Table of Contents
In this homework you should implement linked-list data structure with c++.
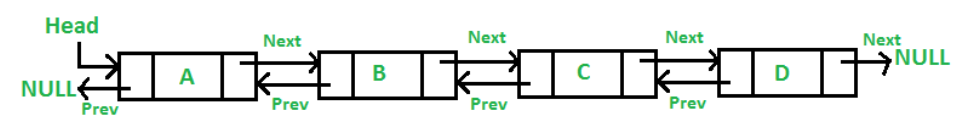
Each node has two pointers, one pointing to the previous node and the other pointing to the next node. Only the first node (head) has its previous node set to null and the last node (tail) has its next pointer set to null.
Major frameworks/libraries used in this project:
LinkedList Class
This class represents each LinkedList object. It has the following methods and member variables.
class LinkedList {
public:
class Node {
public:
Node();
Node(double);
Node* next;
Node* previous;
double getValue() const;
double& getValue();
void setValue(double);
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& stream, const Node& node);
private:
double value;
};
LinkedList();
LinkedList(std::initializer_list<double>);
LinkedList(const LinkedList&);
~LinkedList();
void push_back(double);
void push_front(double);
double pop_back();
double pop_front();
double back() const;
double front() const;
bool empty();
void clear();
void show() const;
int getSize() const;
void extend(const LinkedList&);
double& operator[](int);
private:
int N {};
public:
Node* head;
Node* tail;
};Node class is a nested class, which means that we have defined the class inside another class. LinkedList class has Node class. As you can see, definition of Node class is inside of LinkedList class.
DO NOT change main.cpp.
1. Add a node at the front:
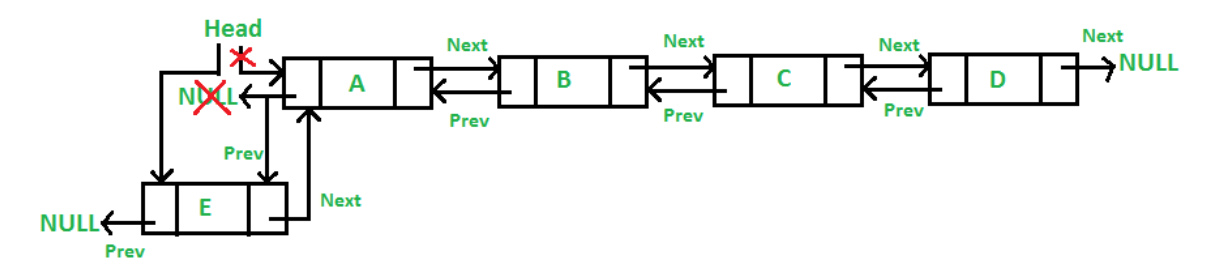
The new node,here, is always placed before the Linked List's head. The freshly inserted node is now the Double Linked List's new head. For instance, if the supplied Linked List is 1234 and item 5 is added to the front, the Linked List becomes 51234. The function that adds to the front of the list will be called push_front(). Because push must update the head pointer to refer to the new node, push_front() must receive a pointer to the head pointer.
void LinkedList::push_front(double data)
{
if (tail == nullptr) {
//Empty Case
tail = new Node(data);
} else {
//Non Empty Case
Node* Current = tail;
while (Current->previous != nullptr) { //The beigining from the tail -> head
Current = Current->previous; //(where cur.prev equal zero)
}
Node* Temp = new Node(data);
Temp->next = Current;
Temp->previous = nullptr;
Current->previous = Temp;
head = Temp;
}
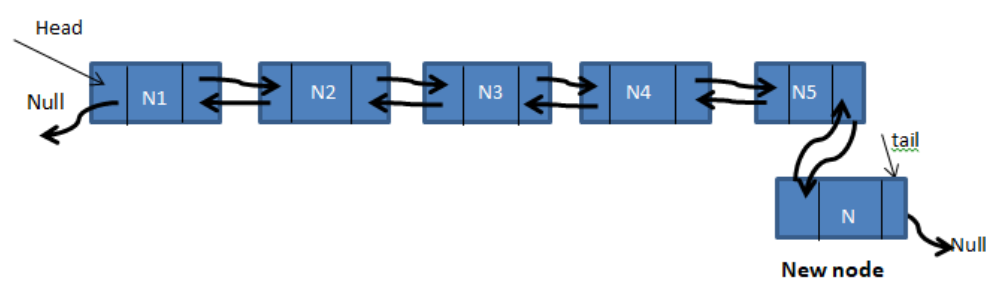
};2. Insertion at the end:
We are given a pointer to a node as prev_node, and the new node is inserted after the given node.
Same as push_front() but here we start from the head up toward tail.
void LinkedList::push_back(double data)
{
if (head == nullptr) {
// Empty Case
head = new Node(data);
// delete[] head;
} else {
// Non Empty Case
Node* Current = head;
while (Current->next != nullptr) {
Current = Current->next;
}
Node* Temp = new Node(data);
Temp->next = nullptr;
Temp->previous = Current;
Current->next = Temp;
tail = Temp;
}
};3. Deleting:
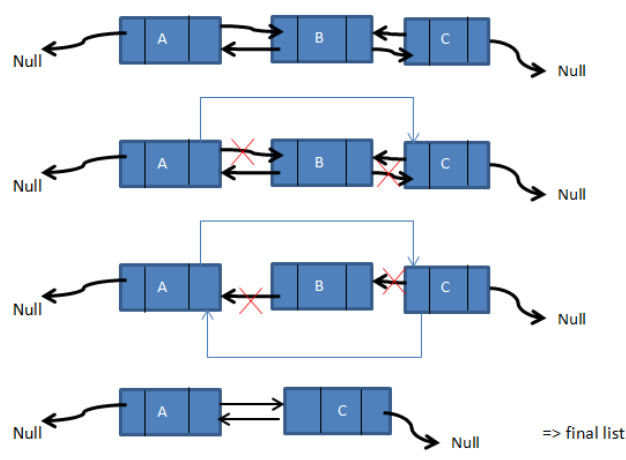
A node in a doubly-linked list can be erased from any position, such as the front, end, or any other place or data.When removing a node from a doubly-linked list, we must first relocate the pointer referring to that node such that the preceding and following nodes have no relationship to the node to be removed. The node can then be simply deleted. Consider the following three-node doubly linked list: A, B, and C. Consider the case when we need to remove node B.
We have shown the deletion of node B from the supplied linked list in the above sequence of diagrams. Even if the node is first or last, the operation sequence stays the same. The only precaution to consider is that if the first node is removed, the prior reference of the second node will be set to null.
Similarly, when the final node is destroyed, the prior node's next pointer is set to null. If the nodes in between are removed, the sequence will be as shown above.
double LinkedList::pop_back()
{
if (head == nullptr) {
//Empty linked list
throw std::out_of_range("Tried to pop empty linked list!");
}
if (head->next == nullptr) {
//Size one case
return head->getValue();
delete head;
head = nullptr;
} else {
//Size 2 or more case
Node* Current = head;
while (Current->next != nullptr) {
Current = Current->next;
}
tail = Current->previous;
Current->previous->next = nullptr;
return Current->getValue(); //after getting the value its better to delete it
delete Current;
}
};
double LinkedList::pop_front()
{
if (tail == nullptr) {
//Empty linked list
throw std::out_of_range("Tried to pop empty linked list!");
}
if (tail->previous == nullptr) {
//Size one case
return tail->getValue();
delete tail;
tail = nullptr;
} else {
//Size 2 or more case
Node* Current = tail;
while (Current->previous != nullptr) {
Current = Current->previous;
}
head = Current->next;
Current->next->previous = nullptr;
return Current->getValue();
delete Current;
}
};etc ...
First of all comment the dll_unittest.cpp folder to avoid faild process. Then build the docker container in the same path,
e.g. by running
docker build -t [desiredname] .
Then run the docker container by: (+interactive )
docker run -v $PWD:/usr/src/app --rm -it [containername] bash -l RUN mkdir obj
After that just make && ./main to execut the files.
Distributed under the MIT License. See LICENSE.txt for more information.
🔎
Rabih ND - @RabihND
Project Link: https://github.com/RabihND/Doubly-LinkedList