This script prepares expected parking cost data for SANDAG MGRA series 15 zones.
The processing includes the following steps organized into separate python modules:
reductions.py: Reduce/organize dataset and estimate model fitimputation.py: Impute missing valuesdistricts.py: Find the parking districtsestimate_spaces.py: Estimate spacesexpected_cost.py: Calculate expected costs
These modules inherit a few helper functions from base.py, which are all then inherited and run with process.py to provide a single point of entry to the program. The script can be controlled with settings.yaml, where users specify inputs, outputs, parameters, and which models to run.
The processing script can be run by either running the run.py script where users may wish to add scripting, or through command line by navigating to the directory containing the "parking" folder and executing the line:
python -m parking
- Spaces
- Cost
- pricing:
- paid
- free
- rate:
- hourly
- daily
- monthly
- location:
- on-street
- off-street
- ownership:
- public
- private
- tod:
- business hours
- non-business hours
Not all segments fully cross with eachother, should collapose some segments to make a flattened data frame.
We do not need all the different segments. Just a dataframe with the following fields for each MGRA:
- Weighted average cost of private and public parking, assuming weight is n-spaces
$= \frac{(n_{private} * cost_{private} + n_{public} * cost_{public})}{n_{private} + n_{public}}$ - Sum of public and private spaces
- Max cost for business hours or after hours
- Collapse on-street/off-street segment
- assuming all on-street are "public"
- assume that off-street residential are "free"
- assume that public space counts are inclusive of private space count
- Reduce business hours and after hours by selecting the max value
- assume peak pricing is most critical in daily pricing
- assume there are no $0 costs in inventory, otherwise they would be considered free spaces or NaN
- assume max daily on-street period is 10 hours (8am to 6pm)?
From the assumptions, the data can be reduced to the following:
- free_spaces = on_street_free_spaces + off_street_free_spaces + off_street_residential_spaces
- paid_space = on_street_paid_spaces + off_street_paid_private_spaces
- hourly_cost = ( on_street_paid_spaces * argmax(on_street_hourly_cost_during_business, on_street_hourly_cost_after_business) + off_street_paid_public_spaces * argmax(off_street_paid_public_hourly_cost_during_business, off_street_paid_public_hourly_cost_after_business) + off_street_paid_private_spaces * argmax(off_street_paid_private_hourly_cost_during_business, off_street_paid_private_hourly_cost_after_business) ) / (on_street_paid_spaces + off_street_paid_public_spaces + off_street_paid_private_spaces)
- daily_cost = (off_street_paid_public_spaces * off_street_paid_public_daily_cost + off_street_paid_private_spaces * off_street_paid_private_daily_cost) / (off_street_paid_public_spaces + off_street_paid_private_spaces)
- monthly_cost = (off_street_paid_public_spaces * off_street_paid_public_monthly_cost + off_street_paid_private_spaces * off_street_paid_private_monthly_cost) / (off_street_paid_public_spaces + off_street_paid_private_spaces)
NAs are skipped so that an average is calculated if there is at least one available value. If all are NA, the NA is preserved for imputation.
Even after reduction, there are many NAs that will need to be imputed. Below are imputation results using Multiple Imputation by Chained Equations (MICE). Basically you use linear regression to iteratively impute missing values from all other available data, then use the imputed values to reimpute other missing data, and finally aggregating the result.
Three step process:
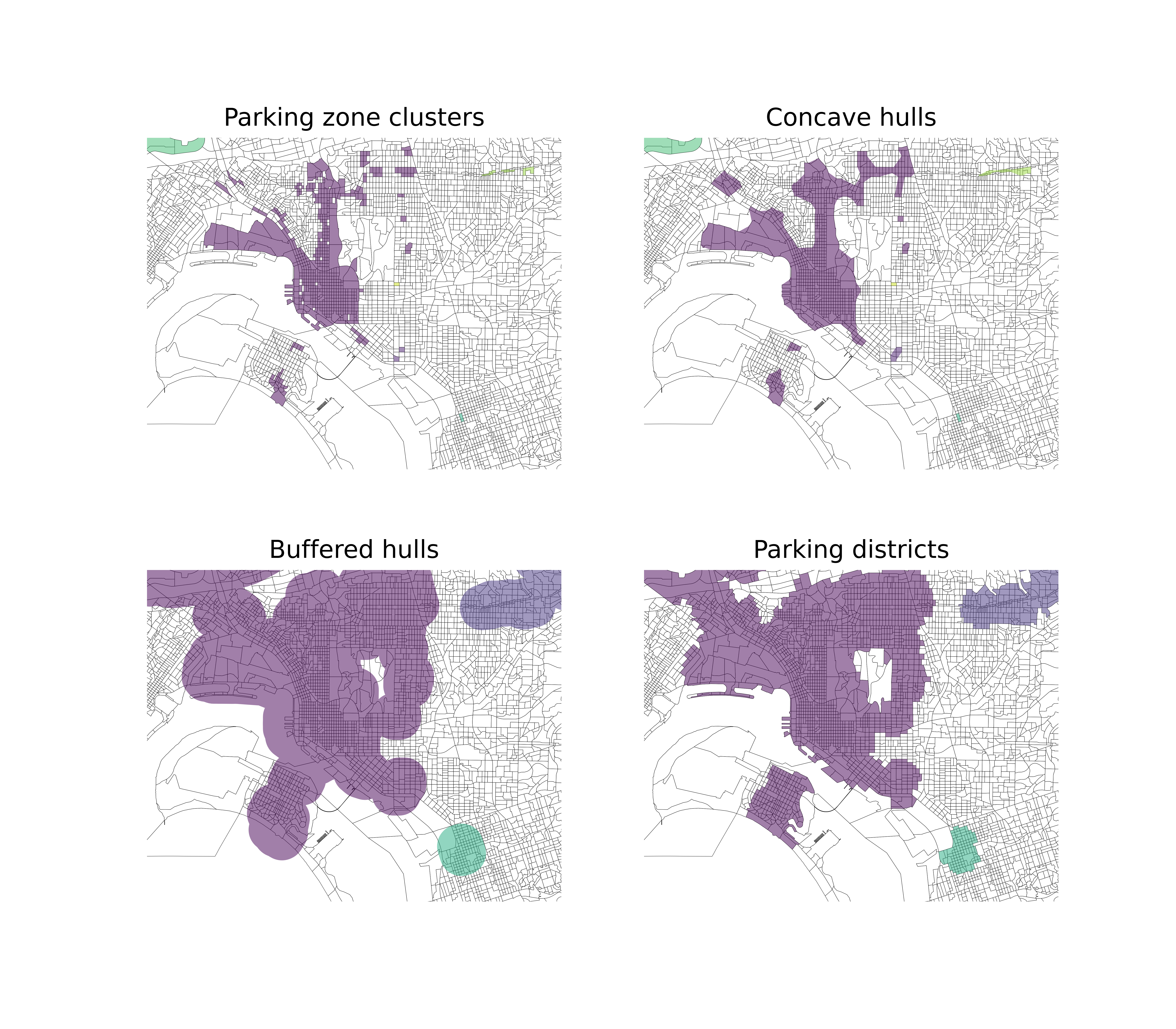
- Spatially cluster zones with paid parking based on a maximum distance threshold
- Create a concave hull for each cluster plus a walking distance buffer around hull
- Join all zones within that hull
Spatial clustering uses a "Agglomerative Clustering" technique where points are grouped into discrete clusters based on distance. Inputs:
- affinity matrix: Pre-computed distance between every geometric polygon. The polygon edge-to-edge distance was used, instead of centroids, to provide a more inclusive and conservative clustering measure.
- distance threshold: The maximum distance before a new cluster is created.
- linkage criterion: Which distance to use between observations, in this case "single" distance is used. It can be thought of as the chained distance where the chain is broken and a new cluster is formed when the distance threshold is exceeded:
- "ward" minimizes the variance of the clusters being merged.
- "average" uses the average of the distances of each observation of the two sets.
- "complete" or ‘maximum’ linkage uses the maximum distances between all observations of the two sets.
- "single" uses the minimum of the distances between all observations of the two sets.
The zones with parking costs can then be grouped together based on the maximum walking distance threshold.
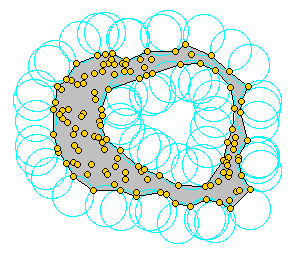
A convex hull is formed from as the minimum shape that included all points. However, a convex hull is not sensitive to concave or "gerrymandered" shapes. To form a concave shape, the "alpha shape" can be formed using a Delaunay triangulation technique.
A concave hull can be created by setting the
Once the concave hull is found for each parking cluster, a simple buffer distance equal to the maximum walking distance is added to buffer around the zone to include additional walkable zones. Using the buffered concave hulls, all MGRA zones are spatially joined if they are within the concave hull envelope, forming discrete "paid parking districts".
- Fetch OSM network
- Filter out the edges for roads that definitely don't have parking
- Intersect the network with zones (slice up network into zones)
- Aggregate road length and intersection count per zone
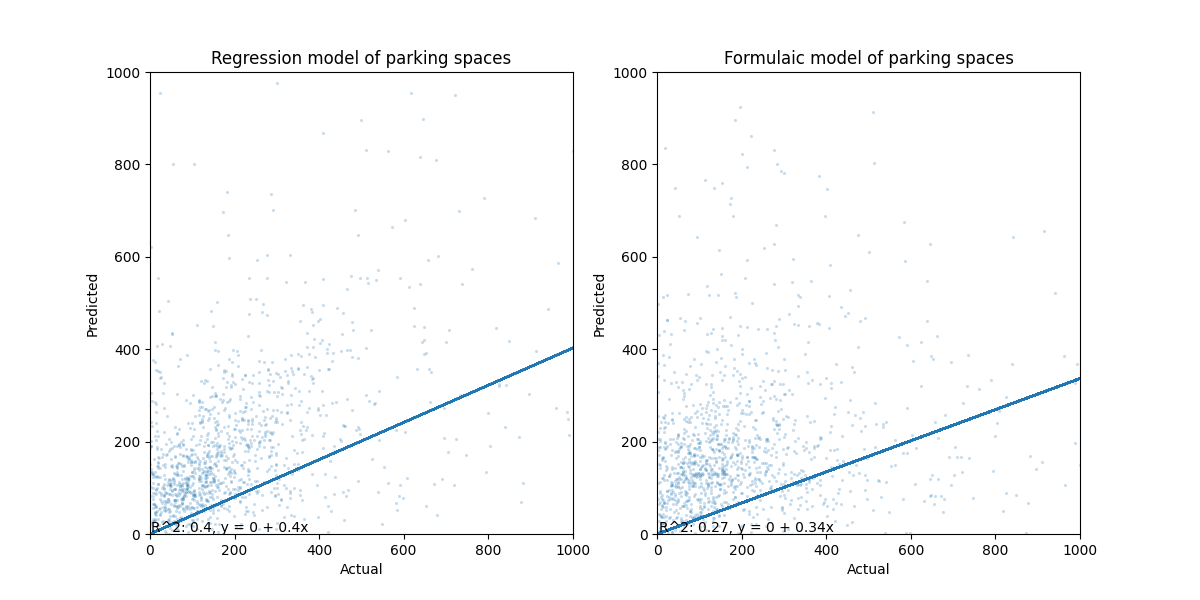
- Model the number of on-street spaces values with network aggregate length/intersection counts
Alternative estimation, parking space = ~10ft to account for parallel and angled, thus:
- N = intersections
- L = total street length
- spaces = 2 * ( L / 10 - N)
- district_dummy = {if outside district gets 1, elseif no space zones in hull get 0, else 1}
- no space zones = concave hull - parking cost zones
- distance_dummy = if dist <= max_dist
- dummy = distance_dummy * district_dummy
$numerator_i = e^{dist * \beta_{walk}} * spaces * cost * dummy$ $denominator_i = e^{dist * \beta_{walk}} * spaces * dummy$
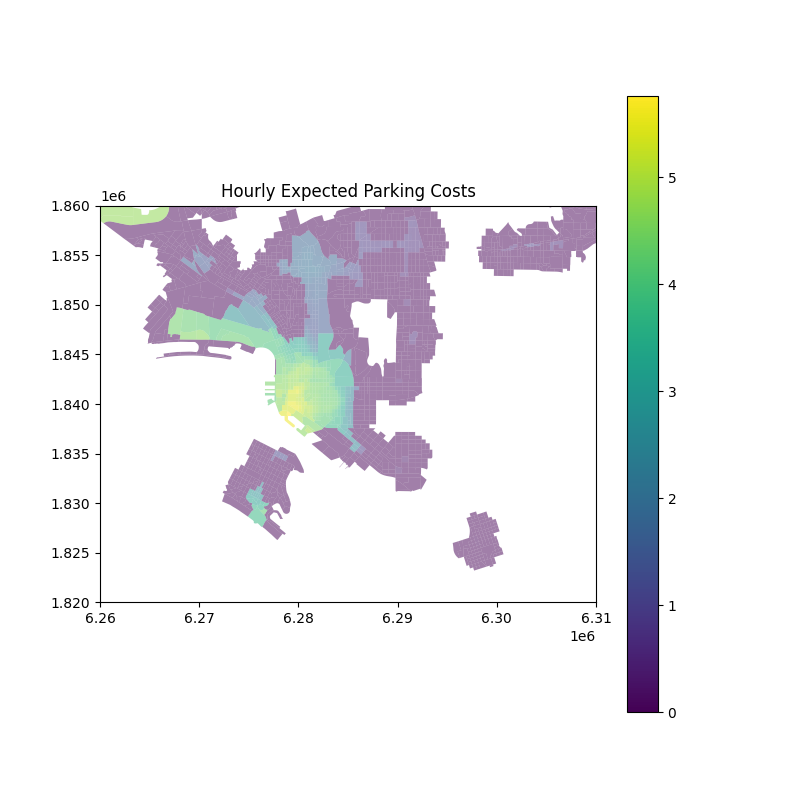
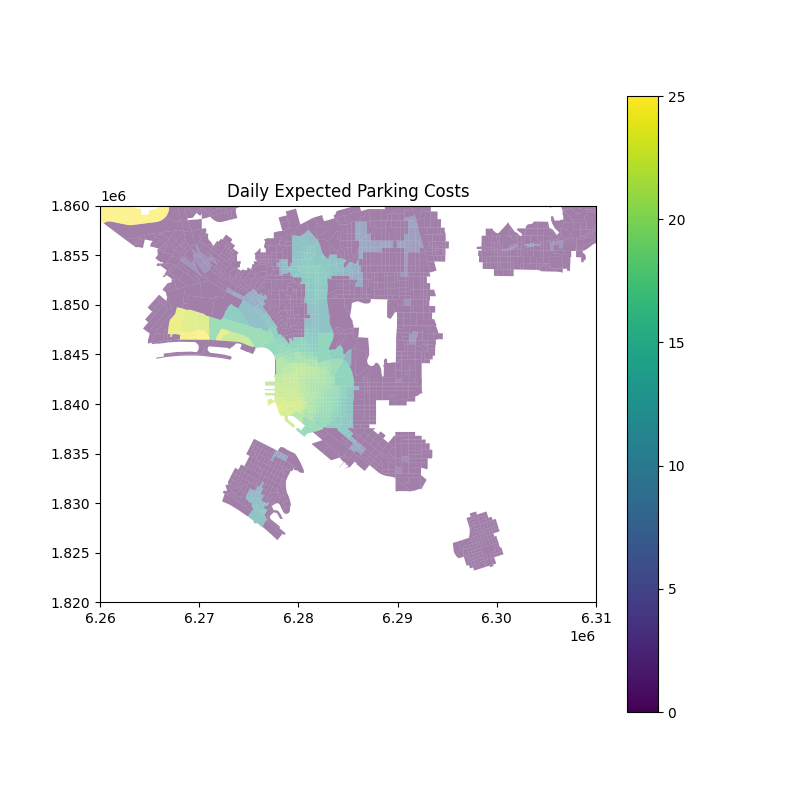
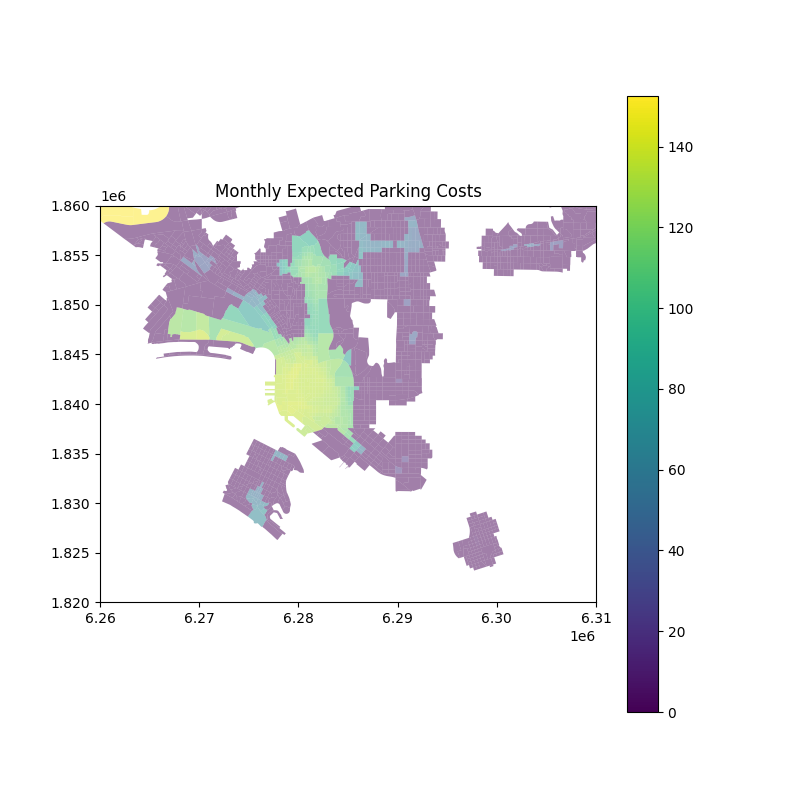
Expected parking cost =