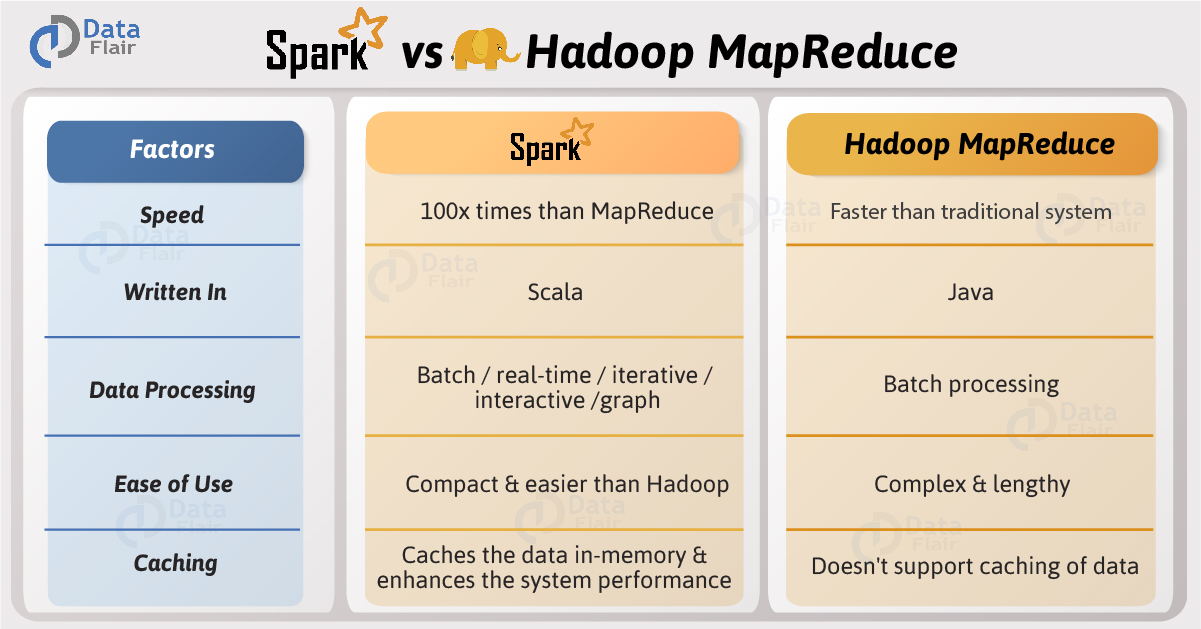
- 100x faster than hadoop mapreduce
- 10x faster is disk
- Use Ram insted of local drive which increase the processing
A Databricks Cluster is a combination of computation resources and configurations on which you can run jobs and notebooks. Some of the workloads that you can run on a Databricks Cluster include Streaming Analytics, ETL Pipelines, Machine Learning, and Ad-hoc analytics.
The workloads are run as commands in a notebook or as automated tasks. There are two types of Databricks Clusters:
- All-purpose Clusters: These types of Clusters are used to analyze data collaboratively via interactive notebooks. They are created using the CLI, UI, or REST API. An All-purpose Cluster can be terminated and restarted manually. They can also be shared by multiple users to do collaborative tasks interactively.
- Job Clusters: These types of clusters are used for running fast and robust automated tasks. They are created when you run a job on your new Job Cluster and terminate the Cluster once the job ends. A Job Cluster cannot be restarted.
The driver and worker nodes can have different instance types, but by default they are the same. A driver node runs the main function and executes various parallel operations on the worker nodes. The worker nodes read and write from and to the data sources.
- Transformation-: It create a new rdd ex: map, flatMap, filter, groupby etc.
- Actions-: It is to perform ceratin computation like count, collect, take, first etc it doesn't create a new rdd
- Windows vs GroupBy-: groupBy is primarily used for summarizing data by groups, while window is used for more advanced analytics and calculations that involve specifying a window or range of rows within each group. You often use window when you need to calculate values that depend on the order of rows within each group or when you need cumulative or rolling aggregations.
Spark Streaming is one of those unique features, which have empowered Spark to potentially take the role of Apache Storm. Spark Streaming mainly enables you to create analytical and interactive applications for live streaming data. You can do the streaming of the data and then, Spark can run its operations from the streamed data itself.
- real time object detection are the example
MLLib is a machine learning library like Mahout. It is built on top of Spark, and has the provision to support many machine learning algorithms. But the point difference with Mahout is that it runs almost 100 times faster than MapReduce. It is not yet as enriched as Mahout, but it is coming up pretty well, even though it is still in the initial stage of growth.
For graphs and graphical computations, Spark has its own Graph Computation Engine, called GraphX. It is similar to other widely used graph processing tools or databases, like Neo4j, Girafe, and many other distributed graph databases.
The Spark SQL is built on the top of Spark Core. It provides support for structured data.
Data ingestion is the process of obtaining and importing data for immediate use or storage in a database. To ingest something is to take something in or absorb something.
- Batch processing In batch processing, the ingestion layer collects data from sources incrementally and sends batches to the application or system where the data is to be used or stored. Data can be grouped based on a schedule or criteria, such as if certain conditions are triggered. This approach is good for applications that don't require real-time data. It is typically less expensive.
- Real-time processing This type of data ingestion is also referred to as stream processing. Data is not grouped in any way in real-time processing. Instead, each piece of data is loaded as soon as it is recognized by the ingestion layer and is processed as an individual object. Applications that require real-time data should use this approach.
Data can be streamed in real time or ingested in batches. In real-time data ingestion, each data item is imported as the source emits it.
It simply means we have some source, driver, and destination. Where we perform Extract, Transform and Load operations.
Data lakes and data warehouses are both widely used for storing big data, but they are not interchangeable terms. A data lake is a vast pool of raw data, the purpose for which is not yet defined. A data warehouse is a repository for structured, filtered data that has already been processed for a specific purpose.

The main difference between Data warehouse and Data mart is that, Data Warehouse is the type of database which is data-oriented in nature. while, Data Mart is the type of database which is the project-oriented in nature. The other difference between these two the Data warehouse and the Data mart is that, Data warehouse is large in scope where as Data mart is limited in scope. So, multiple data mart can attached to one data warehouse.
The Delta Lake design integrates with Apache Spark APIs and sits above your current Data Lake. Delta Lake supports scalable metadata handling, ACID transactions, and the unification of batch and streaming data processing. It utilises your current data lake and is completely compatible with the Apache Spark APIs. In Delta lake ACID property if we try to insert/update anything it will performm 100% or no change.
or
Delta Lake is an open-source storage layer designed to run on top of an existing data lake and improve its reliability, security, and performance. It supports ACID transactions, scalable metadata, unified streaming, and batch data processing.
Data integration is the process of combining data from different sources into a single, unified view. Integration begins with the ingestion process, and includes steps such as cleansing, ETL mapping, and transformation. Data integration ultimately enables analytics tools to produce effective, actionable business intelligence.
It help us to restore our data which we have either deleted or lost. We can use below sql query to see prev version or restore the previous data.
- To get the list of version
describe history employee1 - To call the version ```select * from employee1@v1``
- To delete all recors
delete from employee1 - To restore the table
RESTORE TABLE employee1 to version as of 1remember this code will restore deleted value if and only if schema is preserved not worked wirh drop.
A view is a read-only object composed from one or more tables and views in a metastore. It resides in the third layer of Unity Catalog’s three-level namespace. A view can be created from tables and other views in multiple schemas and catalogs. Temp view doesn't exist in different sparksession and if you restart temp view will lost while global temp view exist in multiple session and will be persisted.