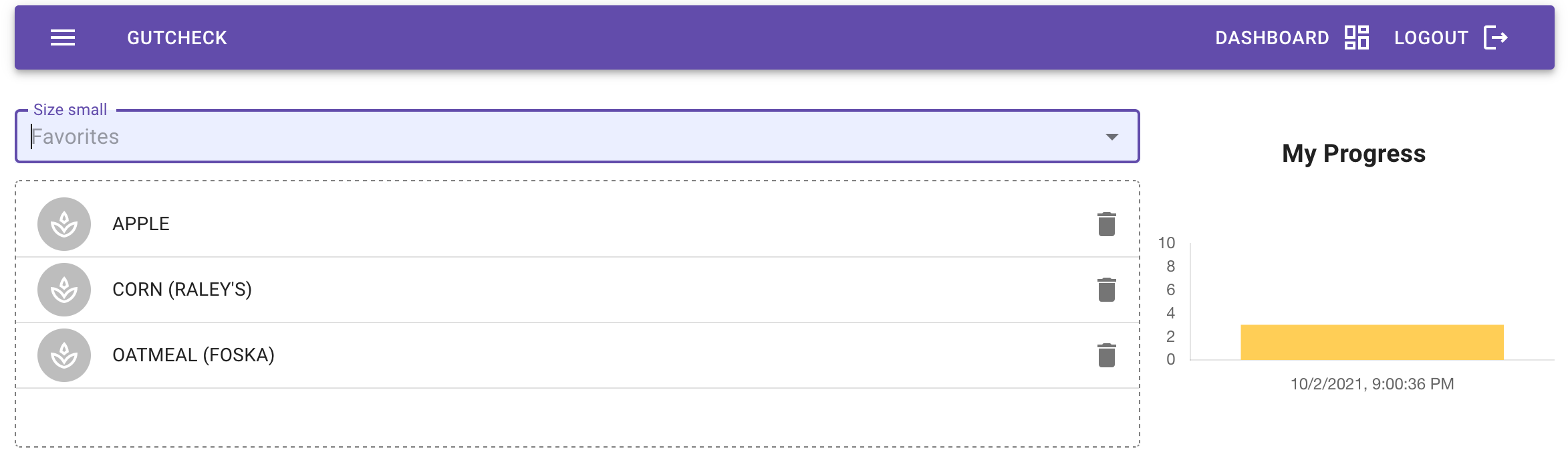
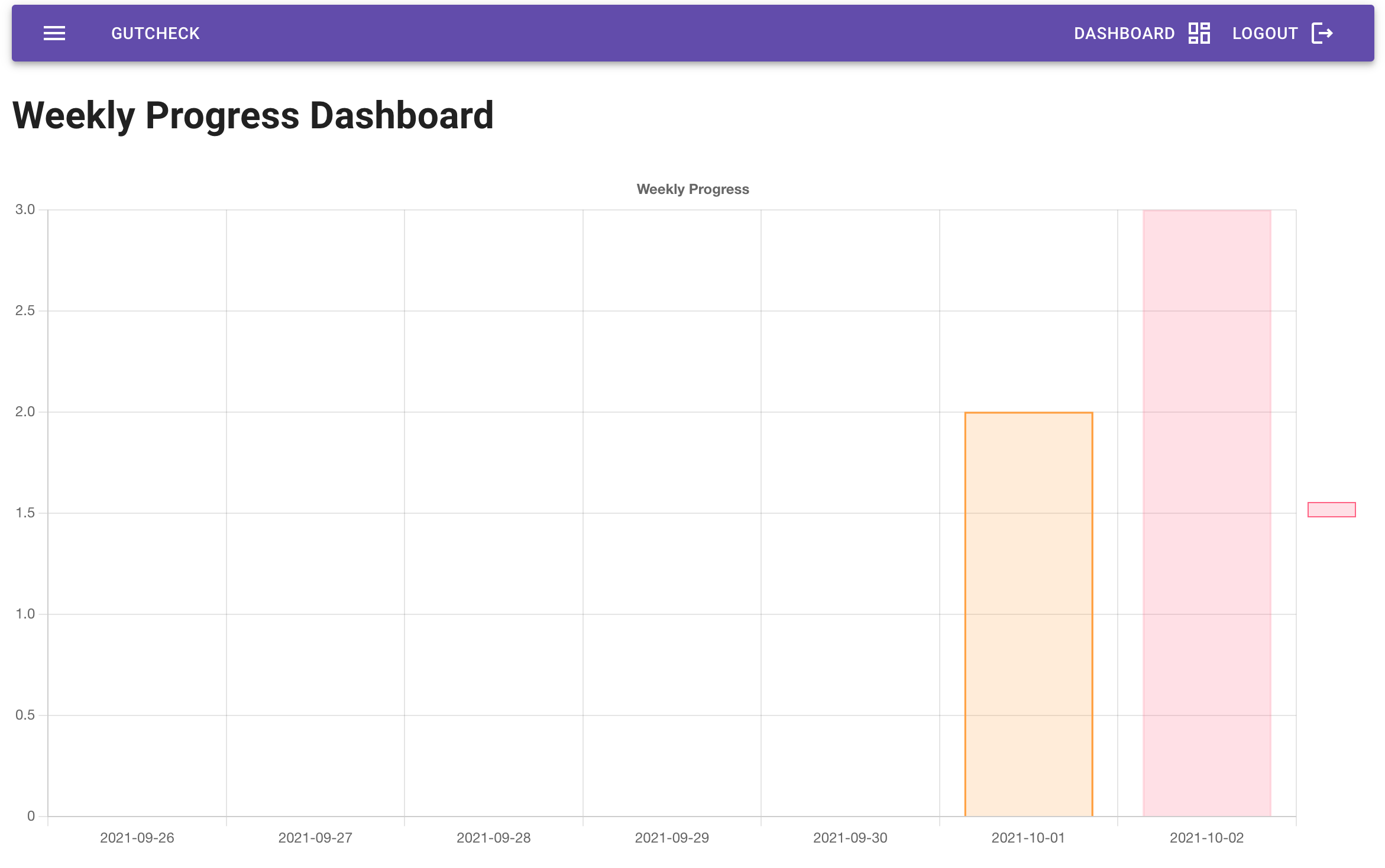
An app to track fiber variety. Read the science here.
Gutcheck consists of a React client and a Node/Express backend with PostgreSQL. Additional technologies used include:
- Chart.js for data visualization
- Okta for authentication/authorization
- Sequelize (ORM)
- Material UI
- USDA API
- Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/team-axolotl2021/gutcheck.git- Install dependencies
yarn- Run the dev server. (Note: Environment must be fully configured. See below.)
yarn devWe must first establish the necessary environment variables in .env.example. This application requires several environment variables to contain valid values in order to properly function.
First, rename the .env.example file to .env so that it is readable by the dotenv library.
Gutcheck uses Okta to provide authentication/authorization functionality.
- Set up a free Okta developer account. https://www.okta.com/free-trial/
- From the dashboard, select
Applicationsin the left navigation menu.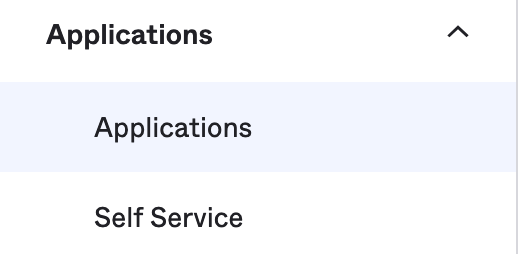
- Select
Create App Integrationand chooseOIDC - Open ID Connectas the sign-in method. - Select
Single Page Applicationas the Application Type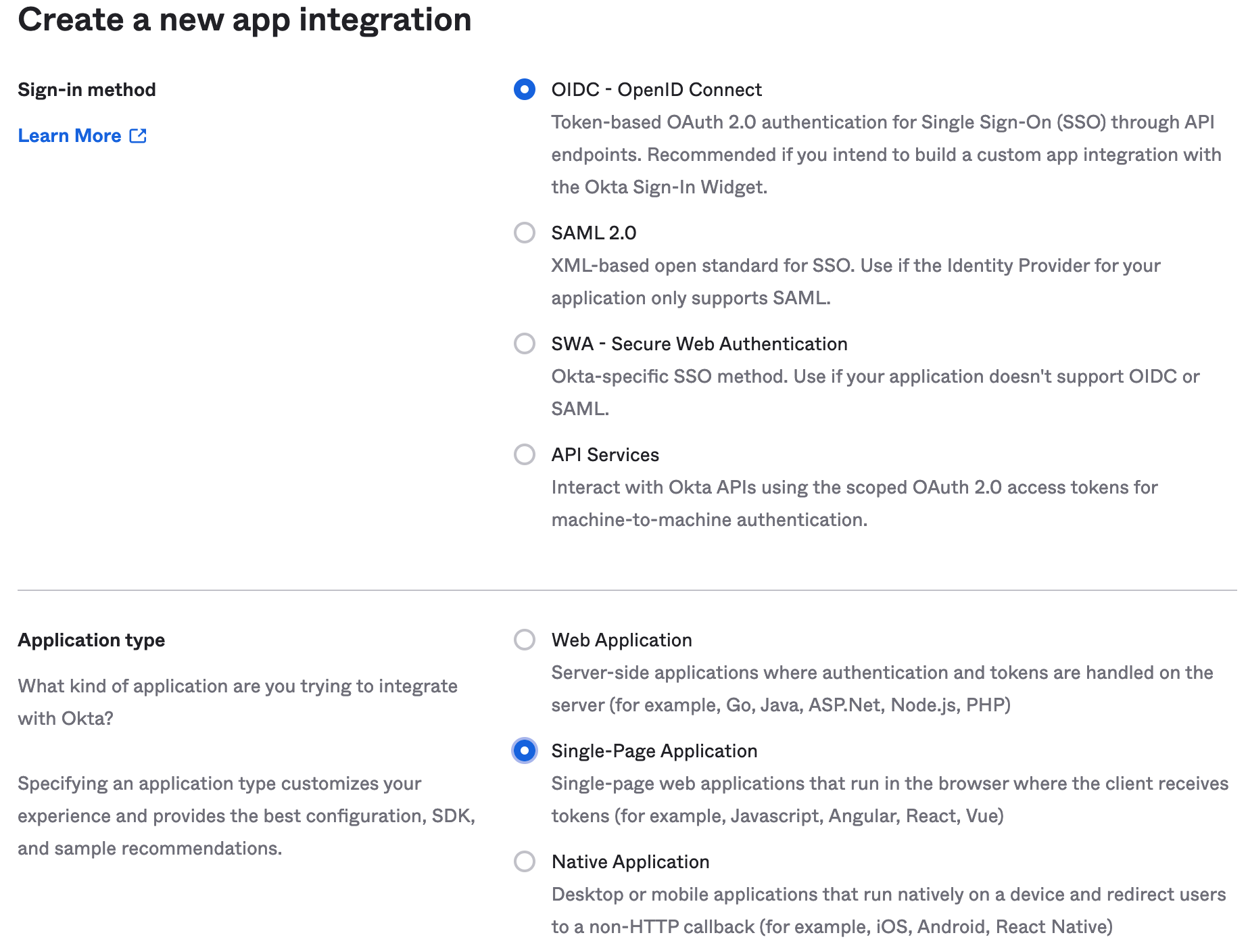
- You will be taken to the Application Dashboard. Take the
Client IDand supply it to the .env.example file in under the variable nameOKTA_CLIENT_ID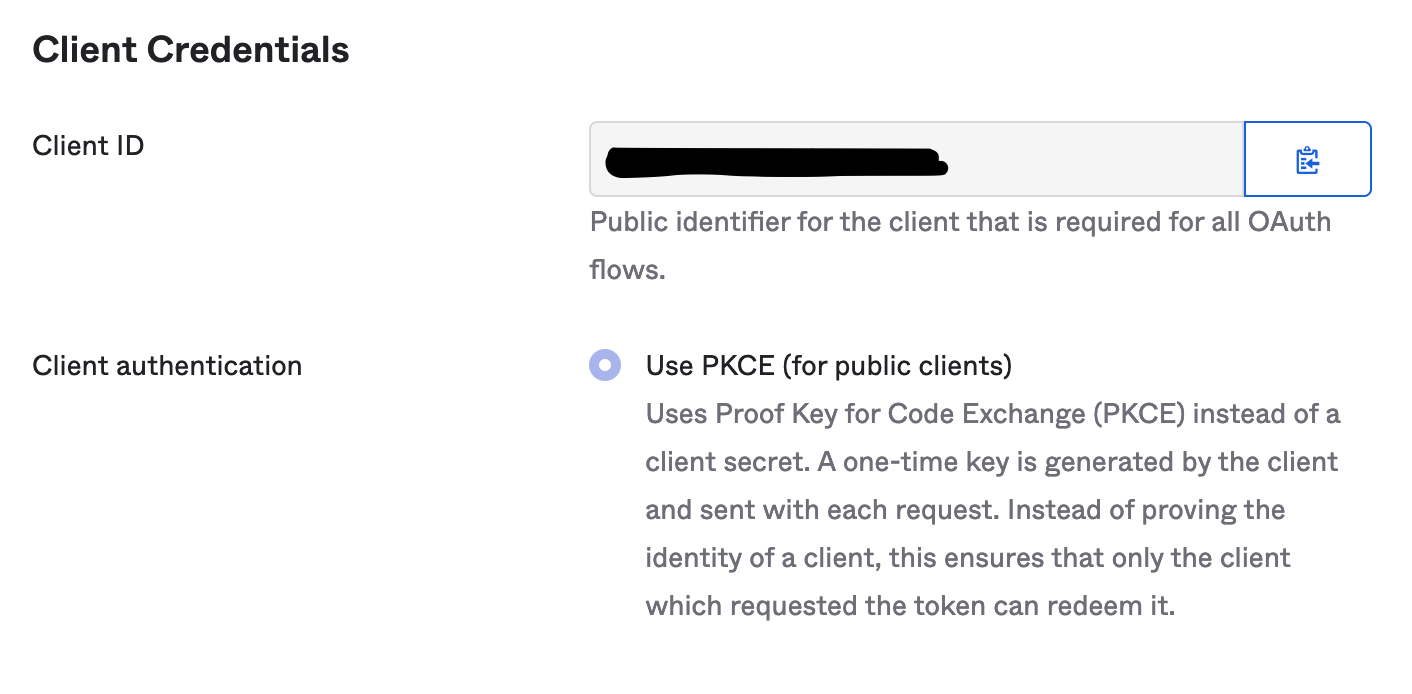
- On the same page, the first field under
General Settingscontains the Okta domain. Take this value and place it after thehttps://in the environment variableOKTA_ORG_URLin .env.example.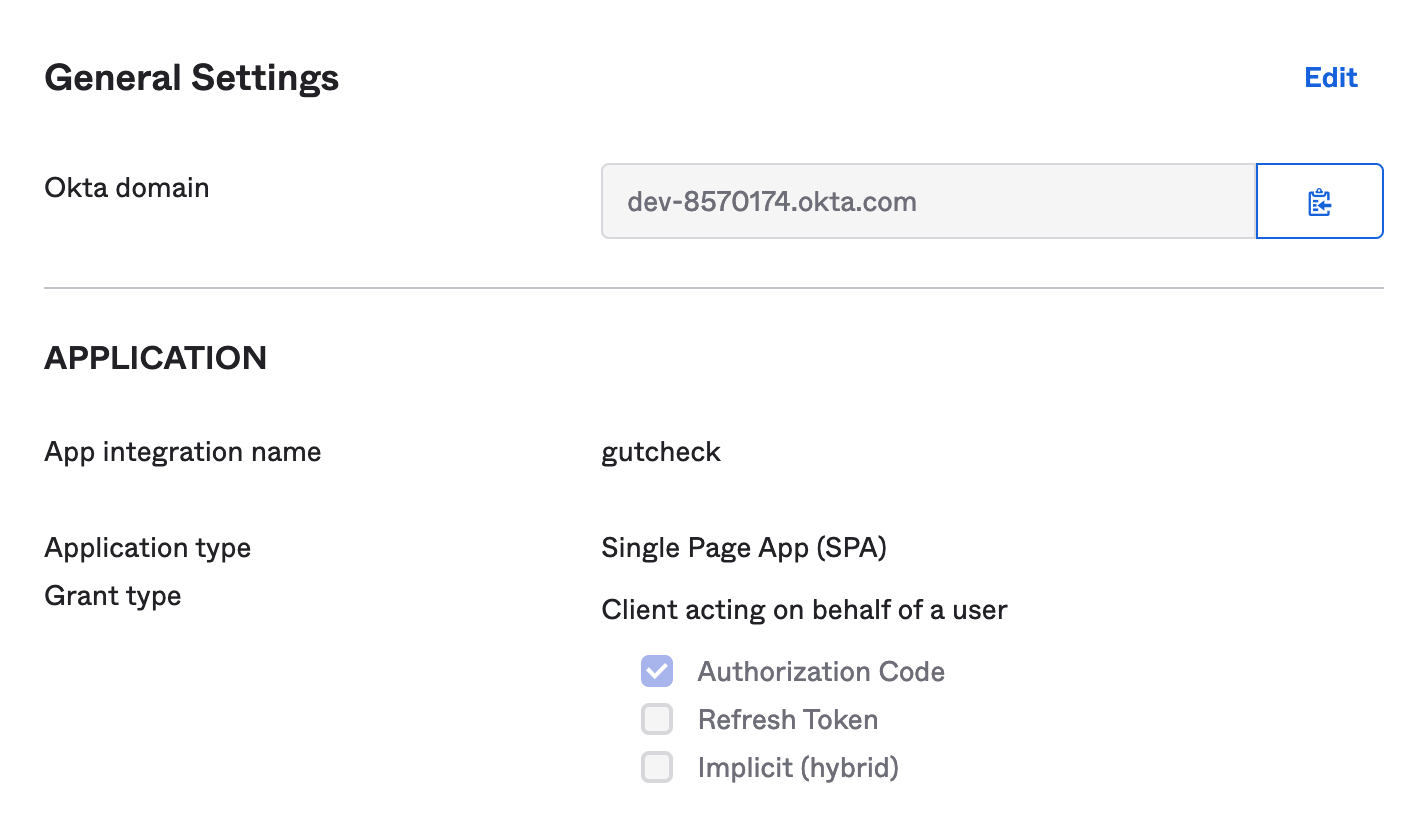
- In the Okta settings, ensure that the login section appears as follows:

- In order to verify tokens, Okta requires an API token that allows the Express server to communicate with the Okta domain. From the dashboard, in the left navigation, locate the
Securityheader and select theAPIlink. - Under the tokens tab, select
Create token. Give the token a descriptive name and clickcreate. SAVE THIS TOKEN -- you will not see it again. Place the token in.envunder the variable nameOKTA_API_TOKEN.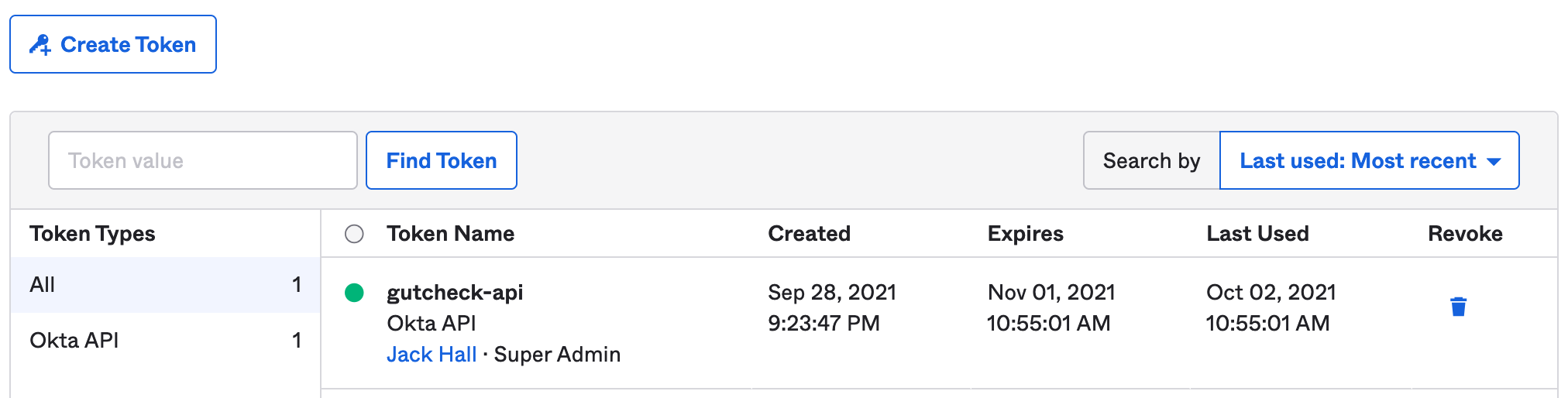
Authentication should now be functional.
PostgreSQL may be setup locally or using a remote database solution. A popular, free solution can be found at https://www.elephantsql.com/.
Remote database setup will vary depending on the provider, but in all cases you should end up with a connection string that resembles the following format:
postgres://<username>:<password>@<postgres hostname>/<database>
- Place the connection string in the
PG_URLenvironment variable in the.envfile.
Local database setups will vary widely, but can be categorized into two general categories: containerized databases or local postgres service. In the containerized scenario, an important consideration will be to ensure that the service port is exposed. In either case, there are a number of variables that must be supplied instead of PG_URL. Further, a minor refactor of sql/sequelize.js is required.
- Modify
.envand supply the following environment variables:
PG_DATABASE=
PG_HOSTNAME=
PG_USERNAME=
PG_PASSWORD=
- Modify
sql/sequelize.js.
// replace this line
const sequelize = new Sequelize(process.env.PG_URL, { dialect: 'postgres' });
// with the following
const sequelize = new Sequelize(
process.env.PG_DATABASE,
process.env.PG_USERNAME,
process.env.PG_PASSWORD,
{
host: process.env.PG_HOSTNAME,
dialect: 'postgres',
}
);