Alpaca-CoT: An Instruction Fine-Tuning Platform with Instruction Data Collection and Unified Large Language Models Interface
This is the repository for the Alpaca-CoT project, which aims to build an instruction finetuning (IFT) platform with extensive instruction collection (especially the CoT datasets) and a unified interface for various large language models. We are constantly expanding our instruction-tuning data collection, and integrating more LLMs. In addition, we also conduct an in-depth empirical study.
You are in a warm welcome to provide us with any non-collected instruction-tuning datasets (or their sources). We will uniformly format them, train Alpaca model (and other LLMs in the early future) with these datasets, open source the model checkpoints, and conduct extensive empirical studies. We hope that our project can make a modest contribution to the open-source process of large language models, and reduce its threshold for NLP researchers to get started.
You can also choose to join our group chat (WeChat) and communicate with more people with the same interests. At present, the number of group members is too large to join the group directly through the group QR code. You need to connect with me first to get into the group.- 4.15: Datasets
webGPT,dolly,baize,hh-rlhf,OIG(part)are collected and formatted. - 4.12: Now you can try Alpaca-CoT on Google Colab.
- 4.11: Added function
multi-turn conversationby @paulcx. - 4.9: Datasets
firefly,instruct,Code Alpacaare collected and formatted, which can be found here. - 4.7: Added functions
Parameter merging,Local chatting,Batch predictingandWeb service buildingby @weberr. - 4.4: Datasets
GPTeacher,Guanaco,HC3,prosocial-dialog,belle-chat&belle-math,xP3andnatural-instructionsare collected and formatted. - 4.3: The Chinese CoT dataset
CoT_CN_data.jsoncan be found here. - 4.1: Checkpoints of Bloom7b fine-tuned from instinwild-CN(47k) + belle(1.5M) can be found here.
- 4.1: instinwild (collected from Twitter, where users tend to share their interesting prompts of mostly generation, open QA, and mind-storm types) has been formatted and collected.
LLaMA [1] is a great work that demonstrates the amazing zero-shot and few-shot ability. It significantly reduces the cost of training, finetuning, and using competitive large language models, i.e., LLaMA-13B outperforms GPT-3(175B) and LLaMA-65B is competitive to PaLM-540M. Recently, to boost the instruction-following ability of LLaMA, Stanford Alpaca [2] finetuned LLaMA-7B on 52K instruction-following data generated by the Self-Instruct [3] techniques. However, at present, the LLM research community still faces three challenges: 1. Even LLaMA-7b still has high requirements for computing resources; 2. There are few open source datasets for instruction finetuning; and 3. There is a lack of empirical study on the impact of various types of instruction on model abilities, such as the ability to respond to Chinese instruction and the CoT reasoning.
To this end, we propose this project, which leverages various improvements that were subsequently proposed, with the following advantages:
-
- This repo contains code, modified from here, which can finetune LLaMA cheaply and efficiently (without performance degradation compared to Stanford Alpaca) by using low-rank adaptation (LoRA) [4], PEFT and bitsandbytes. The
7b,13band30bversions of LLaMA models can be easily trained on a single 80G A100.
- This repo contains code, modified from here, which can finetune LLaMA cheaply and efficiently (without performance degradation compared to Stanford Alpaca) by using low-rank adaptation (LoRA) [4], PEFT and bitsandbytes. The
-
- The models published in this repo significantly improve the CoT (reasoning) capability.
-
- The models published in this repo significantly improve the ability to follow Chinese instructions.
-
- This repo contains a collection of instruction-finetuning datasets that are continuously collected, which so far includes English, Chinese and CoT instructions. In addition, a collection of checkpoints trained with various instruction datasets is also provided.
-
- This repo integrates multiple LLMs and unifies their interfaces, It can be easily switched through hyperparameters. Currently, it includes LLaMA, ChatGLM[5], and Bloom[6], and more will continue to be added in the future for researchers to easily invoke and compare different LLMs.
-
- This repo contains extensive empirical studies and qualitative analysis, which may provide valuable findings and promote the exploration of LLM in the future.
To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first to study CoT reasoning based on LLaMA and Alpaca. Therefore, we abbreviate our work to Alpaca-CoT.
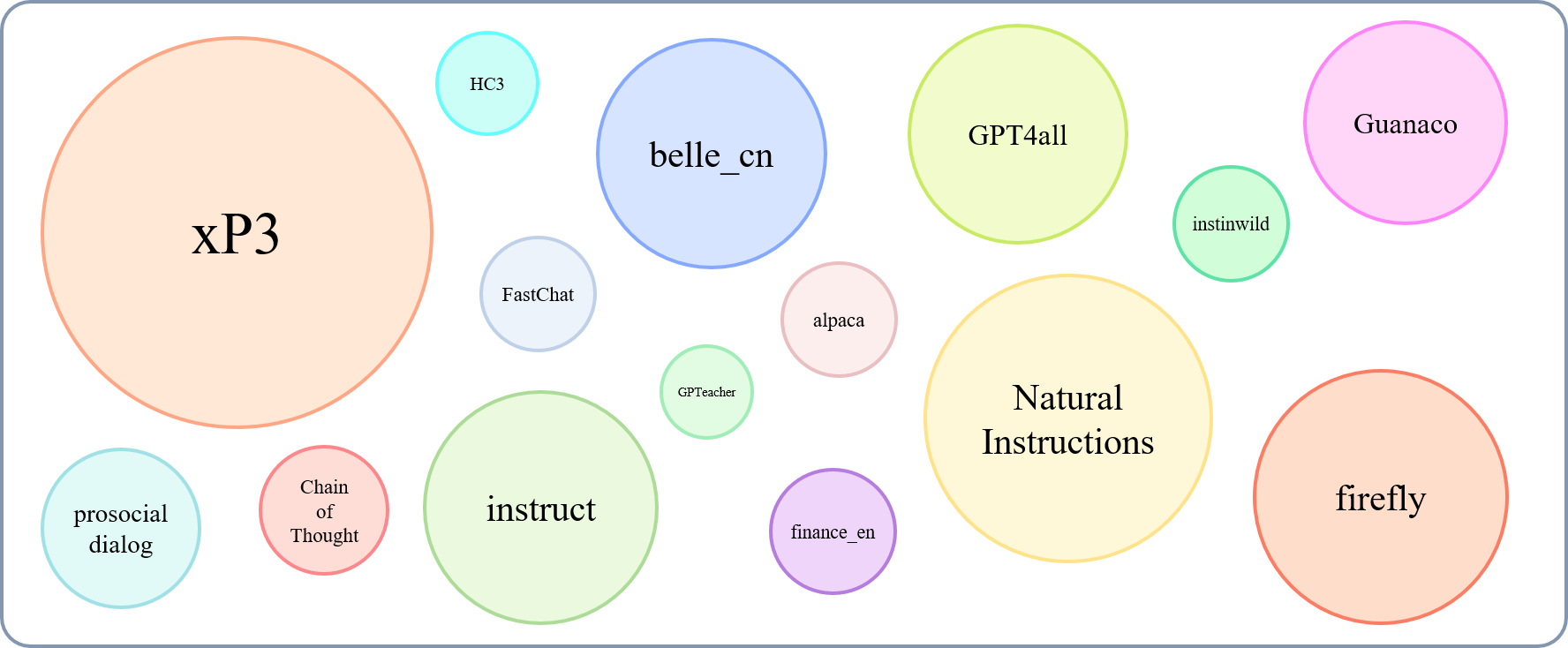
The relative size of collected datasets can be shown by this graph:
Referring to this (@yaodongC), we labeled each collected dataset according to the following rules:
(Lang)Lingual-Tags:
- EN: Instruction datasets in English
- CN: Instruction datasets in Chinese
- ML: [Multi-lingual] Instruction datasets in multiple languages
(Task)Task-Tags:
- MT: [Multi-task] Datasets containing multiple tasks
- TS: [Task-specific] Datasets tailored for specific tasks
(Gen)Generation-method:
- HG: [Human Generated Dataset] Datasets created by humans
- SI: [Self-Instruct] Datasets generated using self-instruct methods
- MIX: [Mixed Dataset] Dataset contains both human and machine generated data
- COL: [Collection of Dataset] Dataset made from a collection of other datasets
| Dataset | Nums | Lang | Task | Gen | Type | Src | Url |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chain of Thought | 74771 | EN/CN | MT | HG | instruct with cot reasoning | annotating CoT on existing data | download |
| GPT4all | 806199 | EN | MT | COL | code, storys and dialogs | distillation from GPT-3.5-turbo | download |
| GPTeacher | 29013 | EN | MT | SI | general, roleplay, toolformer | GPT-4 & toolformer | download |
| Guanaco | 534610 | ML | MT | SI | various linguistic tasks | text-davinci-003 | download |
| HC3 | 37175 | EN/CN | TS | MIX | dialogue evaluation | human or ChatGPT | download |
| alpaca | 52002 | EN | MT | SI | general instruct | text-davinci-003 | download |
| Natural Instructions | 5040134 | ML | MT | COL | diverse nlp tasks | human annotated datasets collection | download |
| belle_cn | 1079517 | CN | TS/MT | SI | general, mathematical reasoning, dialogue | text-davinci-003 | download |
| instinwild | 52191 | EN/CN | MT | SI | generation, open-qa, mind-storm | text-davinci-003 | download |
| prosocial dialog | 165681 | EN | TS | MIX | dialogue | GPT-3 rewrites questions + humans feedback manually | download |
| finance_en | 68912 | EN | TS | COL | financial related qa | GPT3.5 | download |
| xP3 | 78883588 | ML | MT | COL | a collection of prompts & datasets across 46 of languages & 16 NLP tasks | human annotated datasets collection | download |
| firefly | 1649398 | CN | MT | COL | 23 nlp tasks | human annotated datasets collection | download |
| instruct | 888969 | EN | MT | COL | augmented of GPT4All, Alpaca, open-source Meta datasets | augmentation performed using the advanced NLP tools provided by AllenAI | download |
| Code Alpaca | 20022 | EN | TS | SI | code generation, editing, optimization | text-davinci-003 | download |
| Alpaca_GPT4 | 52002 | EN/CN | MT | SI | general instruct | generated by GPT-4 using Alpaca | download |
| webGPT | 18994 | EN | TS | MIX | information retrieval (IR) QA | fine-tuned GPT-3, each instruction has two outputs, select better one | download |
| dolly | 15015 | EN | TS | HG | closed QA , summarization and etc, Wikipedia as references | human annotated | download |
| baize | 653699 | EN | MT | COL | a collection from Alpaca, Quora, StackOverFlow and MedQuAD questions | human annotated datasets collection | download |
| hh-rlhf | 284517 | EN | TS | MIX | dialogue | dialog between human and RLHF models | download |
| OIG(part) | 49237 | EN | MT | COL | created from various tasks, such as question and answering | using data augmentation, human annotated datasets collection | download |
| TODO | |||||||
| FastChat | EN | MT | MIX | general instruct | crowdsourcing to collect conversations between people and ChatGPT (ShareGPT) | ||
| Auto CoT | |||||||
| colossalchat | |||||||
| StackLLaMA |
You can download all the formatted data here. Then you should put them in the data folder.
You can download all checkpoints trained on various types of instruction data from here. Then, after setting LoRA_WEIGHTS (in generate.py) to the local path, you can directly execute the model inference.
All data in our collection is formatted into the same templates, where each sample is as follows:
[
{"instruction": instruction string,
"input": input string, # (may be empty)
"output": output string}
]
Note that, for CoT datasets, we first use the template provided by FLAN to change the original dataset into various Chain-of-Thoughts forms, and then convert it to the above format. The formatting script can be found here.
pip install -r requirements.txt
Note that, make sure python>=3.9 when finetuning ChatGLM.
In order for researchers to conduct systematic IFT research on LLMs, we have collected different types of instruction data, integrated multiple LLMs, and unified interfaces, making it easy to customize the desired collocation:
--model_type: Set the LLM you want to use. Currently, [llama, chatglm, bloom] are supported. The latter two have strong Chinese capabilities, and more LLMs will be integrated in the future.-- data: Set the data type used for IFT to flexibly tailor the desired command compliance ability. For example, for strong reasoning ability, set "alpaca-cot", for strong Chinese ability, set "belle1.5m", for coding and story generation ability, set "gpt4all", and for financial related response ability, set "finance".--model_name_or_path ': This is set to load different versions of the model weights for the target LLM--model_type`. For example, to load the llama's 13b version of weights, you can set decapoda-research/llama-13b-hf.
Single GPU
- for LLaMA
python3 uniform_finetune.py --model_type llama --model_name_or_path decapoda-research/llama-7b-hf \
--data alpaca-belle-cot --lora_target_modules q_proj v_proj \
--per_gpu_train_batch_size 4 --learning_rate 3e-4 --epochs 1
- for ChatGLM
python3 uniform_finetune.py --model_type chatglm --model_name_or_path THUDM/chatglm-6b \
--data alpaca-belle-cot --lora_target_modules query_key_value \
--lora_r 32 --lora_alpha 32 --lora_dropout 0.1 --per_gpu_train_batch_size 2 \
--learning_rate 2e-5 --epochs 1
Note that load_in_8bit is not yet suitable for ChatGLM, so batch_size must be smaller than others.
- for BLOOM
python3 uniform_finetune.py --model_type bloom --model_name_or_path bigscience/bloomz-7b1-mt \
--data alpaca-belle-cot --lora_target_modules query_key_value \
--per_gpu_train_batch_size 4 --learning_rate 3e-4 --epochs 1
Note that you can also pass the local path (where LLM weights saved) to --model_name_or_path. And the data type --data can be freely set according to your interests.
Multiple GPUs
- for LLaMA
python3 -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 4 \
--nnodes=1 --node_rank=0 --master_addr=xxx --master_port=yyy uniform_finetune.py \
--model_type llama --model_name_or_path decapoda-research/llama-7b-hf \
--data alpaca-belle-cot --lora_target_modules q_proj v_proj \
--per_gpu_train_batch_size 4 --learning_rate 3e-4 --epochs 1
- for ChatGLM
python3 -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 4 \
--nnodes=1 --node_rank=0 --master_addr=xxx --master_port=yyy \
uniform_finetune.py --model_type chatglm --model_name_or_path THUDM/chatglm-6b \
--data alpaca-belle-cot --lora_target_modules query_key_value \
--lora_r 32 --lora_alpha 32 --lora_dropout 0.1 --per_gpu_train_batch_size 2 \
--learning_rate 2e-5 --epochs 1
Note that load_in_8bit is not yet suitable for ChatGLM, so batch_size must be smaller than others.
- for BLOOM
python3 -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 4 \
--nnodes=1 --node_rank=0 --master_addr=xxx --master_port=yyy \
uniform_finetune.py --model_type bloom --model_name_or_path bigscience/bloomz-7b1-mt \
--data alpaca-belle-cot --lora_target_modules query_key_value \
--per_gpu_train_batch_size 4 --learning_rate 3e-4 --epochs 1
python3 merge.py --model_type llama --size 7b --lora_dir xxx --merged_dir yyy
python3 server.py --model_type chatglm --lora_dir xxx
python3 predict.py --model_type chatglm --data for_dict_data --lora_dir xxx --result_dir yyy
python3 web.py --model_type chatglm --lora_dir xxx
More details of instruction finetuing and inference can be found here where we modified from. Note that the folders saved-xxx7b are the save path for LoRA weights, and LLaMA weights are automatically downloaded from Hugging Face.
Note: The following figure shows the statistics of the dataset collected as of March 26, which is only displayed as a motivation of data collection. More datasets have been collected, such as financial related instruction datasets.
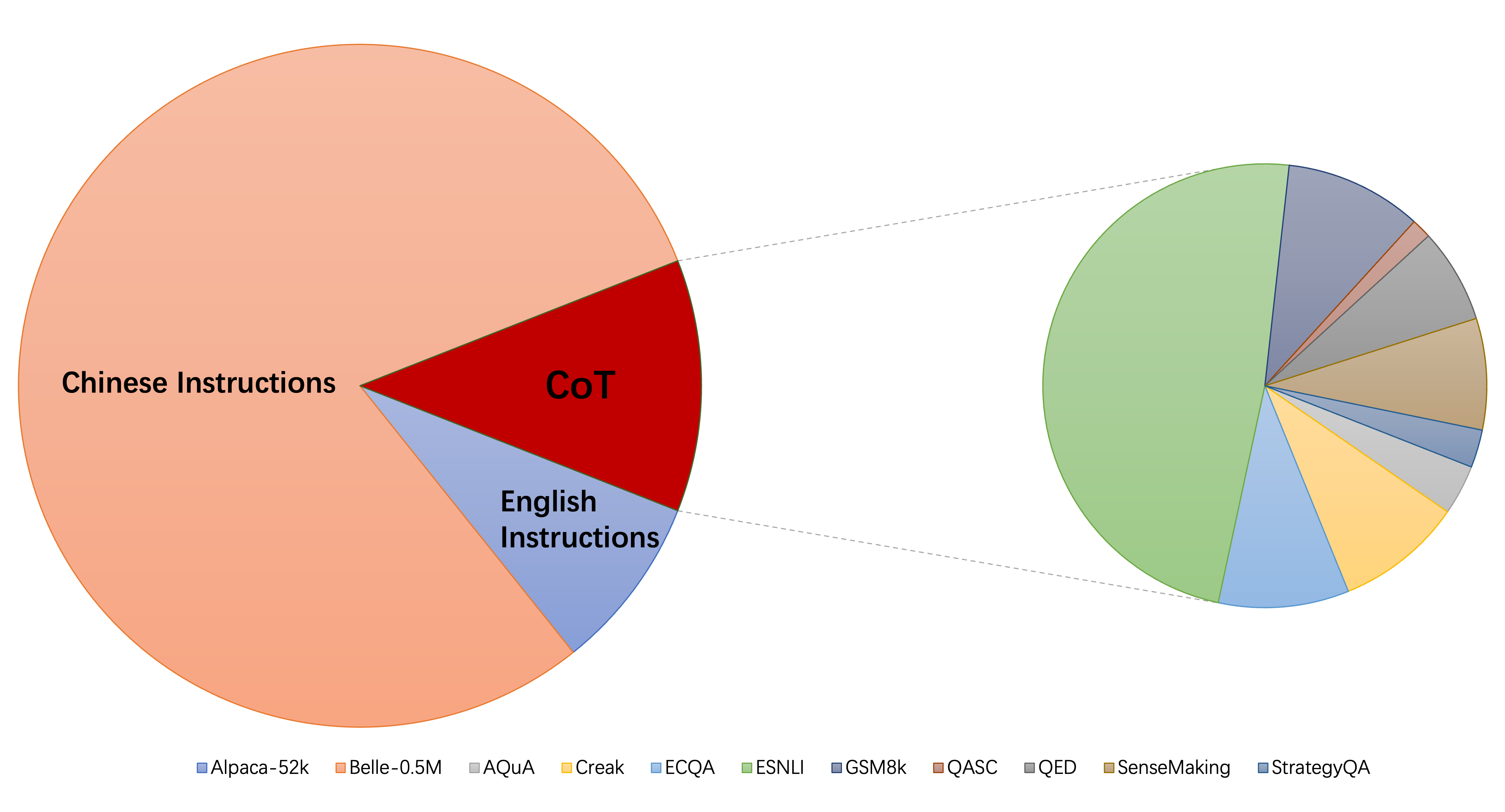 The current collection of instruction-finetuning datasets consists mainly of three parts:
The current collection of instruction-finetuning datasets consists mainly of three parts:
alpaca_data_cleaned.json: about 52K English instruction-following training samples.CoT_data.json: 9 CoT datasets involving about 75k samples. (published by FLAN[7])belle_data_cn.json: about 0.5M Chinese |instruction-following training samples. (published by BELLE [8])
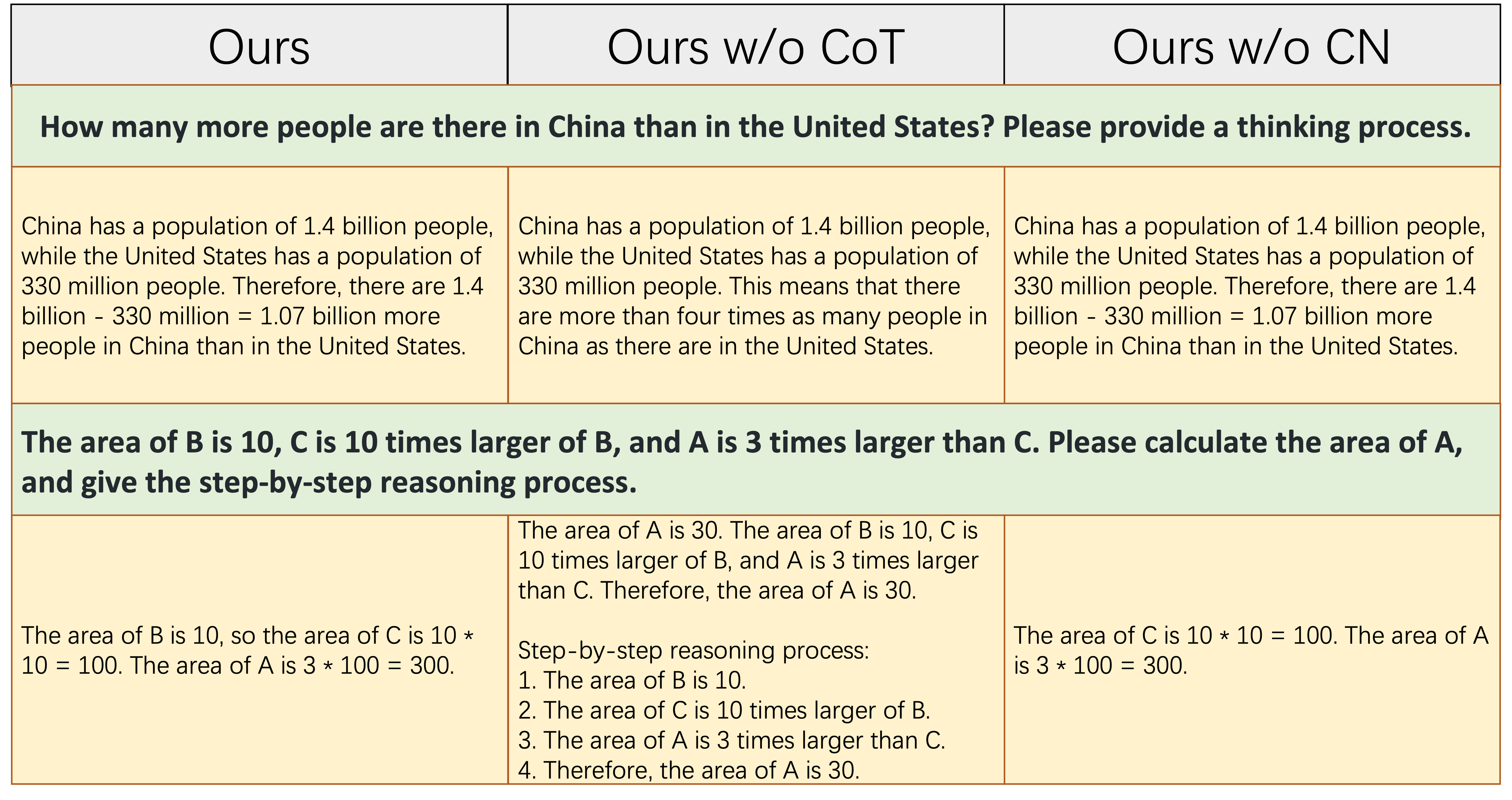 "w/o CoT" and "w/o CN" denote models that exclude CoT data and Chinese instructions from their instruction finetuning data, respectively.
"w/o CoT" and "w/o CN" denote models that exclude CoT data and Chinese instructions from their instruction finetuning data, respectively.
The above table shows two examples (invoving with numerical calculations) that require a certain amount of reasoning ability to respond correctly.
As shown in the middle column, Ours w/o CoT fails to generate the correct response, which shows that once the finetuning data does not contain CoT data, the model's reasoning ability significantly decreases. This further demonstrates that CoT data is essential for LLM models.
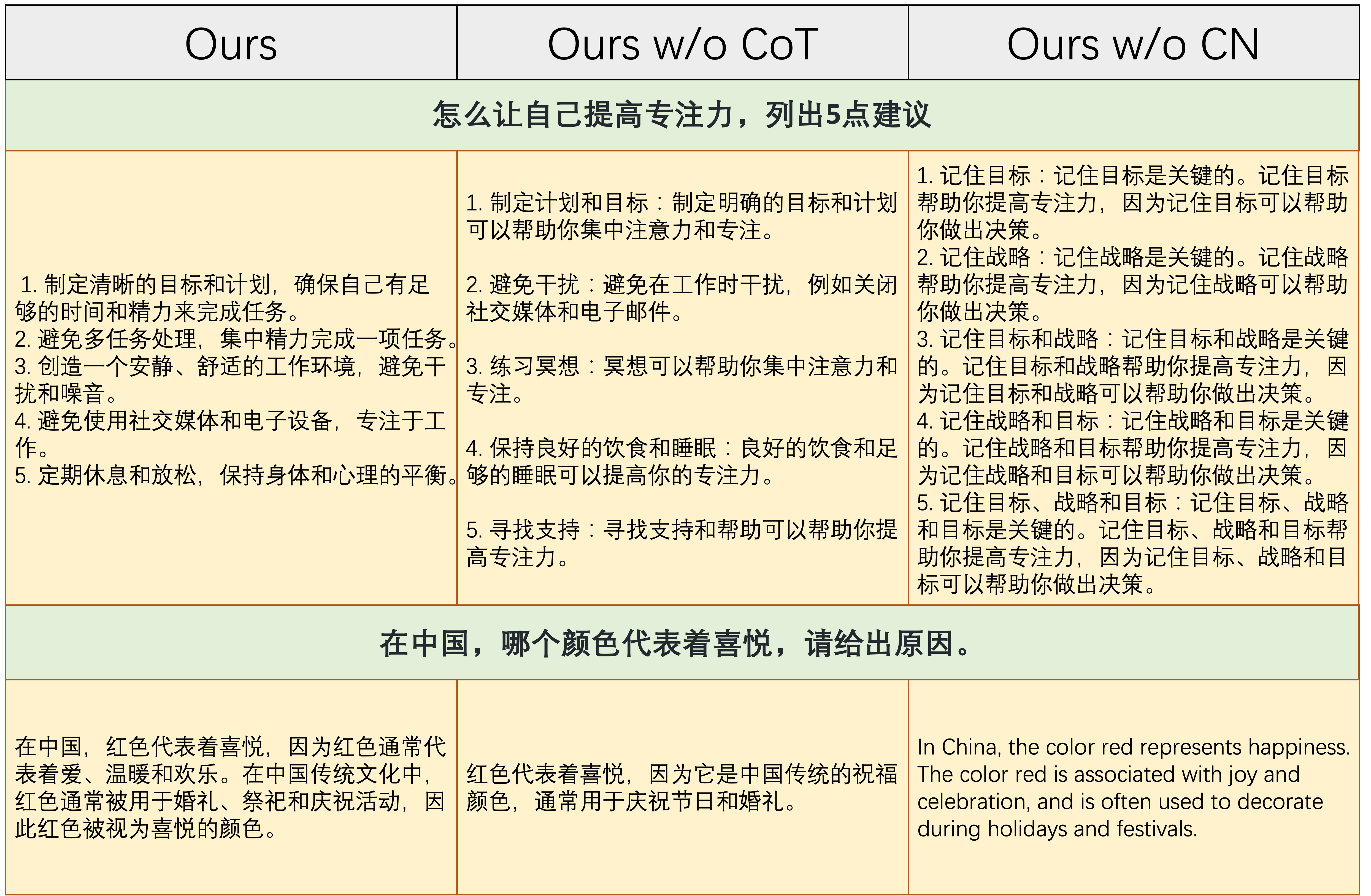
The above table shows two examples that require the ability to respond to Chinese instructions.
As shown in the right column, either the generated content of Ours w/o CN is unreasonable, or the Chinese instructions are answered in English by Ours w/o CN. This shows that removing Chinese data during finetuning will cause the model to be unable to handle Chinese instructions, and further demonstrates the need to collect Chinese instruction finetuning data.
The above table shows a relatively difficult example, which requires both a certain accumulation of knowledge of Chinese history and a logical and complete ability to state historical events. As shown in this table, Ours w/o CN can only generate a short and erroneous response, because due to the lack of Chinese finetuning data, the corresponding knowledge of Chinese history is naturally lacking. Although Ours w/o CoT lists some relevant Chinese historical events, its logic of expression is self-contradictory, which is caused by the lack of CoT data.
`
In summary, the models finetuned from our complete dataset (English, Chinese, and CoT instruction data) can significantly improve model reasoning and Chinese instruction following abilities.
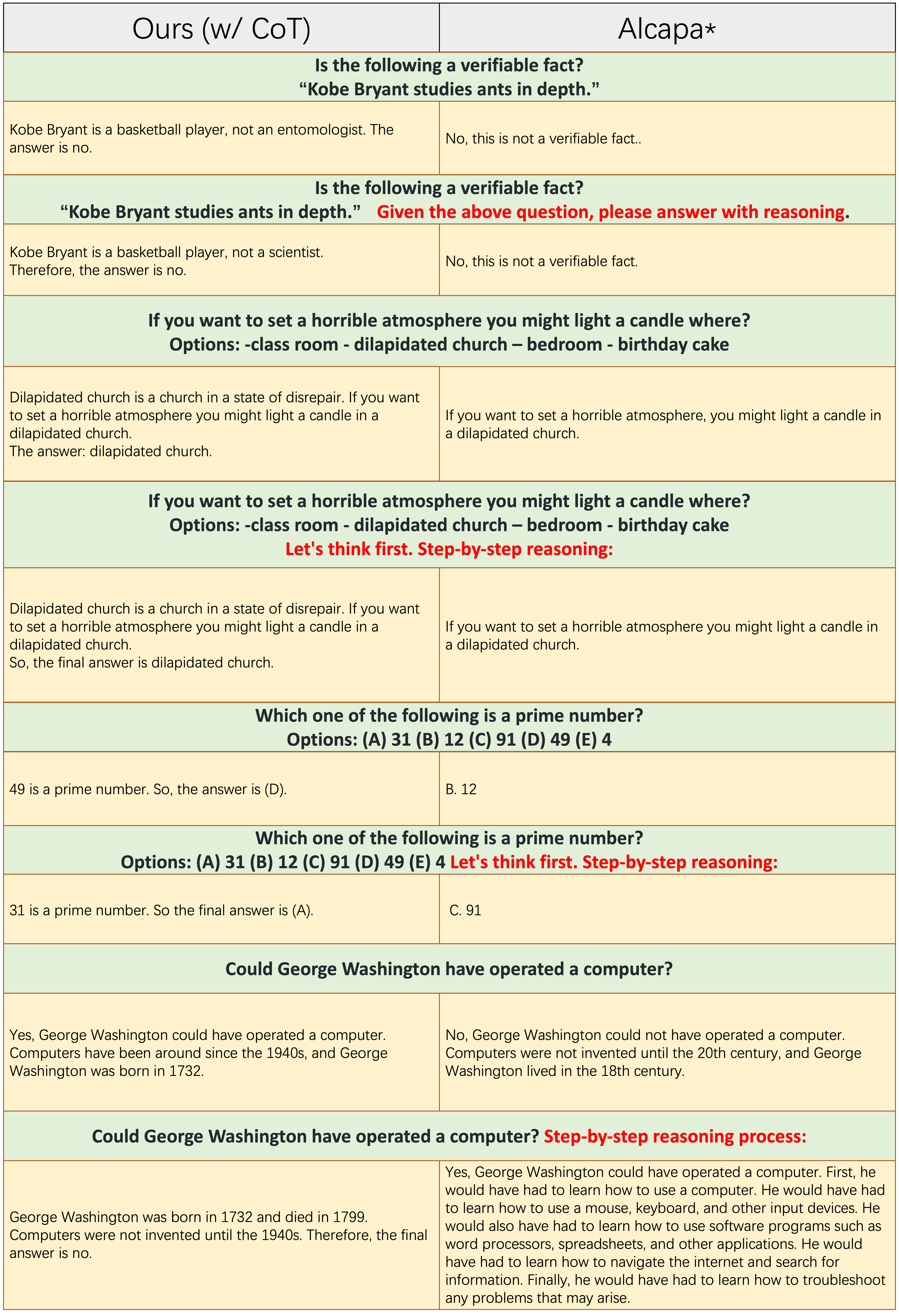 Samples of each odd number of rows do not apply the CoT prompt, such as "step-by-step reasoning." Both
Samples of each odd number of rows do not apply the CoT prompt, such as "step-by-step reasoning." Both Ours(w/CoT) and Alpaca are based on LLaMA-7B, and the only difference between them two is that the instruction-finetuning data of Ours(w/CoT) has a extra CoT data than that of Alpaca.
From the above table, we find that:
Ours(w/CoT)always generates the correct rationale before the answer, while Alpaca fails to generate any reasonable rationale, as shown in the first 4 examples (commonsense questions). This shows that using CoT data for finetuning can significantly improve reasoning ability.- For
Ours(w/CoT), the CoT prompt (e.g., concatenate 'step-by-step' with the input question) has little effect on easy examples (e.g., commonsense questions) and has an important effect on challenging questions (e.g., questions requiring reasoning, like the last four examples). - For Alpaca, CoT prompt always has little effect or even negative impact. For the last two examples, after adding CoT prompt, Aplpaca changes the correct generated answer to the wrong one. This may be due to the inconsistency between the input forms of finetuning and inference.
Quantitative comparison of responses to Chinese instructions.
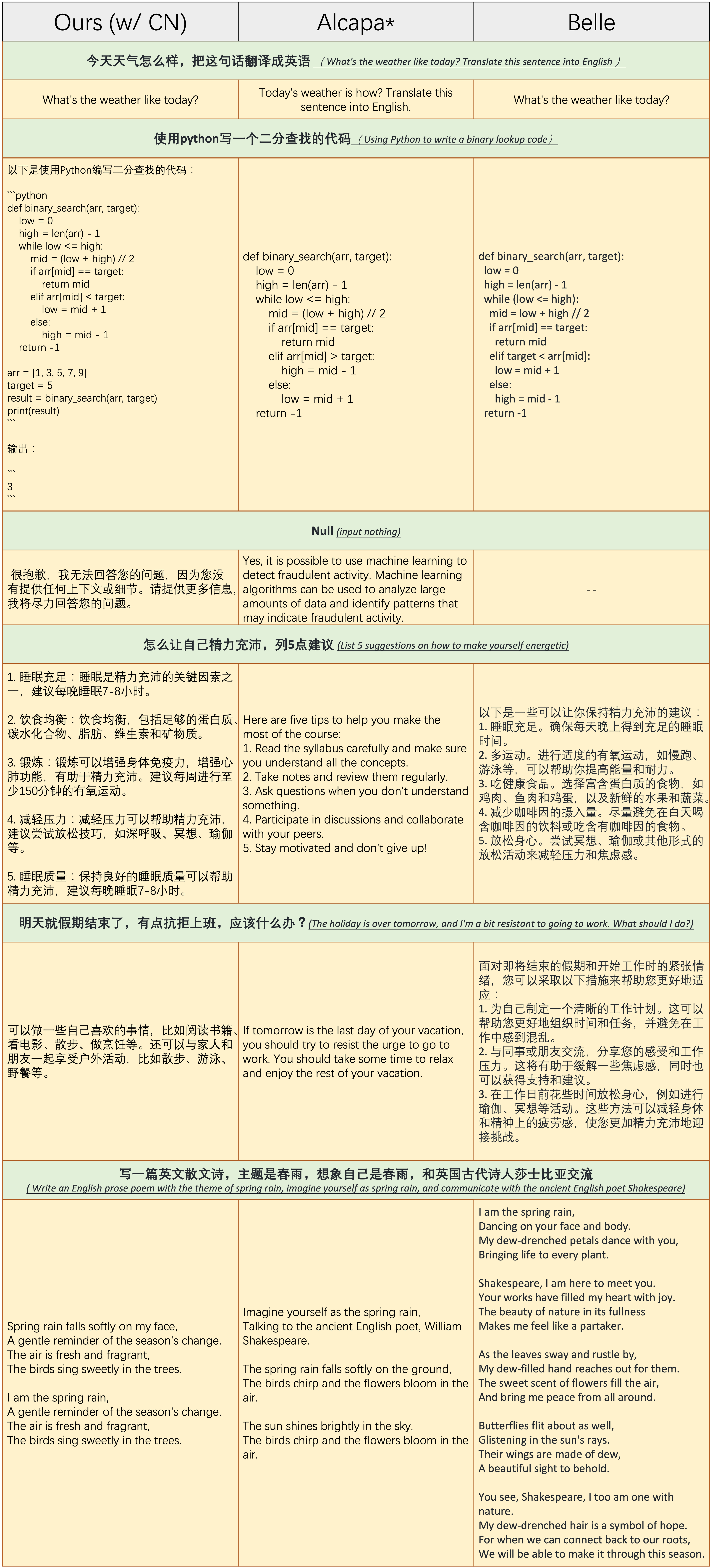
Our model is finetuned from a 7B LLaMA on 52K English instructions and 0.5M Chinese instructions. Stanford Alpaca (our reimplementation) is finetuned from a 7B LLaMA on 52K English instructions. BELLE is finetuned from a 7B BLOOM on 2B Chinese instructions.
From the above table, several observations can be found:
- Compared to Alpaca,
ours (w/ CN)has a stronger ability to understand Chinese instructions. For the first example, Alpaca fails to distinguish between theinstructionpart andinputpart, while we do. - Chinese instruction finetuning data can significant enhance the ability to interact in Chinese. For the second example,
ours (w/ CN)not only provides the correct code, but also provides the corresponding Chinese annotation, while Alpaca does not. In addition, as shown in the 3-5 examples, Alpaca can only respond to Chinese instruction with an English response. - Compared to BELLE,
ours (w/ CN)'s performance on instructions requiring an open response (as shown in last two examples) still needs to be improved. BELLE's outstanding performance against such instructions is due to: 1. Its BLOOM backbone model encounters much more multilingual data during pre-training; 2. Its Chinese instruction finetuning data is more than ours, that is, 2M vs 0.5M.
Quantitative comparison of responses to English instructions. The purpose of this subsection is to explore whether finetuning on Chinese instructions has a negative impact on Alpaca.

From the above table, we find that:
- Finetuning with Chinese instruction data does not weaken the original English instruction–following ability, on the contrary, there is also a certain enhancement in genearting a better response to English intructions. The response of
ours (w/ CN)shows more detail than that of Alpaca, e.g. for the third example,ours (w/ CN)list three more provinces than Alpaca.
- Exploration of few-shot ability.
- Ablation study of various sizes of models.
- Evaluate on instruction-following evaluation suite.
- Collect more instruction finetuning datasets.
Please cite the repo if you use the data collection, code, and experimental findings in this repo.
@misc{alpaca-cot,
author = {Qingyi Si, Rui Liu, Zheng Lin },
school = {Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China},
title = {Alpaca-CoT: An Instruction Fine-Tuning Platform with Instruction Data Collection and Unified Large Lnguage Models Interface},
year = {2023},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/PhoebusSi/alpaca-CoT}},
}
For data, please cite the original Stanford Alpaca, BELLE and FLAN papers as well.
For models, please cite the original LLaMA, Stanford Alpaca, Self-Instruct and LoRA papers as well.
[1]: LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models
[2]: Stanford Alpaca: An Instruction-following LLaMA model
[3]: Self-Instruct: Aligning Language Model with Self Generated Instructions
[4]: LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models
[5]: ChatGLM: An Open Bilingual Dialogue Language Model
[6]: BLOOM: A 176B-Parameter Open-Access Multilingual Language Model
[7]: FLAN: Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models
[8]: BELLE: Bloom-Enhanced Large Language model Engine
[9]: GPT4All: Training an Assistant-style Chatbot with Large Scale Data Distillation from GPT-3.5-Turbo